
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Decoder
1-out-of-n decoder
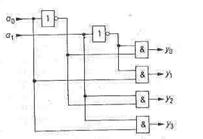
A 1-out-of-n decoder is a circuit with n outputs and ld n inputs. Outputs yJ are numbered from 0 to (n — 1). An output therefore goes to "one" precisely when the input binary number A is identical to the number J of the relevant output. Figure 1.16 shows the truth table for a l-out-of-4 decoder. The variables a0 and al represent the straight binary code of the number A. The sum of the products (disjunctive normal- form) of the receding functions can be taken directly from the truth table. Figure 1.17 shows the corresponding implementation.
| A | a1 | a2 | y3 | y2 | y1 | y0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Fig. 1.16 - Truth table of a l-out-of-4 decoder. Fig. 1.17 - Circuit of a l-out-of-4 decoder. 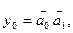
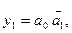
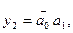
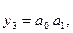
When using monolithic integrated circuits, hand functions are often chosen rather than and functions, so that most of the output variables are complemented (barred).
Types of 1C: TTL CMOS
10 outputs 74LS42 4028
For further 1C types, see the following section on demultiplexers.
Priority decoder
The 1-out-of-n code can be converted to straight binary code by using a priority decoder. At its outputs a straight binary number appears which corresponds to the highest input number which is logic 1. The value of the lower-index input variables is irrelevant, hence the name priority decoder. This property enables the circuit to convert not only the 1-out-of-n code but also a sum code in which not just one variable is 1, but also all the less significant bits. The truth table of the priority decoder is shown in Fig.1.18.
| J | X9 | X8 | X7 | X6 | X5 | X4 | X3 | X2 | X1 | Y3 | Y2 | Y1 | Y0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X | X | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X | X | X | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X | X | X | X | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X | X | X | X | X | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X | X | X | X | X | X | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 0 | 1 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 1 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Fig. 1.18 - Truth table of a priority decoder, x = any.
1C types:
l-out-of-10 code: SN 74147 (TTL) MC 10165 (ECL);
l-out-of-8 code, extendable: SN 74148 (TTL); MC14532(CMOS)
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1717
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Fig. 1.14 - Emitter-coupled multivibrator. Fig. 1.15 - Voltage waveforms. | | | Binary Decoders |