
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSION
1. The determination of hospital infections, classification and conditions promoting the development.
2. Etiology, pathogenesis and clinical forms of hospital infections caused by pathogenic bacteria (salmonelosis, escherichiosis, tuberculosis, chlamidia and micoplasmic urethritis).
3. Opportunistic jatrogenic infections. Hospital strain. Hospital ecotype senseless to antibiotics, antiseptics. The role of medical interference and immunodeficiency. Superinfection by hospital ecotape.
4. Bacteriological diagnostics of hospital infections caused by the pathogenic and conditional pathogenic microorganisms.
5. The principles of prophilaxis and treatment of hospital infections. Sterilization, desinfection, antiseptic, chemotherapeutics, immunoprophylaxis, immunotherapy, åpidemic measures: isolation of the sick, premises and materials. Danger of transfusions.
PROCEDURE OF PRACTICAL SESSION
Task 1. To study the smears from patients material.
Task 2. To study the growth of the Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Klebsiellla pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosae, Escherichia coli.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICAL WORK
Task 1.
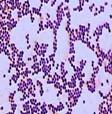 In the smear from the pus Staphylococcus are circum violet microorganisms placed in accumulation as bunch of the grapes.
In the smear from the pus Staphylococcus are circum violet microorganisms placed in accumulation as bunch of the grapes.
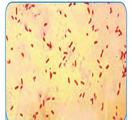
1.2 Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staining by Gram. In the smear Gram negative rods that are one by one can be observed.
 1.3 Candida albicans, staining by Gram. In the smear big oval Gram positive microorganisms can be seen, in some places there are mycelium and budding cells.
1.3 Candida albicans, staining by Gram. In the smear big oval Gram positive microorganisms can be seen, in some places there are mycelium and budding cells.
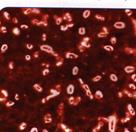
1.4 Klebsiella pneumonia, staining by Burry-Ginse. In the smear we can see colorless capsule and pink cytoplasm on dark field.
Task 2

2.1 Staphylococcus aureuson the EYA. Staphylococcus forms middle, convex, opaque, homogeneous, gold, white or yellow colony. On the EYA growth another bacteria is inhibiting. A ring of the dimness forms a round of the Staphylococcus colony because it is producing enzyme lecitinase.

Date: 2016-01-14; view: 3218
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Laboratory diagnostic of Opportunistic nfections | | | Podać własności średniej arytmetycznej. |