
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Basic salts
Basic salts may form only such bases that have two and more groups OH-. They are products of incomplete substitution of OH--groups of corresponding bases to acid residues.
Preparation
1. Hydrolysis of neutral salts formed by weak base and strong acid:
ZnCl2 + HOH ↔ ZnOHCl + HCl;
2 CuSO4 + 2 HOH ↔ (CuOH)2SO4 + H2SO4.
2. By addition (by drops) of small quantities of alkalis to solutions of neutral salts of metals:
AlCl3 + 2NaOH = Al(OH)2Cl + 2NaCl;
Ca(NO3)2 + NaOH = CaOHNO3 + NaNO3.
3. Interaction with salts formed weak acids with medium salts:
2MgCl2 + 2Na2CO3 + H2O = (MgOH)2CO3↓ + CO2↑ + 4NaCl;
2CuSO4 +2(NH4)2SO3+H2O= CuOH)2SO3↓+SO2↑+(NH4)2SO4.
4. In a few cases by interaction of neutral salts with bases of the same name:
CaCl2 + Ca(OH)2 = 2Ca(OH)Cl;
Ba(NO3)2 + Ba(OH)2 = 2BaOHNO3.
Chemical properties
1. Interaction with acids or acidic oxides forming neutral salts and water (likewise bases):
2Mg(OH)NO3 + N2O5 = 2Mg(NO3)2 + H2O;
Mg(OH)NO3 + HNO3 = Mg(NO3)2 + H2O.
2. Thermal decomposition:
(CuOH)2CO3 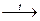 2 CuO + CO2 + H2O;
2 CuO + CO2 + H2O;
2 CaOHCl 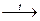 CaCl2 + H2O + CaO.
CaCl2 + H2O + CaO.
3. Some salts may (weaken) loose water with the formation of so-called oxysalts with time or on heating:
Bi(OH)2Br à BiOBr + H2O.
Acidic salts
Acid salts are the products of partial replacement of Hydrogen in acids for atoms of metals or ionic groups. Acid salts may form only such acids that have two and more atoms of Hydrogen.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1224
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Chemical properties | | | Chemical properties |