
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Top management – planning and strategy.
Ex.1. Read the text
The top management of a company has certain unique responsibilities. One of their key tasks is to make major decisions affecting the future of the organisation. These strategic decisions determine where the company is going and how it will get there. For example, top managers must decide which markets to enter and which to pull out of; how expansion is to be financed; whether new products will be developed within the organisation or aquired by buying other companies. These and other such decisions shape a company’s future.
Before doing any kind of strategic planning, the management must be sure of one thing. They must decide what is the mission and purpose of their business. They also need to decide what it should be in the future. In other words, they must know why the business exists and what its main purpose is. Deciding the mission and purpose is the foundation of any planning exercise.
Two examples will make this point clear – one British, the other American. Most people have heard of Marks and Spencer, one of the biggest and most successful retailers in the world. Michael Marks opened his first penny bazaar in 1884, in Leeds, England. Ten years later there were nine market stores, and Marks had taken into partnership Tom Spencer, the cashier of one of his suppliers. In 1926 Marks and Tom Spencer became a public company. At that point, they could have rested on their laurels! However, around that time, they developed a clear idea of Marks and Spencer’s mission and purpose. Their later success was founded on this idea. They decided that the company was in business to provide goods of excellent quality, at reasonable prices, to customers from the working and middle classes. Providing value for money was their mission and purpose. One of the strategies they used was to concentrate on selling clothing and textiles. Later on, food products were added as a major line of business.
Having decided on its mission and purpose, an organisation will have worked out certain more specific objectives. For example, a car firm may have the objective of producing and marketing new models of cars in the medium –price range. Another objective may be to increase its market share by 10% in the next five years. As soon as it has established its more specific , medium-term objectives, the company can draw up a corporate plan. Its purpose is to indicate the strategies the management will use to achieve its objectives.
However, before deciding strategies, the planners have to look at the company’s present performance, and at any external factors which might affect its future. To do this, it carries out an analysis, sometimes called a SWOT analysis (strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats). First, the organisation examines the current performance, assessing its strengths and weaknesses. It looks at performance indicators like market share, sales revenue, output and productivity. It also examines its resources – financial, human, products and facilities. Next, the company looks at external factors, from the point of view of opportunities and threats. It is trying to assess technological, social, economic, political trends in the markets where it is competing. It also examines the activities of competitors.
Having completed the SWOT analysis, the company can now evaluate its objectives and perhaps work out new ones. They will ask themselves questions such as: Are we producing the right products? What growth rate should we aim at in the next five years? Which new markets should we break into?
The remaining task is to develop appropriate strategies to achieve the objectives. The organisation decides what actions it will take and how it will provide the resources to support those actions. One strategy may be to build a new factory to increase production capacity. To finance this, the company may develop another strategy, the issuing of new shares to the public.
Company planning and strategic decision-making are key activities of top management. Once they have been carried out, objectives and targets can be set at a lower levels in the organisation.
Ex.2. What, in your opinion, is the mission and purpose of the following organisation?
- Coca Cola
- International Business Machines
- Sony
- American Express
- Rolls Royce
- McDonald’s
- Yves St Laurent
- Walt Disney Productions
Ex.3. Explain the difference between a strategy and an objective.

 Ex.4. Complete the following sentences using suitable items from the box below.
Ex.4. Complete the following sentences using suitable items from the box below.

 | |||
 | |||
? ? ?
1. A well-known advertising agency aims to achieve a ………… of 20% a year.
2. This ……… is unprofitable. We’ll have to discontinue it.
3. Companies like Unilever and IBM have huge financial ……….. .
4. By re-organising the work of office staff, you can often increase their ……… .
5. We’re a small firm, so we aren’t able to offer a wide ………… .
6. Most of Shell Oil’s ………. comes from overseas subsidiaries.
7. By extending our factory, we have been able to expand our ………… .
8. With the help of their cheap, high-quality word-processor, the Amstrad company were able to greatly increase their ………… in the UK.
Ex.5. Answer the following questions in any way you wish using the phrasal verbs in brackets.
1. What does a firm often have to do if it is not successful in a market? (pull out)
2. What do you do if your main competitor is doing better than you in the market? (work out)
3. After you have made a deal with an overseas agent, what do you usually do? (draw up)
4. How can you find out if there will be a demand for a product you wish to develop? (carry out)
5. What can you do if the demand for your products in your home market is saturated? (break into)
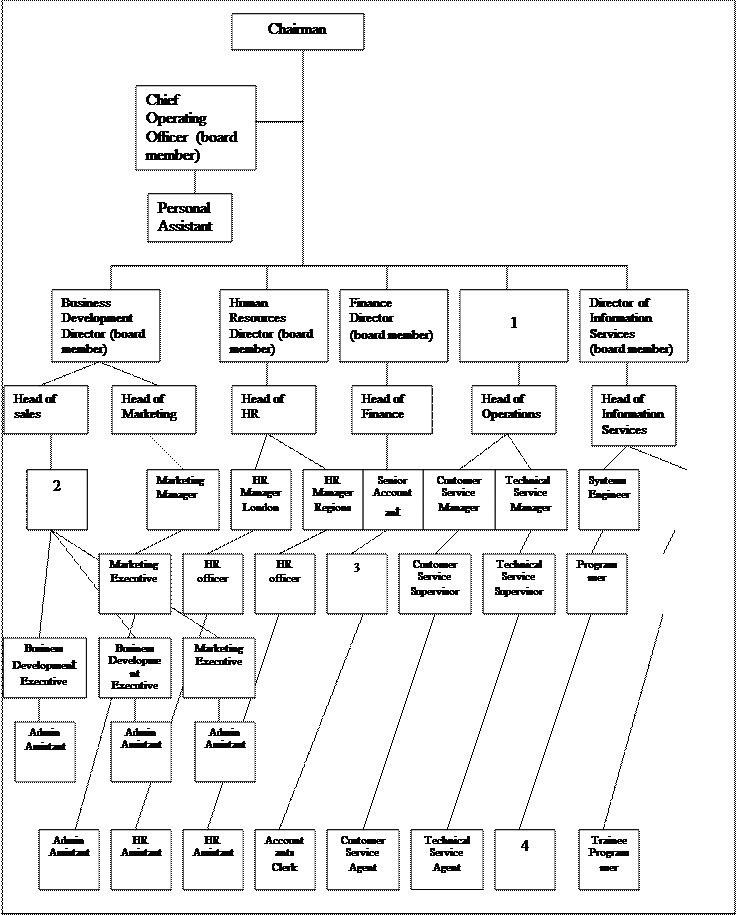
Ex.6. Use the following job titles to complete the chart: Trainee Programmer, Director of Operations (board member), Junior Accountant, Sales, Sales Manager.
|
|

Ex.7. Read the dialogue.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 3034
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Choose the parts and roleplay the situation. | | | Coopers is in financial trouble. |