
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Before After Difference
28 -(minus) 12 16
17 31 -14
36 19 17
35 14 21
32 20 12
33 19 14
Step 3: From now on, only this “Difference” column matters. Rank the “Difference” scores.
· The highest number ranks #6 (there are only 6 numbers in this sample. If there were 10 or 20 then your highest rank would go to 10 or 20).
· The lowest number ranks #1.
· Our ranks for this sample would be:
16 Rank # 4
-14 # 1
17 # 5
21 # 6
12 # 2
14 # 3
Step 4: add up your positive ranks (not the scores, but the rank #s). R=Rank
∑ R+ = 4 + 5 + 6 + 2 + 3 = 20
Step 5: add up your negative ranks (not the scores, but the rank #s). R=Rank
∑ R- = 1
Step 6: T= the smallest of these numbers
T= 1
Step 7: Solve the following equation to find the z score.
T = 1 N (n) = 6 (we had 6 participants in this data set)
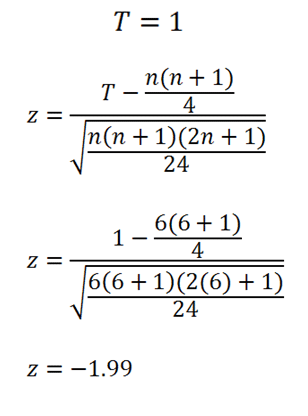
If Z is less than -1.96, or greater than 1.96, you have to reject the Null Hypothesis.
Z = -1.99 (Reject the Null). The IV did make a difference.
T-Test
Not a recommended test to use because our sample size is so small (and it’s considered a parametric test). If you decide to use the t-test be sure to justify its use (for example: saying that although the criteria for parametric tests are not met these tests are very robust). Use this test only if no other statistical test will work.
- Example: Use when you have 1 variable in 2 situations. You want to find the mean (average) between 2 conditions.
STEP 1: Find the mean from your data set.
· Data: 4, 2, 3, 4, 1, 3, 4 = the sum of these is 21 there are 7 scores (N=7)
· Mean = total (21) divided by 7 = 3
· Mean = 3
STEP 2: Subtract the mean from each score.
· 4-3= 1 2-3=-1 3-3=0 4-3=1 1-3=-2
· 3-3=0 4-3=1
STEP 3: Rank the items in order (largest to smallest).
· 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -2
STEP 4: Add the sum of the Positive Ranks.
· 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4
STEP 5: Add the sum of your Negative Ranks.
· -1 + -2 = -3
STEP 6: Take the smallest score (t) from Steps 4 & 5.
· t=-3
STEP 7: If t>1.96 or <-1.96 then p<.05 (significant or valid). This means that the independent variable (IV) did cause the change in the Dependent Variable (DV).
· -3 is less than <1.96 so the test is NOT valid. You must accept the NULL.
· The results are caused by chance, not the IV.
Section G. Discussion Approx. 600 words
The discussion is the final part of the paper. This is an important part of your report, so make sure that you do everything that is set out in the assessment criteria. In this section you:
· Interpret your own results in the light of previous research.
· You must relate your findings to each of the theories or studies referred to in the introduction, and say how your results differed and where they were in line with the study replicated. No new studies or citation should be introduced.
· Then you need to say why you think you achieved the results you did.
· You should analyze and evaluate your methodology. You are not expected to conduct a ‘perfect’ experiment.
· Be sure to discuss the limitations that may have affected the outcome of the experiment.
| Scoring G. Discussion: (8 marks) q Analysis of results is well-developed and complete. q Descriptive and inferential statistics are discussed. q The findings of the student’s experimental study are discussed with reference to relevant background theories or studies. q Limitations of the design and procedure are highly relevant and have been rigorously analyzed. q Modifications are suggested and ideas for further research may be mentioned. q The conclusion is appropriate. |

WORD COUNT ENDS HERE
· The word limit is 1500-2000 words.
· The word count does not include supplementary information such as the abstract, title page, references, and appendices
H. Citation of Sources
This section is often called a Bibliography or References Section. For your IA, you must use APA style (from the American Psychological Association). I have included many sources to help guide you through this process.
· Primary source documents from respected academic journals are best (use WFU library)
· Secondary sources may also be used but are not as strong academically.
· You should use more books than Internet sources.
· Many journal articles are stored on-line (or in on-line databases). If these sources were originally published, list the source by its original published format and date. You can put the URL where the article is now archived (stored).
· Make sure you list all sources in alphabetical order.
· Every source used in your Introduction and Discussion must be listed here.
Your APA format will use the following information:
- Book: author(s), book title, publisher, date of publication, and page number(s) if appropriate.
- Journal: author(s), article title, journal title, date of publication, and page number(s).
- Newspaper: author(s), article title, name of newspaper, section title and page number(s) if desired, date of publication.
- Web site: author(s), article and publication title where appropriate, as well as a URL, and a date when the site was accessed.
Your study must contain proper APA citation format. Every time you refer to your research there should be a citation (reference). The full reference goes here in this section.
Here are several examples of how to cite your source within the text:
· Smith (1998) found that psychology students were motivated by grades.
· In 1998, Smith found that psychology students were motivated by grades.
· Research shows that psychology students are highly motivated by grades (Smith, 1998).
· For in-text citations without page numbers (such as websites), help the reader pinpoint the quote by listing the section name or paragraph number instead.
Plagiarism (copying someone’s words or work without giving credit) is an automatic zero (F) in IB and can cost you your certificate or diploma.
Here are some tutorials to help you learn the APA style:
How to Write an APA Style Paper | eHow.com, http://www.ehow.com/how_2002020_apa_style_paper.html#ixzz1untWl5FB
http://www.apastyle.org/learn/index.aspx
http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/
http://psychology.about.com/od/apastyle/a/apageneral.htm
http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_apa_format_examples.shtml
http://psychology.vanguard.edu/wp-content/uploads/2011/07/apastyleessentials.pdf
Appendix (Appendices, plural)
In this section include blank copies of any supplementary information (anything too bulky for the main text). Number in order with lower case Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi, etc).
· One copy of standardized instructions
· One copy of any briefing/debriefing notes
· One copy of any materials used (like a word list)
· One copy of informed consent letters
· Any calculations. Tables of raw data must be included here, but it is not necessary to include all participant responses.
· Make sure that each appendix is numbered and has an appropriate title (example: Appendix for Calculation of the Mann-Whitney U).
Special Thanks:
Dr. David W. Martin, NC State, Department of Psychology for his book: Doing Psychology Experiments, 7th Edition, Thomson Publishing, 2008.
John Crane, IB Psychology.
Numerous other IB Psychology teachers who have shared their experience in the IA process.
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 1322
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Experimental Group Control Group | | | Important Types of Tour Operators |