
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Chemical properties
1. Interaction with basic oxides with forming of neutral salts and water:
2NaHSO4 + Na2O = 2Na2SO4 + H2O;
2. Interaction with amphoteric oxides with forming of neutral salts and water:
Zn(HSO4)2 + ZnO = 2ZnSO4 + H2O;
3. Interaction with bases with forming of neutral salts and water:
NaHSO4 + NaOH = Na2SO4 + H2O;
Ca(H2PO4)2 + 2 Ca(OH)2 = Ca3(PO4)2↓ + 3 H2O.
4. Interaction with amphoteric hydroxides with forming of salts and water:
Zn(HSO4)2 + Zn(OH)2 = 2ZnSO4 + 2H2O;
5. Interaction with active metals with forming of neutral salts and free Hydrogen isolation:
2NaHSO4 + 2Na = Na2SO4 + H2↑
6. Thermal decomposition with medium salts formation:
Ca(HCO3)2 → CaCO3↓ + ŃO2↑+ H2O.
Double and mixed salts may be considered as the sort of neutral salts. Double salts may be prepared by interaction between any multibasic acid and different bases:
H2SO4 + KOH + NaOH = NaKSO4 + 2H2O.
or during synchronous crystallization of different salts:
K2SO4 + Al2(SO4)3 + 24H2O = 2KAl(SO4)2·24H2O.
Mixed salts may be prepared by interaction of multiacidic bases and different acids. For example, preparation of bleaching powder:
Ca(OH)2 + HCl + HClO = CaCl(ClO) + H2O.
8. Structural-graphic formulas of chemical compounds
These schemes show the order of atom combination in molecules of substance.
The rules for graphic formula’s compilation are the following:
Ø It may directly connect ions to opposite charges only;
Ø Quantity of chemical bonds for each atom is equal to its charges (modulo) in most cases.
For example:
H2SO4; H+2 S6+ O2-4
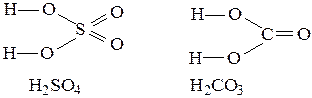
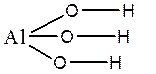 Al(OH)3 ; Al3+(O2-H+)3 or H+3Al3+O2-3
Al(OH)3 ; Al3+(O2-H+)3 or H+3Al3+O2-3
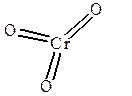
CrO3; Cr6+O2-3
Mg(HCO3)2 ; Mg2+ (H+ C4+ O2-3)2
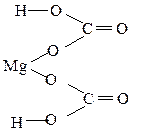
|


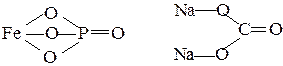
FePO4 Na2CO3
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
1. To determine the oxidation numbers of elements in compounds: Fe2O3, H2S, FeS, HNO2, H4P2O7, Ca3(PO4)2, Fe2(SO4)3, Ni(NO3)3, Na3AlO3, KAlO2, LiFe(SO4)2, CaHAsO4, Na2O2, MnSO3, (NH4)H2PO4.
2. Which oxides may react with water directly: BaO, Cu2O, P2O5, SO3, SO2, K2O, N2O3, CoO, Cl2O7, ZnO, NO2, SiO2, MnO2, FeO, SrO? To write the corresponding equations of chemical reactions.
3. Which oxides do correspond to the next compounds: H2SO3, Ca(OH)2, NaOH, Fe(OH)3, HNO3, Co(OH)3, H4P2O7, CuOH, NAOH, CaBeO2, HMnO4, H2CrO4, K2MnO4?
4. To compile equations for the transformations given below:
Al ® Al2O3 ® Al(NO3)3 ® Al2(SO4)3 ® Al(OH)3;
Zn® ZnO ® ZnSO4 ® Zn(OH)2 ® K2ZnO2 ® ZnCl2 ® Zn3(PO4)2 ® Na2ZnO2.
5. To compile structural-graphic formulas of chemical compounds given below:
Cr2O3, Ni(OH)3, H3PO4, Al2(SO4)3, Ca3(PO4)2.
6. What oxides may react with each other (by pairs): Na2O, CaO, SO2, H2O, P2O3, ZnO?
7. To write reactions for conversing of Iron (III) Dihydroxychloride and Calcium Dihydrophosphate in neutral salts.
8. To write all possible reactions between: a) Aluminium Hydroxide and Orthophosphoric Acid; b) Barium Oxide and Sulfuric Acid (taking into account the possibility of neutral, acidic and basic salts forming).
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1201
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Basic salts | | | LABORATORY TRAINING |