
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Theory of dissociation
It is experimentally established that solutions of certain substances in water may conduct an electric current (for example, solution of table salt in water) while the solution of sugar may not. The first group of substances was named electrolytes, the second one - non-electrolytes.
In order to understand the unique properties of electrolyte solutions, we will look briefly at the theory of Svante Arrhenius (1859-1927). His work forms the basis of the modern theory of ions in aqueous solutions, the solutions in which water is the solvent. Arrhenius considered the ions to be electrically charged. As a whole the solution contains equal numbers of positive and negative charges. He concluded that ions were produced by “ionization” of molecules in aqueous solution.
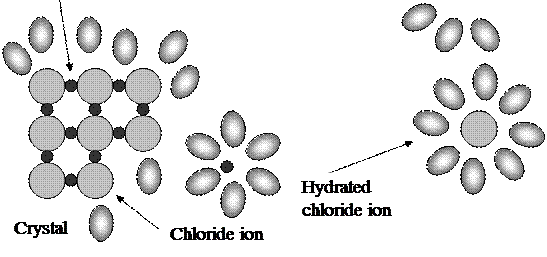
Water - solvent in aqueous solution - is not inert component. The polarity of water molecules plays an important role in the formation of solutions of ionic compounds in water. Molecule of H2O is a polar particle called “doublet”:
H+ ─ OH-_

The charged ends of water molecules attract the ions in the ionic compounds and bring them into solution. The energy released when an ion is attracted to a water molecule also affects the heat of solution of the ionic compound in water.
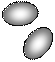
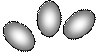
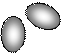
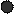
The solution process for ionic compounds. Suppose we drop a few crystals of Sodium Chloride into a beaker of water. At the crystal surface, water molecules come into contact with Na+ and Cl- ions. The positive ends of the water molecules are attracted to Cl- ions; the negative ends are attracted to Na+ ions. The attraction between water molecules and the ions is strong enough to draw the ions away from the crystal surface and into solution, as illustrated in Fig. 15.
|








|


 | |||||
 | |||||
 | |||||
|

 | |||
 |
Figure 15. Table salt (Sodium Chloride) dissolves in water forming hydrated Sodium and Chloride ions
This solution process with water as the solvent is referred to as hydration. The ions are said to be hydrated. The attraction between ions and water molecules is strong enough that each ion in solution remains surrounded by water molecules.
The separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves is called dissociation (means disintegration, decay, decomposition). The equations representing the dissociation of Sodium Chloride in water are:
NaCl (s)  Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
where (s) - solid phase;
(aq) - aqueous solution
or in simplified form
NaCl  Na+ + Cl-.
Na+ + Cl-.
4. Degree of dissociation
Degree of dissociation (α) of electrolyte is the ratio:
α = 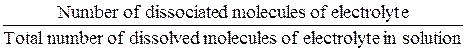 .
.
α measures in percents (0…100%) or per unit (0…1). Degree of dissociation depends on:
Ø nature of chemical bonds in solute and solvent;
Ø concentration of solute;
Ø temperature of solution.
The main trends of these interdependences are:
- Degree of dissociation is rising with decreasing of concentration of electrolyte;
- Degree of dissociation is rising with rise in temperature.
Depending on degree of dissociation, all electrolytes are subdivided into three types: strong, medium and weak. This subdivision is relative, though.
Degree of dissociation of strong electrolytes is more than 30%, medium - from 3% till 30%, weak - less or equal than 3%. In Appendix 9 it is presented the division of main classes of inorganic substances as electrolytes.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1702
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Molarity (molar concentration) | | | Ionic equations |