
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Theme 1 SUBJECT AND METHOD OF ECONOMIC THEORY
Good oral health is important not only for our appearance but also for our overall health. Cavities and gum diseases may influence many serious conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory diseases, etc. Untreated cavities can also be painful and lead to serious infections. Proper oral hygiene is the practice of keeping the mouth and teeth clean in order to prevent dental problems and bad breath. Good oral health should be a priority at all life stages, in order to keep the teeth till old age. Smoking is a major risk factor for oral and dental disease; it may cause oral cavity cancer.
There are 5 steps to keep oral health:
∑ see your dentist regularly; some pre cancerous lesions often are detected by dentist when the patient comes for check up.
∑ clean your teeth twice a day. Use a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and bacteria causing cavities, periodontal and gum diseases. Fluoride makes the surface of teeth more resistant to acids during the process of demineralization. The use of dental floss is an important element of the oral hygiene, since it removes the plaque between teeth. Make flossing your habit and do it regularly.
∑ eat a well-balanced diet. Healthy food is good for your general health and your oral health. Bread and cereals are rich in vitamin B while fruits and vegetables contain vitamin C, both of which contribute to healthy gum tissue. Lean meat, fish, and poultry provide magnesium and zinc for teeth. Drink fluoridated water.
∑ check your mouth regularly. Be aware of warning signs of periodontal disease. Gum disease is one of the main reasons why adults lose their teeth.
∑ donít smoke or chew tobacco.
Dental caries is another name for tooth decay where bacterial infection affects the hard outer layer lining of the teeth which consists of enamel, cementum and dentin. The bacteria live in plaque and break down sugars from diet to produce acid. Diagnosis for tooth caries is quite simple. Less obvious decays can only be detected by an X-ray test. The decayed part of the tooth is removed using a dentistís drill and is filled in with paste. If the decay is beyond repair, the tooth will be extracted.
Periodontal disease also called Periodontitis or Gum Disease is a bacterial infection that destroys the supporting structures holding the teeth in their place. The main etiologic agent is bacterial plaque. Left untreated, this disease can lead to bone grafts, gum grafts, and ultimately tooth loss. Some of the early warning signs are slight bleeding when you brush, gums are getting softer and are changing their colour from pink to red.
Thrush of mouth is a yeast infection that may appear in an individualís mouth that is caused by uncontrollable growth of an organism known as Candida albicans. One of the leading and primary reasons of oral thrush is gorge of antibiotics. Candidiasis is not generally a critical condition. The exception is that it enters the blood and then multiplies in organs particularly in people with weakened immune systems. For this reason an antifungal prescription can be administered.
The best way to prevent dental diseases is to practice good oral and to make your check up regularly.
Task 1. Learn the following words by heart:
| acid | ['æsɪd] |
| appearance | [ə'pɪər(ə)ns] |
| caries=tooth decay | ['kɛəri:z] [tu:θ] [dɪ'keɪ] |
| untreated | [ʌn'tri:tɪd] |
| resistant to | [rɪ'zɪst(ə)nt] |
| cavity | ['kævətɪ] |
| plaque | [plɑːk] |
| dental floss | ['dent(ə)l] [flɔs] |
| enamel | [ɪ'næm(ə)l] |
| fluoride | [ˈflʊərʌɪd] |
| filling | ['fɪlɪŋ] |
| hygiene | ['haɪʤi:n] |
| inflammation | [ֽɪnflə'meɪʃ(ə)n] |
| thrush of mouth | [θrʌʃ] [əv] [mauθ] |
| oral diseases | ['ɔːr(ə)l] [dɪ'zi:zəz] |
| periodontal disease | [ˌpɛrɪəˈdɒntəl] [dɪ'zi:z] |
| periodontitis | [ˌpɛrɪədɒnˈtʌɪtɪs] |
Task 2. Find the following words and word-combinations in the text, reproduce the context they are used in and translate it into Russian.
1. oral health,
2. untreated cavities,
3. proper oral hygiene,
4. to keep the teeth till old age,
5. a major risk factor,
6. to brush teeth,
7. dental floss,
8. contribute to healthy gum tissue,
9. fluoridated water,
10. dental caries,
11. an X-ray test,
12. is filled in with paste,
13. gum disease,
14. bacteria infection,
15. leading to inflammation,
16. an antifungal prescription,
17. way to prevent dental diseases.
Task 3. Answer the questions:
1. Why is good oral health important?
2. What serious conditions of health can cavities and gum diseases influence?
3. How can we define a proper oral hygiene?
4. What should people do to practice proper oral hygiene?
5. Can you name bad habits being risk factors for oral diseases?
6. What causes dental caries?
7. Which sings are the early warnings of periodontitis?
8. What is oral thrush caused by?
9. What is the main reason of oral thrush?
10. What is the best way to prevent dental diseases
Task 4. Match the English sentences to their Russian equivalents.
| 1. Most dental disorders arise directly or indirectly from two basic diseases of the teeth and their supporting tissues Ėcaries and periodontal diseases. |
| 2. Oral thrush is a kind of yeast infection that is caused by uncontrollable growth of an organism known as Candida albicans. |
| 3. Good oral health should be a priority in all stages of life, in order to sustain the teeth till old age. |
| 4. The main etiologic agent is bacterial plaque. |
| 5. Unremoved plaque forms a porous deposit that is called tartar. |
| 6. An antifungal prescription can be administered to treat candidiasis. |
| 7. Dentists state tooth decay or caries to be probably the commonest disease of civilization. |
| 8. Oral hygiene consists simply of keeping the teeth free of food debris, thus preventing plague formation which leads to dental diseases. |
| 9. As a general rule, the earlier a decaying tooth is detected, the easier the treatment would be to fix it. |
| 10. Healthy food is good for your general health and your oral health. |
Task 5. Translate the given sentences into Russian, close your book and translate them back into English.
1. Dental caries is characterized by demineralization of the mineral portion of enamel and dentine followed by disintegration of their organic material.
2. In order to maintain a good oral hygiene you need to keep the teeth free of plaque.
3. Some pre cancerous lesions often are found by dentist when a patient comes for checking up.
4. You can use a soft-bristle toothbrush to brush your teeth and brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and bacteria.
5. Make flossing your habit and do it regularly.
6. A proper nutrition is important for strong teeth and gums that can resist diseases.
7. Smoking is a major risk factor for oral and dental disease, it may even cause oral cancer.
8. Dental caries is another name for tooth decay where bacterial infection affects the hard outer layer of the teeth.
9. Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that destroys the supporting structures holding the teeth in their place.
10. Tobacco reduces blood flow to the gums therefore, the gums are deprived of proper oxygen supply and nutrients needed to stay healthy and prevent bacterial infections.
Task 6. Retell the text.
Theme 1 SUBJECT AND METHOD OF ECONOMIC THEORY
1 Subject of economic theory
2 Methods of economic theory
3 Functions of economic theory
1 Subject of economic theory
As known, each science has own subjects of the research. The economic theory is a social science, because economical phenomena (appearances) happened with participation of public relations between people. Each social science has own wide range of problems (except sociology, which studying society in a whole). Politologyst researches the spheres of policy, history - development process by the society; pedagogues - educational and teaching problems. At the center of attention of the economic theory is economic, production life of the society, economical relations and treatments between the people in a process of creation, distribution, exchange and consumption of the different material welfares.
Proff. P.Samuelson gave next can be possible definitions about the subject of economic theory: 1. The science about types of activities linked with exchange and money deals around the people; 2. Science about using limited resources to creation different goods and distribution their between the members of society to consumption; 3. The science about everyday professional life of the people, getting them to earns oneís living and using these materal means; 4. Science about relationships in production, distribution, exchange and consumption spheres; 5. Science about a riches.
The subject of the economic theory is cooperation by peoples about seeking process of effectively ways (decisions) of using limited nature resources to be satisfied social material welfares. Economic theory studied economical life of society searching the ways amount to maximal social-economic efficiency.
Economic theory has an important place in the economic science system. Look at the Scheme 1.
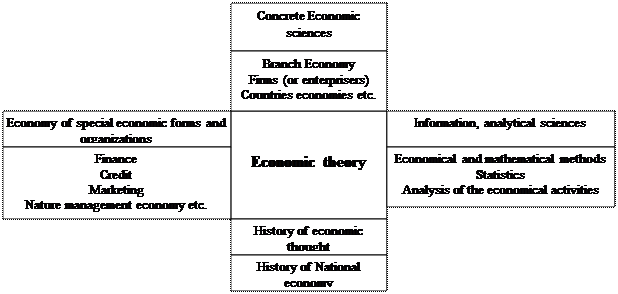 |
Scheme 1. The place of the economic theory in economy science system
Date: 2014-12-28; view: 1920
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Oral Health and Hygiene | | | Methods of economic theory |