CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Distributions of electrons in atoms on energy levels and sub-levels may be presented in the form of electronic formulas.
It may be compelled in the following way:
∑ Note Arabian figure, which indicates the main quantum figure (energy level);
∑ Note symbol of orbital, that determined electronic sub-level;
∑ Quantity of electrons on this sub-level is made by Arabian figure above it in the right upper corner.
Example: To show electronic formula of Nitrogen: 7N 1s2 2s2 2p3. Atom of Nitrogen has 7 electrons, 2 - on the first level on s-sub-level, and 5 others Ė on the second level, s and p-sub-levels.
Principles, according to which the electrons are distributed in atoms, are shown in the Table 5.
Table 5. General rules for electronic formulas compilation
| Name | Formulation | Using | ||||||
| Principle of energy minimum | Minimum of energy responds to the most stable state of electrons in atom | Electron occupies a atomic orbital with minimum energy | ||||||
| Pauliís Principle | Atom may not have two electrons with the same values of all four quantum figures | N=2n2 (quantity of 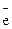 on the level)
Max quantity of on the level)
Max quantity of 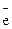 on the sub-level is equal to 2×(2l+1)
s=2; p=6; d=10; f=14 on the sub-level is equal to 2×(2l+1)
s=2; p=6; d=10; f=14
| ||||||
| Rule of Klech-kovsky | Energy sub-levels are filled up according increasing of sum n+l | Indicate an order of sub-levels occupation | ||||||
| Rule of Hound | Summary spin value of electrons on sub-level must be maximum | Indicate an order of occupation of equal atomic orbitals:
Correctly
Incorrectly
|
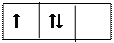
In addition to electron formulas graphic pictures of electrons distributions in atoms is widely used. Orbitals are represented by rectangle
 |
where may be unpaired electrons or paired electrons with antiparallel spins:
|
|
For each atom different quantity of electrons states, notable for energy, is possible. The most stable state of electrons in atom corresponds to minimum possible value of its energy. Such state is named as normal (ground) one. All other states are named as excited ones. Atoms may pass on to excited state if they have free orbitals and take energy from the outside. At the same time electrons may be separated.
Example. 17—l 1s22s22p63s23p5

Electrons located on the last, third level, may go into free d-sublevel when atom was excited.
|
|

Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1452
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Figure 2. Scheme of Electron orbital | | | Valency and Oxidation number as function of electrons distribution |