
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Figure 11. Depending of boiling-points (B.Pt) of double Hydrogen-contained compounds from nature of the second atom and presence of Hydrogen bonding
Ø The evaporation of sweat, used by many mammals to cool themselves, achieves this by the large amount of heat needed to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
Ø Moderating temperature shifts in the ecosystem (which is why the climate is more moderate near large bodies of water like the ocean).
Multiple hydrogen bonds in alive objectes:
Ø hold the two strands of the DNA double helix together:
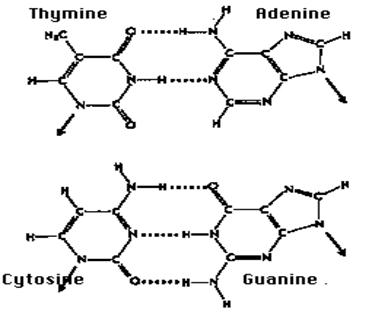
Ø hold polypeptides together in such secondary structures as the alpha helix and the beta conformation;
Ø help enzymes bind to their substrate;
Ø help antibodies bind to their antigen
Ø help transcription factors bind to each other;
Ø help transcription factors bind to DNA.
2. Why does Chemical Bond occur?
The fascinating variety of materials in the world around us is possible because chemical bonds unite atoms of the elements in so many different combinations. Some elements are found in nature only in chemical compounds. Even the atoms of elements that can be found in nature in uncombined form - such as Oxygen and Nitrogen in the air, of Gold and Copper in the Earth’s crust - do not exist as independent atoms. They are bonded together.
If their potential energy is lowered by the change, two atoms will form a chemical bond. Throughout nature, changes that decrease potential energy are favored. Books fall off desks, and the result is lower potential energy for the books. Most atoms have lower potential energy in bonds than as independent atoms.
Chemical-bond formation is often energy - releasing process. Experiments also show that the reverse - breaking chemical bonds - is often an energy-absorbing process. Atoms separated by breaking a chemical bond have a higher total potential energy than when they were bonded. Whether or not a given chemical reaction occurs spontaneously is partly dependent on whether or not forming new bonds in the products produced enough energy to break bonds in the reactants.
Covalent, ionic and metallic bond all decrease the potential energy of the combined atoms.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1230
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Figure 10. Formation of Hydrogen Bonds between water molecules | | | PRACTICE PROBLEMS |