
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Ionic equations
Double replacement reactions and other reactions of ions in aqueous solution are usually represented by that are known as “net ionic equations”. To write a net ionic equation, one firstly writes an equation in which all strong electrolytes are shown as dissociated ions in solution (without steps, of course). For example:
1. Formation of slightly soluble substance:
CuSO4 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH)2¯ + Na2SO4



 Cu2+ + SO42- + 2Na+ + 2OH- = Cu(OH)2¯ + 2Na+ + SO42- -
Cu2+ + SO42- + 2Na+ + 2OH- = Cu(OH)2¯ + 2Na+ + SO42- -
this is a complete ionic equation.
Cu2+ + 2OH- = Cu(OH)2¯ - this is net ionic equation.
2. Formation of weak electrolyte:
a) HCl + KOH = KCl + H2O,



 H+ + Cl- +K+ + OH- = K+ + Cl- + H2O,
H+ + Cl- +K+ + OH- = K+ + Cl- + H2O,
H+ + OH- = H2O.
 b) ÑH3COONa + HCl = CH3COOH + NaCl,
b) ÑH3COONa + HCl = CH3COOH + NaCl,


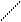 CH3COO- + Na+ + H+ + Cl- = CH3COOH + Na+ + Cl-,
CH3COO- + Na+ + H+ + Cl- = CH3COOH + Na+ + Cl-,
CH3COO- + H+ = CH3COOH.
3. Formation of gas:



 à) K2CO3 + 2HNO3 = 2KNO3 + CO2 + H2O,
à) K2CO3 + 2HNO3 = 2KNO3 + CO2 + H2O,
2K++ CO32- + 2H+ + 2NO3- = 2K+ + 2NO3- + CO2 + H2O,
CO32- + 2H+ = CO2 + H2O.
b) FeS + 2HCl = FeCl2 + H2S.
 Iron (II) Sulfide is slightly soluble and Hydrogen Sulfide is a weak electrolyte (gas). Therefore:
Iron (II) Sulfide is slightly soluble and Hydrogen Sulfide is a weak electrolyte (gas). Therefore:
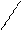 FeS + 2H+ + 2Cl- = Fe2++ 2Cl- + H2S,
FeS + 2H+ + 2Cl- = Fe2++ 2Cl- + H2S,
FeS + 2H+ = Fe2++ H2S.
Interactions in the solutions of electrolytes are realized completely if in the result the following will be formed:
à) weak electrolyte;
á) sediments;
â) gases.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
1. Write the dissociation equation for the ions of the following compounds:
H2SO4, HClO4, Ca(OH)2, AlCl3, Fe2(SO4)3, K2CO3, Bi(NO3)3, Na2HPO4, NH4HCO3, Co(NO3)3.
2. Write molecular, complete and net ionic equations:
Ø BaCl2 + Fe2(SO4)3 →
Ø Cu(NO3)2 + Na2CO3 →
Ø Na2SiO3 + H2SO4 →
Ø FeCl3 + KOH →
Ø H3PO4 + Ba(OH)2 →
Ø Cu(OH)2 + HCl →
Ø Na2HPO4 + CaCl2 →
3. Which of two reactions does proceed in the solution up to the end and why? Draw the corresponding molecular, complete and net ionic equations:
Ø Calcium Chloride + Magnesium Nitrate →
Ø Sodium Carbonate + Zinc Chloride →
Ø Lithium Sulfate + Potassium hydroxide →
Ø Iron (II) Sulfate + Sodium hydroxide →
Ø Iron (III) hydroxide + Nitric Acid →
4. Draw molecular equations of the reactions between substances interacted in aqueous solution according to the following scheme:
Ø Ba2+ + SO42- → BaSO4;
Ø Fe(OH)3 + 3H+ → Fe3+ + 3H2O;
Ø CaCO3 + 2H+ → Ca2+ + CO2 + H2O;
Ø 3Mg2+ + 2PO43- → Mg3(PO4)2;
Ø Ca2+ + 2 F- → CaF2.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 987
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Theory of dissociation | | | HYDROLYSIS OF SALTS |