
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Figure 2. Scheme of Electron orbital
Motion of electrons around nucleus is described by energy and structure of atomic orbital. State of electron is described by values of 4 quantum figures (Tables 3, 4).
Table 3. Names and physical content of quantum figures
| Names | Symbol | What’s determined? | Possible values |
| Main (Principal) | N, n | Orbital energy (main energy level) | Algebraic integers from 0 to ∞ (infinity) |
| Secondary (Azimutal) | L | Orbital form (energy sub-level) | Algebraic integers from 0 to n-1 |
| Magnetic | ml | Spatial orientation of orbital | From –l to +l (ml=2l+1) |
| Spin | ms | Own magnetic moment of electrons | + ½ and - ½ |
Table 4. Schematic description of atomic orbital
| l | ml | Quantity of orbitals | Schematic imagination | |
| s | 
| |||
| p | -1 0 +1 | 
| ||
| d | -2 –1 0 +1 +2 | 
| ||
| f | -3 –2 –1 0 +1 +2 +3 | 
|
Example: To show a p-orbital:
l=1, ml= -1; 0; +1;
p-orbital has 3 variants of space orientation:
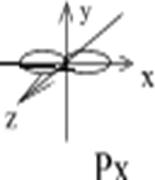
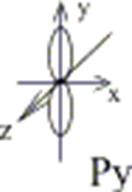
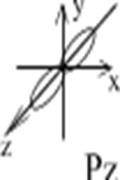
Figure 3. Spatial orientation of p-orbitals
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1379
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Theories of atomic structure | | | Distributions of electrons in atoms on energy levels and sub-levels may be presented in the form of electronic formulas. |