
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
INDUSTRIAL AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT OF UKRAINE
Prepared by: Kan Emiliya, group 212
Almaty, 2014
Salt – elastic good
Substitutes: soy sauce, sea salt, sour juice (lemon juice), garlic, herbs
Salt is usually used for adding it into our food as a spice, to make a meal more delicious. Scientifically proved, that salt is good for our organisms in certain amounts per day and it is pretty dangerous to consume salt in big amounts. Generally speaking, salt – is an inseparable part of most people’s lives nowadays, which makes it difficult to refer to the elastic or inelastic good.
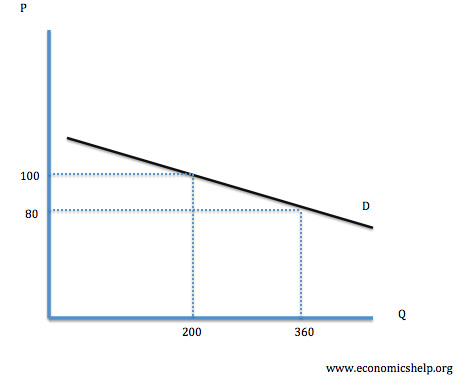
Salt is considered to be an elastic good; as first of all, there are many substitutes for this good. If the price for salt dramatically increases at a time, so people can’t afford buying it, they will not rush into the groceries and get tons of salt. Most people will consider it unreasonable to pay more for the good, they don’t use in big amounts. Popular soy sauce, lemon juice or garlic will become a good substitute for this product and save people’s money (if the price for them won’t increase reasonably).
In fact, only 6% of all salt manufactured goes into food. Therefore, salt is not a life necessity indeed, as people’s health does not suffer, it only gets better actually.
Salt has a low price elasticity of demand, which means that if a product, such as salt, is very inexpensive, consumers are relatively indifferent about a price increase.
Bread – inelastic good
Substitutes: diet bread, bran cereal, rice cakes
Complements: oven, wheat
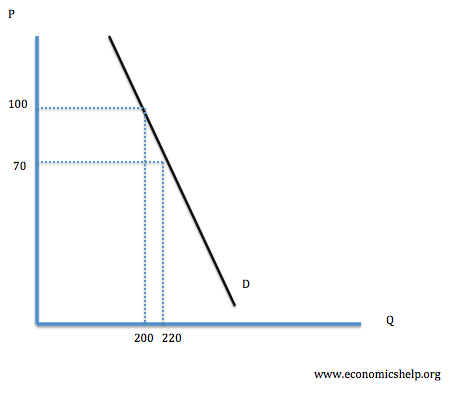
It is hard to imagine our lives without eating bread, especially for the countries, which know what the war is. The mentality of our country proceeds that bread – is our basic food. Kazakhs, Russians, Koreans and others, all of their national cuisines include lots of bread. Most people are just used to eat it and it’s difficult for them to feel gorged without having bread.
Consequently, if the bread is considered to be our main food, how can people stop buying it, even if will cost thousands of tenge.
To my mind, the substitutes of bread will not fully satisfy consumers, as there is no goods with approximately exact nutritional value, as bread has. That is why people will still strive to buy bread by any means – proving, that bread is an inelastic good.
Oil – inelastic good
Substitutes: gas, ethanol or Å85 (mix of ethanol and oil) – biofuels
Complements: car, airplanes, ships
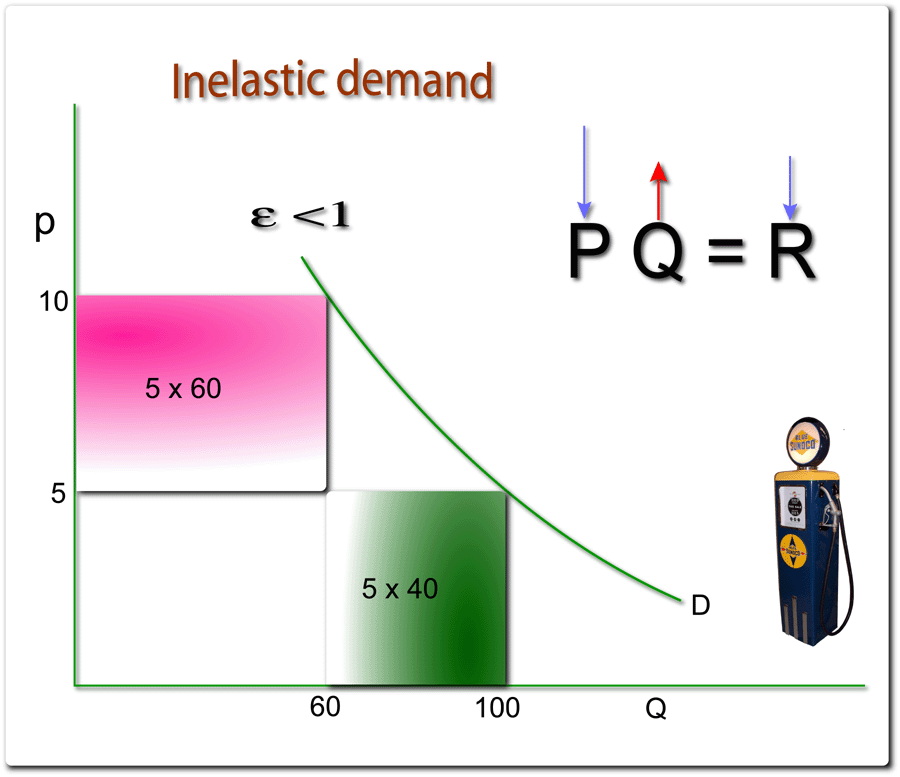
Oil – is probably the most essential product in modern times. It is necessary for such world processes as: transport, heating, production of plastic, rubber and other materials.
It creates the comfortable details of our living that we don’t even notice now. For example, if I want to go to the university, I have to get a cab (which certainly uses oil to run) and it is hour and half to go to my studying by car.
Conclusion: will I be able to come to the lessons if I had a bicycle? And if I lived near the university, will I be able to visit my family whenever I want? Of course it would be difficult for all people not only to travel but even to do such daily operations like going to the market.
Heating oil for our homes is essential. As we know, oil, coal and other minerals are nonrenewable, which means that even if oil is ended up on the planet, we’ll use the coal which will run out: it’s just a matter of time.
Oil is essential, and truthfully saying, there are no really effective substitutes for it and if there are, we still have no clue about their existence.
Computer – elastic good
Substitutes: tablet, cell phones
Complements: mouse, monitor, printer, loudspeakers, modem
We live in the epoch of information and new technologies, so it logical that lately brand new gadgets become old in some period of time, until better and newer technologies appear.
Here what is happening to computers nowadays. We may observe that every day people use tablets, cell phones more than computers. There are tons of advantages of using the tablet: it does not take lots of space, it has same functions as computer does, it is easy in handling (touch screens) and etc.
Most pluses are for tablets and they become smarter and smarter with each season.
Computers are totally elastic goods, besides better substitutes, as people choose if they want to buy a computer or not.
99.7 percent of the world's population does not have a tablet.
“In addition, the rapid increase in the number of active computers entails increasing the number of obsolete, unused machines. This year, according to Gartner, will be charged more than 180 million computers. Some of them will be sold or recycled, the rest - just buried.” (http://compulenta.computerra.ru/archive/science/360803/)
Car – elastic good
Substitutes: bicycle, motorbike, public transport (buses, trolleys)
Complements: oil, spare parts, decorative elements
Cars are expensive and a 10% increase in the price of a car may make the difference whether people will choose to buy the car or not. Therefore, cars have a comparatively high price elasticity of demand.
*Note:
Depending on the type of car, it could either be elastic or inelastic. It could be a luxury car, or some rust box.
Cars – are elatic goods as you can substitute a car for a lower priced car, or switch to public transportation, biking or commuting.

INDUSTRIAL AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT OF UKRAINE
In its economic history, Ukraine has evolved first from an agricultural to an industrialized, and then to a service-oriented country. Major industries include coal, electric power, machinery, chemicals, food processing, woodworking, and tourism. The industrialization of Ukraine started in 1930s when it was a part of the Soviet Union. Having inherited a huge industrial potential from the USSR, Ukraine, as an independent country, has lost part of its industrial capacity due to ongoing inner political and economic crises. Dependence on Russian energy supplies is also a problem as are non-economic, social factors, including an under-developed institutional and social infrastructure and corruption, which have further delayed Ukraine’s transition to a fully developed industrial/service economy.
But now Ukrainian industry is growing again. After economic stagnation, Ukrainian industry is investing and growing, creating a historical window of opportunity to restructure obsolete plants and apply more energy efficient and environmentally friendly technologies and business practices. This would enhance the international competitiveness of the industrial sector and improve quality of life of citizens. Nowadays, the major industries are power generation, fuels, ferrous and non-ferrous processing, chemicals, gas, machine-building, machinery-building, woodworking, and food production. Ukraine is also known for its highly developed defense industry producing and supplying military equipment to the countries throughout the world. Most present Ukrainian industrial enterprises are located in the south-eastern part of the country.
Ukraine as a developing country has great economic potential. In Soviet times, the economy of Ukraine was the second largest in the Soviet Union, being an important industrial and agricultural component of the country's planned economy. With the dissolution of the Soviet system, the country moved from a planned economy to a market economy. The transition process was difficult for the majority of the population which plunged into poverty. A significant number of citizens in rural Ukraine survived by growing their own food, often working two or more jobs and buying the basic necessities through the barter economy. Prices stabilized only after the introduction of new currency, the hryvnia, in 1996. In the early 2000s, the economy showed strong export-based growth of 5 to 10 percent, with industrial production growing more than 10 percent per year. And although Ukraine was hit by the economic crisis of 2008, it was able to, more or less, recover from the crisis results by the beginning of the year 2011.
A relatively cheap local labor force and favorable climate conditions, make it very attractive for the foreign investors. The main trade/investment partners of Ukraine are Russia, Turkey, Germany, Poland, Italy, Turkmenistan, and United States. Ukraine exports ferrous and non-ferrous metals, fuel, petroleum products, chemicals, machinery, and imports energy and some types of machinery and equipment. Ukraine produces nearly all types of transportation vehicles and spacecrafts. Antonov airplanes and KrAZ trucks are exported to many countries. The majority of Ukrainian exports are marketed to the European Union. Since independence, Ukraine has maintained its own space agency, the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). Ukraine became an active participant in scientific space exploration and remote sensing missions. Between 1991 and 2007, Ukraine has launched six self-made satellites and 101 launch vehicles, and continues to design spacecraft.
The country imports most energy supplies, especially oil and natural gas, and to a large extent depends on Russia as its energy supplier. While 25 percent of the natural gas in Ukraine comes from internal sources, about 35 percent comes from Russia and the remaining 40 percent from Central Asia through transit routes that Russia controls. At the same time, 85 percent of the Russian gas is delivered to Western Europe through Ukraine.
The World Bank classifies Ukraine as a middle-income state. Growing sectors of the Ukrainian economy include the information technology (IT) market, which topped all other Central and Eastern European countries in 2007, growing some 40 percent.
1. Read the sentences and say whether they are true (T) or false (F).
1. Ukraine is classified by The World Bank as a high-income state.
2. Ukraine was hit by the economic crisis in 2008.
3. In Soviet times, the economy of Ukraine was the second largest in the Soviet Union.
4. The information technology market of Ukraine topped all other Central and Eastern European countries in 2011.
5. The transition process after the dissolution of the Soviet system was easy for the majority of the Ukrainian population.
6. Now Ukraine is a service-oriented country.
7. 40 % of the natural gas in Ukraine comes from internal sources.
2. Match the given words with their definitions.
| 1.income | a.suddenly bring into a specified condition or state |
| 2.participant | b.a person or organization that buys stocks or shares, or pays money into a bank in order to receive a profit. |
| 3.enterprise | c.a system of money in general use in a particular country |
| 4.investor | d.money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments |
| 5.to plunge | e.a company or business |
| 6.to inherit | f.a person who takes part in something |
| 7.currency | g.receive or be left with something from a predecessor or former owner |
3. Answer the following questions.
1. Which country does Ukraine depend on as its energy supplier at present?
2. Why was the transition process difficult for the majority of the Ukrainian population after the dissolution of the Soviet system?
3. How does the World Bank classify Ukraine nowadays?
4. Does Ukraine have its own space agency? If yes, what is its name?
5. What delayed Ukraine’s transition to a fully developed industrial/service economy after the declaration of its independence?
6. When did the industrialization of Ukraine start?
7. How does Ukraine receive natural gas from Central Asia?
4. Choose the most suitable word(s) to complete each sentence.
1) The majority of Ukrainian exports are marketed to the ______________ .
a)USA
b)European Union
c)UK
2) In 2008 Ukraine was hit by the ______________ .
a)famine
b)strikes
c)economic crisis
3) Ukraine produces nearly all types of transportation vehicles and _______ .
a)spacecrafts
b)airplanes
c)hang gliders
4) 85 percent of the Russian gas is _______ to Western Europe through Ukraine.
a)delivered
b)transmitted
c)forwarded
5) Ukraine is known for its highly developed defense industry producing and supplying _______ equipment to the countries throughout the world.
a)army
b)navy
c)military
6) In Soviet times, the economy of Ukraine was an important industrial and _______ component of the country’s planned economy.
a)farming
b)agricultural
c)territorial
7) Antonov airplanes and KrAZ _______ are exported to many countries.
a)vehicles
b)cars
c)trucks
5. Find in the text synonyms for:
1) machines; 2) power; 3) (is/are) situated; 4) money; 5) to increase; 6) to stay alive; 7) beggary.
6. Find in the text antonyms for:
1) modern; 2) passive; 3) external; 4) import; 5) expensive; 6) to stop; 7) consumer.
7. Translate the following sentences into English.
Date: 2014-12-21; view: 2283
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Basics of economic theory | | | INFECTIOUS DISEASES |