
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
List the main SI units of measurements.
Give a definition of metrology. Explain its physical meaning as an object of measurements.
Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement. Metrology is defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures , as "the science of measurement, embracing both experimental and theoretical determinations at any level of uncertainty in any field of science and technology.
Metrology is a very broad field and may be divided into three basic activities, though there is considerable overlap between the activities:
- Definition of internationally accepted units of measurement.
- Realization of these units of measurement in practice
- Application of chains of traceability linking measurements made in practice to reference standards.
Metrology also has three basic subfields, all of which make use of the three basic activities, though in varying proportions:
- Scientific or fundamental metrology
- Applied, technical or industrial metrology
- Legal metrology.
Theoretically, metrology, as the science of measurement, attempts to validate the data obtained from test equipment. Though metrology is the science of measurement, in practical applications, it is the enforcement, verification and validation of predefined standards for:
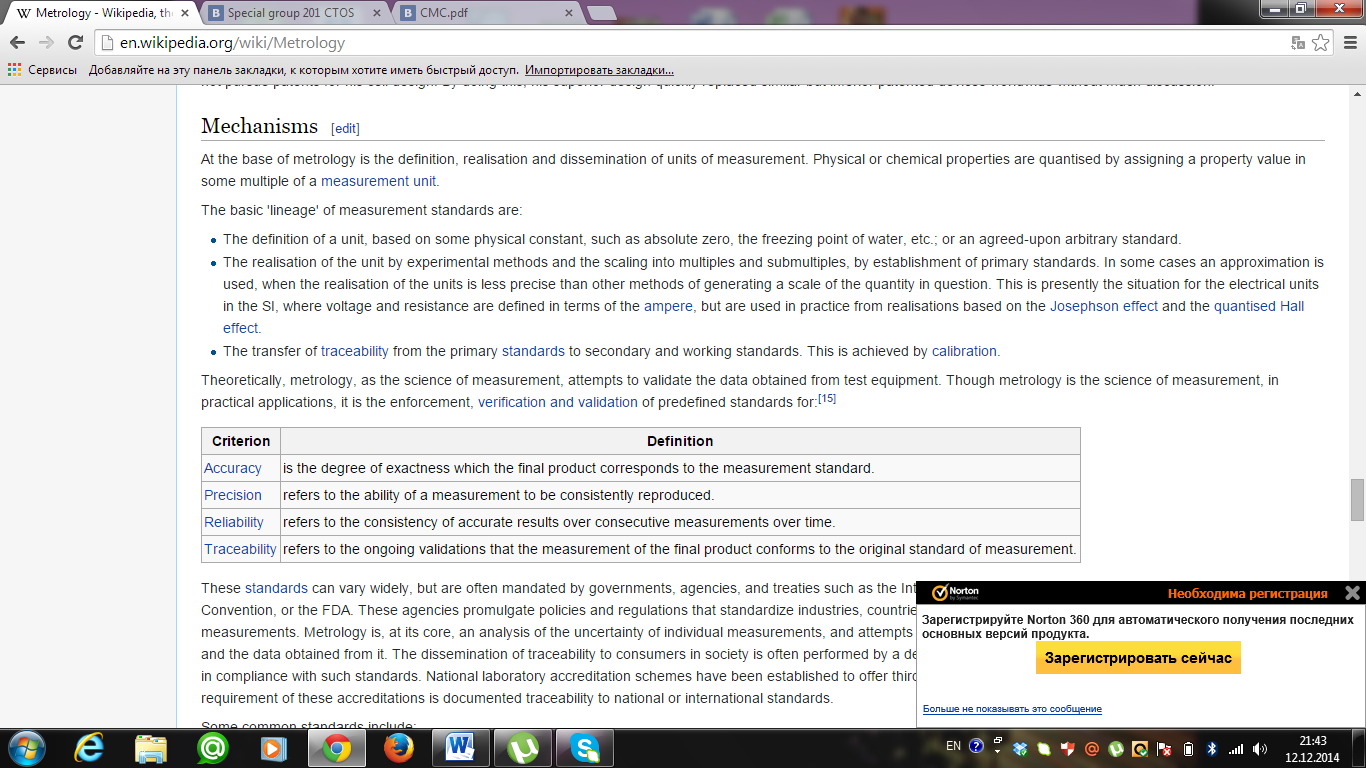
These standards can vary widely, but are often mandated by governments, agencies, and treaties such as the International Organization for Standardization,. These agencies promulgate policies and regulations that standardize industries, countries, and streamline international trade, products, and measurements. Metrology is, at its core, an analysis of the uncertainty of individual measurements, and attempts to validate each measurement made with a given instrument, and the data obtained from it. The dissemination of traceability to consumers in society is often performed by a dedicated calibration laboratory with a recognized quality system in compliance with such standards. National laboratory accreditation schemes have been established to offer third-party assessment of such quality systems. A central requirement of these accreditations is documented traceability to national or international standards.
List the main SI units of measurements.
SI units of measurement, used by scientists around the world, derive their name from the French Système International d’Unités. Fundamental units (base units) from which all others are derived are listed in Table 1-1. Standards of length, mass, and time are the meter (m), kilogram (kg), and second (s), respectively. Temperature is measured in kelvins (K), amount of substance in moles (mol), and electric current in amperes (A).

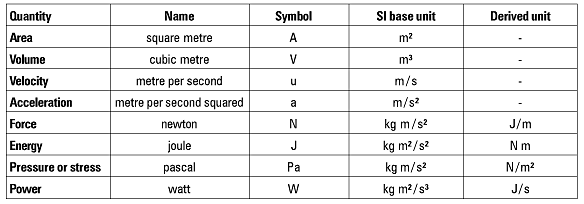
SI-derived units:
Date: 2016-01-14; view: 4878
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| THE EVOLUTION OF DATA COMMUNICATIONS | | | Call and describe the methods of measurements. |