
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Nonsystematic convolutional codes correcting capability research
Objective: To study the basic principles of error-correcting coding and decoding convolutional code (7, 5) by Viterbi algorithm. To determinate the quality parameters of the system in a channel with AWGN.
Laboratory emulator:
After opening the file VIT_7_5 you will propose to enter initial data from the table 3.7, where p0 error probability, L amount of bits.
Table 3.7 Data for laboratory experiment
| p0 | 0,07 | 0,05 | 0,03 | 0,01 | 0,005 |
| L | 2·105 | 5·105 | 8·105 | 106 | 5·106 |
| kd1 | |||||
| W |
In the result of the experiment, you get next parameters:
- kd1 errors coefficient in the output of decoder; kd1 =m/L.
- m amount of uncorrected errors at the output of decoder;
- W coding gain, W=p0/kd1.
After filling the table 3.7, you need to build the characteristics kd1 = f0(p0) and kd2 = f3( 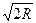 h) using fig. 3.7.
h) using fig. 3.7.
Laboratory task:
1. To run the program VIT_7_5.
2. To fill the table 3.7.
3. To build the diagrams kd1 = f0(p0) and kd2 = f3( 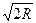 h). Estimated errors probabilities in the DSC can be selected from the table 3.8.
h). Estimated errors probabilities in the DSC can be selected from the table 3.8.
Table 3.8 Error probabilities for laboratory experiment
| Number of brigade | ||||||||
| p01, *10-2 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,4 | 7,6 | 7,8 | 7,9 | |
| p02, *10-2 | 2,8 | 2,7 | 2,5 | 2,4 | 2,3 | 2,2 | 2,1 | |
| p03, *10-3 | 7,3 | 7,4 | 7,6 | 7,8 | 7,5 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,9 |
Home task:
1. To learn items 1.3.1, 1.3.3 of this teaching manual.
2. To write down the answers to the general questions.
3. To prepare the table 3.7 in the protocol.
4. To prepare blank using Application B.
General questions:
1. Which classes do convolutional codes with Viterbi algorithm belong to?
2. Determine the main parameters of CvC (7, 5).
3. What is the state diagram of the nonsystematic CvC? How does it build?
4. What is the trellis diagram of the nonsystematic CvC? How does it build?
5. What is paths metrics, branches metrics and state metrics according to Viterbi algorithm?
6. What is surviving path according to Viterbi algorithm?
7. Describe the process of decoding using Viterbi algorithm.
Protocol content:
1. Subject and objective.
2. Executed home task.
3. Graph and table according to laboratory task.
4. Conclusion. Compare two characteristics of kd2 = f3( 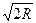 h) from the laboratory works 5 and 4.
h) from the laboratory works 5 and 4.
Laboratory work 6
Date: 2016-01-14; view: 1105
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Systematic convolutional codes correcting capability research | | | Digital communication system with a concatenated coding research |