
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
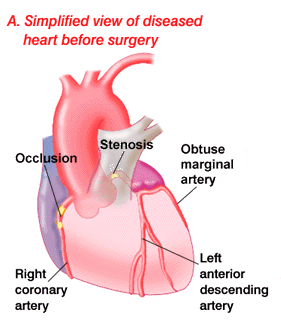
Ischemic heart disease.
IHD classification (WHPO):-
- 1. Acute blood flow arrest
- 2. Stenocardia
- 3. Myocardial infarction
- 4. Heart failure
- 5. Cardiac rhythm disorders
IHD clinical picture:-
- Angina pectoris: (chest pain on exertion, in cold weather or emotional situations)
- Acute chest pain: acute coronary syndrome, unstable angina or myocardial infarction("heart attack", severe chest pain unrelieved by rest associated with evidence of acute heart damage)
- Heart failure: (difficulty in breathing or swelling of the extremities due to weakness of the heart muscle)
IHD diagnostics:-
- ECG
- Echocardigraphy
- Coronarography
- Ventriculography
IHD treatment:-
- Non-invasive surgical treatment
- (could help to turn up the heart on working in conditions of decreased coronary circulation)
- Percutaneus coronary intervention (PCI) (balloon angioplasty or coronary stenting)
- Open heart operation
IHD invasive treatment:-
- The best revascularization – is full revascularization
Indications for IHD surgery treatment:-
- Both PCI and CABG are more effective than medical management at relieving symptoms Rihal C, Raco D, Gersh B, Yusuf S (2003)
- CABG is superior to PCI in multivessel coronary disease (SoS trial)
- Patients treated with CABG had lower rates of death and of death or myocardial infarction than treatment with a coronary stent
IHD surgery treatment:-
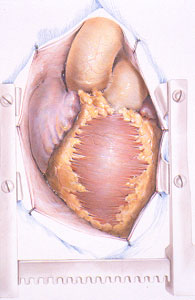
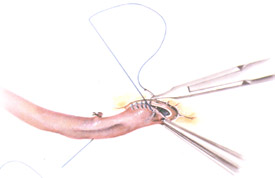
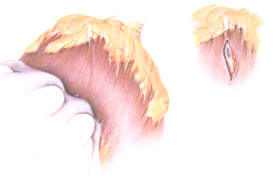
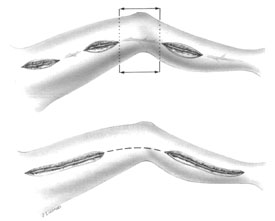
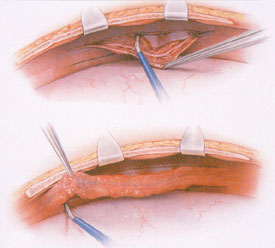
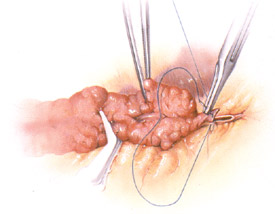
- Coronary-aortic bypass grafting (CABG)
- LIMA–to-LAD grafts
Indications for CABG:-
- Significant left main coronary artery stenosis.
- Left main equivalent: significant (70 %) stenosis of the proximal LAD and proximal left circumflex arteries.
- 3. Three-vessel disease.
- 4. Two-vessel disease with significant proximal LAD stenosis and either ejection fraction <0.50 or demonstrable ischemia on noninvasive testing.
- 5. One- or 2-vessel stenosis without significant proximal LAD stenosis, but with a large area of viable myocardium and high-risk criteria on noninvasive testing
- .
- 6. Disabling angina despite maximal noninvasive therapy, when surgery can be performed with acceptable risk.
2004 ACC/AHA CABG guidelines:-
- Disease of the left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- Disease of all three coronary vessels (LAD,LCX and RCA).
- Diffuse disease not amenable to treatment with a PCI.
| 
|  
|
| 
| 
|
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 1766
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Piotr Ostaszewski | | | The Story about one Bench |