
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Unit 18.The circulatory system.Respiration.
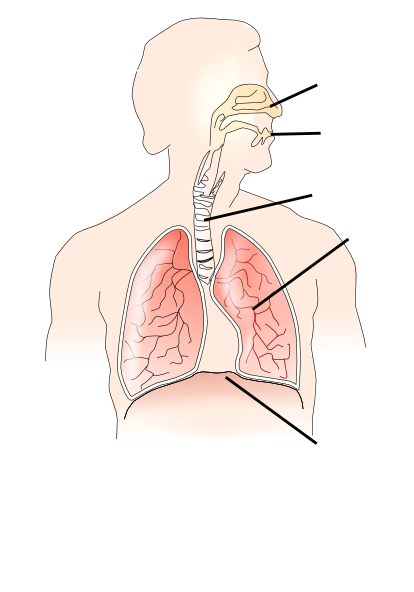
WARM-UP: Try to label the respiratory system
VOCABULARY: Learn the following words and word combinations.
| Artery vein capillary circulatory system cavity atrium ventricle mitral valve to pump bleeding platelet fibrin clot scab acidity alkalinity external nares nostrils pharynx nasal cavity palate to be lined with mucus-secreting epithelium larynx trachea glottis epiglottis bronchus bronchiole alveolus to inhale to exhale air sac |
Guess the meaning of.the following words.
Heart; fluid; lung; aorta; respiration; sense organ; blood; red blood cells; skin; nutrients; body temperature; exchange of gases; to cool organs; living organism; to breath; tube; to swallow; chest wall; chest region.
Practice the following for pronunciation.
artery [ˈɑː.tr.i]
vein [veɪn]
capillary [kəˈpɪl.ər.i]
circulatory system [ˈsɜr·kjə·ləˌtɔr·i]
atrium [ˈeɪ.tri.əm]
ventricle [ˈven.trɪ.kl]
aorta [eɪˈɔː.tə]
acidity [əˈsɪd.ɪ.ti]
alkalinity [ˈæl.kəl.aɪnɪ.ti]
nostril [ˈnɒs.trəl]
pharynx [ˈfær.ɪŋks]
nasal cavity [ˈneɪ.zlˈkæv.ɪ.ti]
palate [ˈpæl.ət]
larynx [ˈlær.ɪŋks]
trachea [trəˈkiː.ə]
glottis [ˈglɒt.ɪs]
epiglottis [ˌep.ɪˈglɒt.ɪs]
platelet [ˈpleɪt.lət]
bronchus [ˈbrɒŋ.kəs]
bronchiole [ˈbrɒŋ.ki.əʊl]
alveolus [ˌæl.viˈəʊ.ləs]
diaphragm [ˈdaɪ.ə.fræm]
cardiovascular system [ˌkɑː.di.əʊˈvæs.kjʊ.lə]
READING: Read the text and do the tasks that follow.
The cardiovascular system is the system of blood circulation. By the cardiovascular system we mean the heart, the arteries, the veins and the capillaries of the human body. The center of the circulatory system is the heart. It lies in the thoracic cavity and has four chambers.
Blood itself is made up of a liquid called plasma and two main types of cells – red cells and white cells. Red cells contain a chemical called hemoglobin, which is responsible for carrying oxygen to all the body’s cells. White cells are far fewer in number than red cells. Their job is to attack invading germs. There are also small particles in blood called platelets, which help the blood to clot when we cut ourselves.
When we cut ourselves, blood vessel walls break. The bleeding stops when enough platelets have stuck to the broken walls and signaled other substances to come. These substances form strands called fibrin, which form a web over the red blood cells to create a clot. The scab is the clot on the skin.
Blood is the vital tissue in the circulatory system, transporting nutrients and oxygen to all the cells and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes from them. Blood also serves other important functions. It transports hormones, the secretions of the endocrine glands, which affect organs sensitive to them. Blood also acts to regulate the acidity and alkalinity of the cells via control of their salt and water content. In addition, the blood acts to regulate the body temperature by cooling certain organs and tissues when an excess of heat is produced (such as exercising muscles) and warming tissues where heat loss is great (such as in the skin).
The term “respiration” means the exchange of gases, which takes place between the living organism and the environment. It is the process by which the body cells and tissues make use of oxygen and carbon dioxide or the waste products of respiration are removed. Air is breathed through either the mouth or the external nares (nostrils) into oral cavity (pharynx). The nostrils, which contain small hairs to filter incoming air, lead into the nasal cavities, which are separated from the mouth below by the palate. The nasal cavities contain the sense organs of smell, and are lined with mucus-secreting epithelium which moistens the incoming air.
Then air passes through the voice box (larynx) into the trachea. The larynx is often called the “Adam’s apple”, anâis more prominent in men than women. Stretched across the larynx are the vocal cords. The opening to the larynx, called the glottis, is always open except when swallowing, when a flap-like structure (the epiglottis) covers it.
The trachea divides into two smaller tubes (bronchi), one is going to each lung. The bronchi divide into tiny passage-ways that are named bronchioles, which lead to air sacs (alveoli). The exchange of life-giving gases is effected through the walls of the alveoli.
Each lung, as well as the cavity of the chest in which the lung rests, is covered by a thin sheet of smooth epithelium, the pleura. The pleura is kept moist, enabling the lungs to move without much friction during breathing.
The chest cavity is closed and has no communication with the outside. It is bounded by the chest wall, which contains the ribs on its top, sides, and back, and the sternum anteriorly. The bottom of the chest wall is covered by the diaphragm. It separates the chest region from the abdominal region, and plays a crucial role in breathing by contracting and relaxing, changing the intrathoracic pressure.
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 2132
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| POST-READING TASKS | | | POST-READING TASKS |