
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
DETERMINATION OF LIQUID VISCOSITY COEFFICIENT
| The purpose of the work: to study the transport phenomena; to determine the internal friction coefficient by the Stockís method | Devices and accessories 1. Glass cylinder with glycerin. 2. Metal and aluminum balls of different diameters. 3. Stop-watch. 4. Microscope ŐŌ¬-2. |
Task 1. Determination of time of balls falling down
1.1. Take 5 balls.
1.2. Measure diameter of each ball ŗi by means a number of peaches of microscope ŐŌ¬-2. Repeat measurements 3 times. Calculate average values ai ave of the ball diameter. Enter the obtained results into table 1.
Table 1
| Exp. No | Ball diameter, ŗi, pitchers | Average value of ball diameter, ai ave, pitchers | Scale factor of microscope, N, mm | Average value of ball radius, ri ave, m | Height, the ball falls from l, m | Time, the ball falling down ti, s | Viscosity, 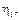 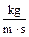
|
| The first ball | |||||||
| The second ball | |||||||
| The third ball | |||||||
| The forth ball | |||||||
| The fifth ball | |||||||
1.3. Calculate average value of ball radius ri ave for each ball according to the formula:

where n = 3 is amount of measurements. Enter the results into table 1.
1.4. Measure the distance between the upper and the lower scores l of the cylinder by a ruler. Enter the results into table 1.
1.5. Take the first ball with known radius  and fall it down in liquid. Measure the time the ball takes to fall the distance l. Repeat measurement with all other balls. Enter the results into table 1.
and fall it down in liquid. Measure the time the ball takes to fall the distance l. Repeat measurement with all other balls. Enter the results into table 1.
1.6. Measure the liquid temperature by a thermometer. Enter the results into table 2.
1.7. Enter values of material density r the balls made of and liquid density rl into table 2.
1.8. Calculate the internal friction coefficient for each ball according to the formula:
 .
.
Enter the results into table 1.
Table 2
| Liquid temperature, Tl, | Material density the balls made of, r, kg\m3 | Liquid density, rl, kg/m3 |
Task 2. Calculation of viscosity measurement error
Calculate average value of the viscosity according to the formula: 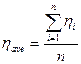
where n = 5 is amount of measurements. Enter the results into table 3.
2.2. Calculate deviation from average value Δηi according to the formula: 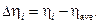
Table 3
| Exp. No | Viscosity 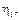 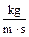
| Average value of vicosity 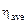 , , 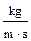
| Deviation of mean value 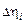 , , 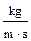
| Root-mean-square deviation 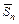
| Absolute error, Dh, 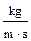
| Fractional error, 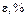
|
2.3. Calculate root-mean-square error of the arithmetic mean 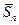 according to the formula:
according to the formula: 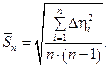
2.4. Determine the viscosity measurement absolute error according to the formula: Dh = tSt 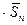 .
.
where the Studentís coefficient is tSt = 2,78 (n = 5 and a = 0,95)
2.5. Calculate the viscosity measurement fractional error according to the formula: 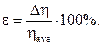
2.6. Write down the result in a form: 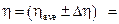 ____________________________,
____________________________, 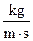
Conclusions
The data of laboratory work fulfillment
Pass mark Signature
Mark of laboratory work defending Signature
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work and its defending
1. Name the transport phenomena. What quantity is transferred during each of them?
2. Explain the cause of internal friction.
3. Explain the cause of heat conductivity.
4. Explain the cause of diffusion.
5. Write and explain Newtonís law for a steady laminar stream.
6. How does the coefficient of internal friction depend on temperature?
7. What is physical sense of velocity gradient?
8. Describe the Stockís method for the coefficient of internal friction determination.
9. What forces make the ball move in liquid?
10. Deduce the formula for calculation of the coefficient in our experiment.
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1647
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| DYNAMICS OF ROTATIONAL MOTION. DETERMINATION OF LOADS INERTIA MOMENT USING OBERBECHíS PENDULUM | | | DETERMINATION OF GAS SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITIES RELATIONSHIP |