
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Properties of emulsions
The emulsions satisfy the following criteria:
1. Emulsions show all the characteristic properties of colloidal solution such as Brownian movement, Tyndall effect, electrophoresis etc.
2. These are coagulated by the addition of electrolytes containing polyvalent metal ions indicating the negative charge on the globules.
3. The size of the dispersed particles in emulsions in larger than those in the sols. It ranges from 1000 Å to 10,000 Å. However, the size is smaller than the particles in suspensions.
4. Emulsions can be converted into two separate liquids by heating, centrifuging, freezing etc. This process is also known as demulsification. [21,22]
Many advances have been made in the field of emulsions in recent years. Emulsion stability depends on presence of adsorbed structures on the interface between the two liquid phases. Emulsion behavior is largely controlled by the properties of the adsorbed layers that stabilize the oil-water surfaces [23].
The knowledge of surface tension alone is not sufficient to understand emulsion properties, and surface rheology plays an important role in a variety of dynamic processes. When a surface active substance is added to water or oil, it spontaneously adsorbs at the surface, and decreases the surface tension. In the case of small surfactant molecules, a monolayer is formed, with the polar parts of the surface-active molecules in contact with water, and the hydrophobic parts in contact with oil, Figure 9 [24].
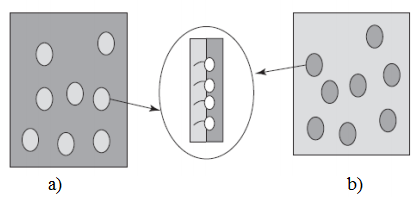
Figure 9. Schematic representation of emulsion structures: a) O/W emulsion; b) W/O emulsion.
Emulsions of crude oil and water can be encountered at many stages during drilling, producing, transporting and processing of crude oils and in many locations such as in hydrocarbon reservoirs, well bores, surface facilities, transportation systems and refineries [25,26].
1.3 Breakdown processes in emulsions.
The various breakdown processes are illustrated in Figure 10. The physical phenomena involved in each breakdown process are not simple, and it requires analysis of the various surface forces involved. In addition, the above-mentioned processes may take place simultaneously rather than consecutively and this complicates the analysis.Model emulsions, with monodisperse droplets, cannot be easily produced, and hence, any theoretical treatment must take into account the effect of droplet size distribution. Theories that take into account the polydispersity of the system are complex, and in many cases, only numerical solutions are possible. In addition, measurements of surfactant and polymer adsorption in an emulsion are not easy and one has to extract such information from measurement at a planer interface. In the following sections, a summary of each of the above-mentioned breakdown processes and details of each process and methods of its prevention are given.[27]
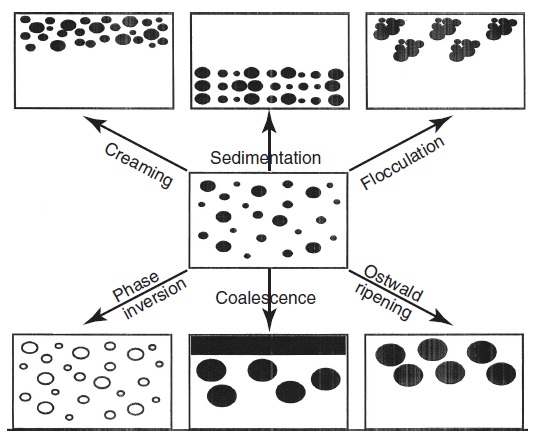
Figure 10. Schematic representation of the various breakdown processes in emulsions.
Date: 2016-04-22; view: 1489
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Естетика експресіонізму. Філософська основа експресіонізму. | | | Creaming or sedimentation |