
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Digital communication system with a concatenated coding research
Objective: To study the principles of serial concatenated coding methods. To research the correction ability of serial coding with the outer CC (15, 11) and inner CvC (14, 7) in a binary symmetric channel (BSC).
Laboratory emulator
After opening the file “Kaskad.exe” you can see interface like fig. 3.8.
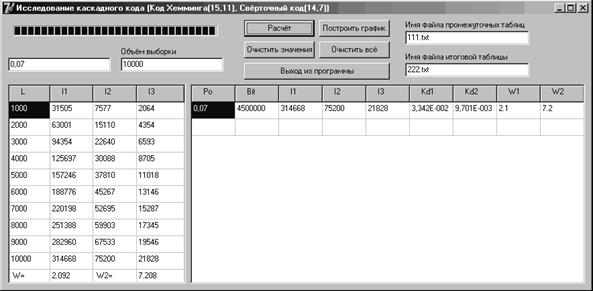
Figure 3.8 – Interface of laboratory work
For the simulation of the concatenated code codec as the outer code is selected cyclic code (15, 11) with the decoding by Meggitt algorithm, and as inner - convolutional code (14, 7).
You will propose to enter initial data from the table 3.9, where p0 – error probability, L – amount of codewords.
Table 3.9 – Data for laboratory experiment
| p0 | L | Bit | i1 | i2 | i3 | kd1 | kd2 | W1 | W2 |
| 0.05 | 105 | ||||||||
| 0,03 | 5·105 | ||||||||
| 0,02 | 2·106 | ||||||||
| 0,01 | 2·106 | ||||||||
| 0,008 | 2·106 |
In the result of the experiment, you get next parameters:
- Bit – amount of bits, transferred through the channel;
- i1 – amount of errors at the output of the DSC;
- i2 – amount of errors at the output of the inner decoder;
- i3 – amount of errors at the output of the outer decoder;
- kd1 – errors coefficient at the output of inner decoder, kd1 = i2/(Bit/2);
- kd2 – errors coefficient at the output of outer decoder, kd2 = i3/(L∙15∙11);
- W1 – coding gain at the output of inner decoder, W1 = p0/kd1;
- W2 – coding gain at the output of outer decoder, W2 = p0/kd2.
You can get the diagram kd1 = f1(p0)after putting the button “Ïîñòðîèòü ãðàôèê”. Then you need to build the diagram kd2 = f2(p0).
Laboratory task:
1. To open file “Kaskad.exe”.
2. To fill the table 3.9.
3. To build the diagram of probability characteristics of decoding the inner code kd1 = f1(p0)and outer kd2 = f2(p0), using Application A.
4. For given error probability in table 3.10 to determine in how many times decreases the error probability at the output of inner decoder (kd1, W1) compared with outer decoder (kd2, W2).
Table 3.10 – Error probabilities for laboratory experiment
| Number of brigade | ||||||||
| p0 | 0,01 | 0,015 | 0,02 | 0,025 | 0,03 | 0,035 | 0,04 | 0,05 |
Home task:
1. To learn items 1.2.5, 1.4.1, 1.4.2 of this teaching manual.
2. To write down the answers to the general questions.
3. To prepare the table 3.9 in the protocol.
4. To prepare blank using Application A.
General questions:
1. Which classes do learned codes belong to
2. Describe the principle of the serial concatenated coding.
3. How is the minimum code distance of CnC determinated?
4. What for are interleaver and deinterleaver needed?
5. What types of interleavers do you know? Describe them.
6. Describe the principle of Meggitt decoder.
7. Tell the advantages of Meggitt decoder comparing to syndrome decoder.
Protocol content:
1. Subject and objective.
2. Executed home task.
3. Graph and table according to laboratory task.
4. Conclusion. Compare three characteristics kd = f(p0) from the laboratory work 2, kd1 = f0(p0) from the laboratory work 4 and kd2 = f2(p0) from the laboratory work 6.
Laboratory work 7
Date: 2016-01-14; view: 1169
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Nonsystematic convolutional codes correcting capability research | | | Turbo-codes with iterative soft-decision Viterbi decoding algorithm corrective capability research |