
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
DETERMINATION OF GAS SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITIES RELATIONSHIP
| The purpose of the work: To study the heat capacity theory of perfect gases and the first law of thermodynamics; to determine adiabatic exponent | Devices of and accessories 1. Installation for determination of air heat capacities relationship. 2. Manometer. 3. Ruler. |
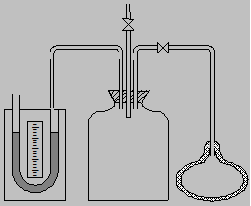 Task 1. Measurement of the liquid levels difference in the manometer tubes h1
Task 1. Measurement of the liquid levels difference in the manometer tubes h1
1.1. Open the tap 3 and close it when the levels of the liquid in both manometer tubes are the same.
1.2. Open the tap 4 and carefully pump some air into the vessel. Stop pumping and close the tap 4 when the difference between the liquid levels reaches 150 Ė 200 mm.
1.3. Wait for 3ó5 minutes, until the difference between levels stops changing. Count the difference between the manometer levels h1.
Enter the results into table 1.
Task 2. Measurement of the liquid levels difference in the manometer tubes h2
2.1. Open the tap 3 and again quickly close it in that moment when the liquid levels in manometer tubes are the same.
2.2. Wait 3ó5 minutes, when position of liquid levels in manometer stop changing count the difference between the manometer levels h2
2.3. Repeat 5 times measurements according to items 1.1ó2.2.
Enter the results of h1 and h2 into table 1.
Table 1
| Exp. No | Liquid level h1, mm | Liquid level h2, mm | Adiabatic exponent g | Average value of adiabatic exponent 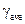
| Deviation from mean value 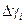
| Absolute error 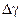
|
Task 3. Calculate value of adiabatic exponent and measurement error.
3.1. Calculate adiabatic exponent according to the formula:
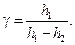
Enter the results into table 1.
3.2. Calculate the error of adiabatic exponent determination.
Calculate mean value according to the formula:
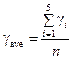
where n = 5 is amount of measurements
Enter the results into table 1.
3.3. Determine deviation from mean value according to the formula:
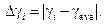
Enter the results into table 1.
3.4. Calculate root-mean-square deviation according to the formula:
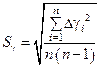 = .
= .
3.5. Determine the absolute error of measurements according to the formula:
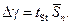
where the Studentís coefficient is tSt = 2,78 (n = 5 and a = 0,95)
Fulfill calculation for four significant digits.
Enter the results into table 1.
Conclusions
The data of laboratory work fulfillment
Pass mark Signature
Mark of laboratory work defending Signature
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
and its defending
1. Write down equation of state for perful gas. Explain its sense.
2. What is physical sense of internal energy of perfect gas?
3. What is physical sense of Universal gas constant?
4. Formulate the first law of thermodynamics and apply it for isoprocess of perfect gas.
5. Give definition, write down equation and draw graphs of isohoric and isobaric proces≠ses of perfect gas.
6. What is called adiabatic process?
7. What is body heat capacity? What does heat capacity depend on?
8. What types of body heat capacities do you know?
9. What is bigger —– or —v? Explain your answer.
10. How is the heat capacity —– and —v determined in accordance to molecular-kinetic theory?
11. Perfect gas heat capacity at adiabatic and isothermal process.
12. What is the number of degrees of molecule freedom?
13. Deduce the formula for adiabatic exponent calculation.
14. Deduce the formula for adiabatic exponent calculation by experimental method.
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1261
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| DETERMINATION OF LIQUID VISCOSITY COEFFICIENT | | | MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES |