
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Processing: CPU
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the part of the computer where work gets done. Many computers today have more than one processing chip, resulting in more complex but faster processing.
Main Memory stores the commands that the CPU executes and the results.
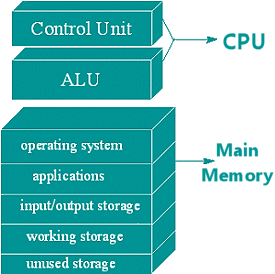
 Click on each of the labels in the diagram. You'll be shown an explanation below.
Click on each of the labels in the diagram. You'll be shown an explanation below.
 Show all explanations at once
Show all explanations at once
Explanation:
Processing: Machine Cycle
The computer can only do one thing at a time. Each action must be broken down into the most basic steps. One round of steps from getting an instruction back to getting the next instruction is called the Machine Cycle.
| The Machine Cycle | |
| Fetch - | get an instruction from Main Memory |
| Decode - | translate it into computer commands |
| Execute - | actually process the command |
| Store - | write the result to Main Memory |
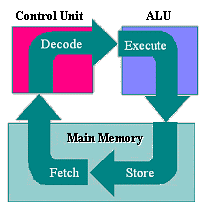
For example, to add the numbers 5 and 6 and show the answer on the screen requires the following steps:
| 1. | Fetch instruction: | "Get number at address 123456" |
| 2. | Decode instruction. | |
| 3. | Execute: | ALU finds the number. (which happens to be 5) |
| 4. | Store: | The number 5 is stored in a temporary spot in Main Memory. |
| 5 - 8 Repeat steps for another number (= 6) | ||
| 9. | Fetch instruction: | "Add those two numbers" |
| 10. | Decode instruction. | |
| 11. | Execute: | ALU adds the numbers. |
| 12. | Store: | The answer is stored in a temporary spot. |
| 13. | Fetch instruction: | "Display answer on screen." |
| 14. | Decode instruction. | |
| 15. | Execute: | Display answer on screen. |
Speed
The immense speed of the computer enables it to do millions of such steps in a second.
In fact, MIPS, standing for millions of instructions per second, is one way to measure computer speeds.
Processing: Memory Addresses
We need a method of naming the places where Main Memory stores data.
Each location needs a unique name, just like houses in a town need a unique street address.

| 
|
Rather than a street name and house number, memory addresses are just numbers.
A memory address holds 1 byte of data where
| 1 bit = | 0 or 1, on or off |
| 1 byte = | 8 bits |
| 1 kilobyte (K or KB) = | 1024 bytes |
| 1 megabyte (MB) = | 1024 kilobytes |
You might wonder why 1024 instead of 1000 bytes per kilobyte. That is because computers don't count by tens like people. Computers count by twos and powers of 2. 1024 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2, that is 2 times itself ten times. It's a rather convenient size number (for computers!).
Update: Things are changing faster than I can type! The explanation above is no longer entirely true (July 2000). Different scientific and technical areas are using the words differently. For data storage devices and telecommunications a megabyte is 1 000 000 bytes. For data transmission in LANs a megabyte is 1 048 576 bytes as described above. But for data storage on a floppy disk a megabyte is 1 024 000 bytes!
A new set of words has been created to make it clear what size is really being used. See http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/binary.html  for a further explanation.
for a further explanation.
È
We all are impatient and want our computer to work as fast as possible, and certainly faster than the guy's at the next desk!
Many different factors determine how fast your computer gets things done. Processor speed is one factor. But what determines the processor's speed?
Processor Speed affected by:

| System clock rate = rate of an electronic pulse used to synchronize processing (Only one action can take place between pulses.) Measured in megahertz (MHz) where 1 MHz = 1 million cycles per second or gigahertz (GHz) where 1 GHz = 1 billion cycles per second. This is what they are talking about if they say a computer is a 2.4 GHz machine. It's clock rate is 2.4 billion cycles per second. Bigger number = faster processing |

| Bus width = the amount of data the CPU can transmit at a time to main memory and to input and output devices. (Any path bits travel is a bus.) An 8-bit bus moves 8 bits of data at a time. Bus width can be 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 so far. Think of it as "How many passengers (bits) can fit on the bus at once to go from one part of the computer to another." Bigger number = faster transfer of data |

| Word size = a word is the amount of data the CPU can process at one time. An 8-bit processor can manipulate 8 bits at a time. Processors can be 8-, 16-, 32-, or 64-bit so far. Bigger the number = faster processing |
You want a nice match between the word size and the bus size and the clock. It wouldn't do any good to have a bus that can deliver data 128 bits at a time, if the CPU can only use 8 bits at a time and has a slow clock speed. A huge line of data would form, waiting to get off the bus! When computers gets clogged like that, bad things can happen to your data. It's like people waiting to get into the theater. After a while, some of them may leave!!
Processing: Physical Components
There are several physical components of a computer that are directly involved in processing. The processor chip itself, the memory devices, and the motherboard are the main ones.

| Microprocessor- | a single silicon chip containing CPU, ALU, and some memory. The ROM (Read Only Memory) contains the minimum instructions that the computer needs to get started, called booting. What a user does on the computer cannot change what is stored in ROM. There may also be another chip dedicated to calculations. The microprocessor chip is located on a large circuit board called the main board or motherboard. The physical size of a computer chip is very small, as the ant below illustrates.  Processor speed is measured in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz).
Processor speed is measured in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz).
|
Memory Devices:
| Vacuum tube - |  Copyright (c) 123RF Stock Photos
Oldest type. Didn't hold up long and generated a lot of heat.
Copyright (c) 123RF Stock Photos
Oldest type. Didn't hold up long and generated a lot of heat.
|
| Core - | Small metal rings. Magnets tip a ring to left or right, which represents on and off. Relatively slow even way back when this was used. |
| Semiconductor - | Integrated circuit on a chip. This is what modern computers use for memory. Pictured below is a 72-pin SIMM. 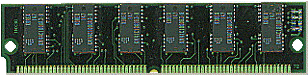
|
Memory Speed
RAM (Random Access Memory) is what the computer uses as Main Memory. Memory speed measures the time it takes to move data in or out of memory. It is measured differently for different kinds of memory chips:
- in nanoseconds (ns ) (smaller is faster) for EDO and FPM
1 ns = 1 billionth of a second. - in megahertz (MHz) (higher is faster) for SDR SDRAM, DDR, SDRAM, and RDRAM.
The capacity of a memory chip is measured in megabytes or gigabytes. For example, 256 MB of RAM is required to run WindowsXP and 512MB is much better. For Windows 7 the requirements are 1 gigabyte (GB) RAM (32-bit) or 2 GB RAM (64-bit).
Several such memory boards can be installed in the computer to increase the amount of RAM available. Motherboards have only so many slots for memory so there are limits. Some motherboards require that all slots be filled and that all slots contain the same size memory board. It can get frustrating as there are no warning labels about this!
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 2147
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Input: Summary | | | Processing: Summary |