
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Give an example Model Checking for CTL formulas. Formal Semantics of CTL. Marking algorithm for CTL formulas.

AX  - formula
- formula  performed all of the following conditions
performed all of the following conditions
EX  - formula
- formula  performed in at least one following state
performed in at least one following state
AF  (inevitably
(inevitably  ) - on all routes from the current state formula
) - on all routes from the current state formula  ever executed
ever executed
EF  (possibly
(possibly  ) - from the current state there is a path on which formula
) - from the current state there is a path on which formula  ever executed
ever executed
AG  - on all routes from the current state of all the states of these pathways formula
- on all routes from the current state of all the states of these pathways formula  performed
performed
EG  - there is a way out of the current situation, in all states which performed formula
- there is a way out of the current situation, in all states which performed formula 
A (  1U
1U  2) - on all routes from the current state ever executed formula
2) - on all routes from the current state ever executed formula  2, and before that in all states performed formula
2, and before that in all states performed formula  1
1
E (  1U
1U  2) - from the current state there is a path on which ever executed
2) - from the current state there is a path on which ever executed  2, and before that in all the states of the path runs
2, and before that in all the states of the path runs  1
1
CTL * - Computational Tree Logic * - this is one of the possible branching time logics
In the logic of linear time LTL except atomic statements and operations of propositional logic are introduced temporal operators {U, X} (except them convenient to use another F and G)
The logic CTL * added quantifiers way, allowing different properties of different ways
Formula CTL * is defined for a particular interpretation (structure Kripke) and all of its possible calculation
CTL is a subset of CTL * - in the CTL formulas each temporal operator is preceded by a quantifier way
Example is:

22. Define algorithm for Model Checking: a basic (EX, AF, EU).Syntactic analysis of formula. Example Model Checking
EX  - formula
- formula  performed in at least one following state
performed in at least one following state
AF  (inevitably
(inevitably  ) - on all routes from the current state formula
) - on all routes from the current state formula  ever executed
ever executed
EU-Exist Until
For LTL example
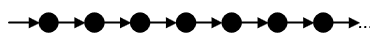
GFq - always in the future
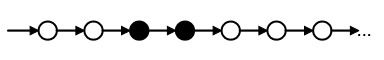
Fq - at least once in the future
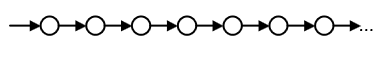
 F q - never in the future
F q - never in the future
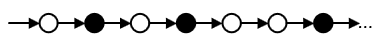
GFq - infinitely many times in the future
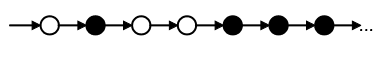
FGq - to a certain point, constantly
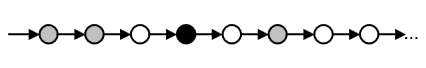
p->Fq - on the river in the response q s0 will sometime in the future
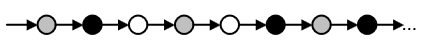
G [p->Fq] - always on the river will be the response q
For CTL* example

"If the message m will arrive at the entrance to the channel, then sometime in the future it will output"
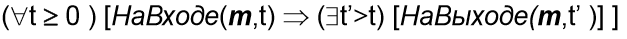
"Lift never pass by the floor n, from whom did not yet meet the needs of" p(t)- position lift at the moment t.
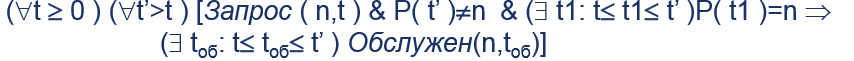
"We are not friends until you apologize"
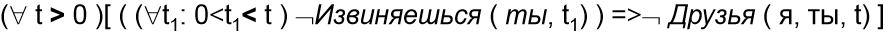
Date: 2016-01-03; view: 2636