
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Lecture 2 International Organization for Standardization - ISO
Lecture plan:
1 History
2 Objectives, targets the functions of ISO
3 The organizational structure of the ISO
4 Activities of the ISO
1 History
Start of direct cooperation between different countries in the field of standardization refers to 1921, when the first conference was held seven national standards committees. This conference has developed the organizational principles on which in 1926 was established the International Federation of National Associations for Standardization (ISA), which consisted of 20 national standards organizations. ISA has developed nearly 180 international recommendations on standardization , but with the outbreak of the Second World War, its activities were discontinued. After the Second World War, the development of international trade and international cooperation in all fields of human activity objectively led to the need to harmonize ( harmonize ) national standards, the development and widespread use of international ( regional) standards .
The International Organization for Standardization - ISO was established in 1946 by twenty-five national organizations for standardization at a meeting of the UN Committee . After the ratification of the Constitution and rules of procedure on February 23 , 1947 . officially launched as a voluntary , non-governmental organizations having consultative status of the UN. When you create the organization and selection of its title into account the need to abbrevatura names sound the same in all languages. To do this, it was decided to use the Greek word isos - equal . In all the languages of the world International Organization for Standardization is the short name ISO ( ISO). The scope of ISO - standardization in all fields except electrical engineering and electronics. At present, the ISO has more than 125 countries by their national standardization organizations. In total, more than 80 ISO committees - members.
2 Objectives, targets the functions of ISO
The purpose of the ISO declared its Charter - promoting standardization on a global scale in order to facilitate the international exchange of goods and mutual expansion of cooperation in intellectual , scientific, technological and economic activity (Figure 1).
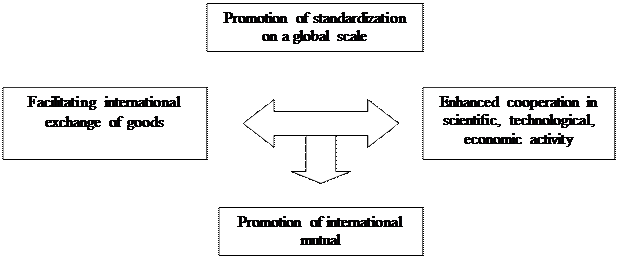
Figure 1. Objectives of ISO
The main functions of the ISO are the following:
1) the establishment of international standards , with the consent of all the members of the ISO ;
2 ) Promoting and facilitating the use of new advanced standards;
3 The main objects of the ISO standards and the number of emerging standards (in % of the total number of standards ) :
Mechanical engineering - 29, chemistry -13, non-metallic materials -12, ores and metals -9, Information Technology -8, agriculture -8, construction - 4, special equipment -3, health and medicine - 3, the basic standards of 3, environment -3 , packing and transportation of goods - 2 .
In recent years, ISO has paid much attention to the standardization of quality systems - development and production of international standards.
4 The organizational structure of the ISO
The organizational structure consists of the ISO guidelines and working bodies (Figure 2)
The governing bodies - the General Assembly , the Council , Technical leadership offices;
The working parts - technical committees (TCs) , subcommittees (SC) , the technical advisory group (TAG) ;
General Assembly - a collection of officials and delegates appointed committee member . Each member shall be entitled to not more than three delegates. Corresponding members and members of the subscribers involved as observers ;
Tip - directs the work of ISO in between sessions of the General Assembly . Has the right to send members to the committees questions for consultation and charging the member bodies of the 






 ir solutions.
ir solutions.
Figure 1. The organizational structure of the ISO
5 Activities of the ISO
ISO Council obey seven committees : Plaka ( technical guidelines bureau), Stuckey (Committee for the Study of the scientific principles of standardization ) , CASCO (Committee for Conformity Assessment ) INFKO (Committee on Information Systems and Services ) , DEVCO (Committee to assist developing countries ) , COPOLCO (Committee on consumer Protection ) , Remco (Committee on reference materials ) .
Stuckey - provides technical assistance and information to the ISO Council on the principles and techniques of international standards development , studies the fundamental principles of standardization and making recommendations to achieve optimal results in this area , is engaged in terminology and organization on the application of international standards in international trade
Plaka - prepares a planning proposal by ISO, the organization coordinating the technical side , is considering proposals for the establishment and growth of the TC , which defines the area of standardization committee has been
CASCO - deals with the confirmation of conformity of products, services , processes, and quality systems requirements of the standards , examines the practice of this activity and analysis. Developing guidelines for testing and evaluation of products, services , processes, and quality systems , validation of competence of testing laboratories and certification organizations . Promotes mutual recognition and acceptance of national and regional systems of certification, the use of international standards in the field of testing and conformity
KAPOLKO - ensures the interests of consumers through the standardization of training programs for consumers , provides information on international standards , publishes periodicals for consumers , developing standard methods for studying the performance of consumer products.
DEVCO - examines the requests of developing countries in the field of standardization, develops recommendations in this area.
REMCO - develop guidance on issues relating to reference materials ( standards , coordinates the activities of the ISO with international metrology organizations.
INFKO - performs work on information support of the standardization .
Work on the development of international standards are technical committees (TCs) and subcommittees established by them (PC) and Working Groups ( WG) in specific activities .
Technical committees are divided into general technical and committees working in specific areas of technology. 26 TC solve common technical general technical and interdisciplinary task. These include, for example, include TC 3 ' Limits and fits , " TC 10 " Technical drawings ", TC 12 " Units " TC 19 " Preferred numbers , " TC 37 " Terminology ". The rest of the TC act in specific areas of technology ( TC 22 "Cars" , TC 39 " machines ", etc.) .
If the work carried out by Technical Committee covers a wide range of issues , within the limits of the technical committees are subcommittees . For example, the TC 20 "Aviation and Space Vehicles " includes ten subcommittees.
The procedure for the development of an international standard is as follows.
Interested in developing an international standard side " in the face of a member of the ISO technical committee ISO Council or committee (or the organization that is not a member of the ISO) to the Council of an application for development of ISO standards .
The Secretary-General shall submit to the ISO Council Executive Bureau of the proposal to establish an appropriate TC .
If the Executive Bureau is confident the international importance of the proposed standard , the majority of its members voted "yes" and at least five of them are going to be members of the working group , in this case, a technical committee to develop a standard.
All the questions in the course of work are usually decided by consensus of members who are actively involved in the activities of the TC.
After reaching a consensus on the draft standard TC transmits it to the Central Secretariat for circulation to all members to vote.
In addition to the principle of consensus, the vote on the draft international standard , ISO provides more transparency and binding rules for development of standards that are understandable to all stakeholders . If the project is approved 75 % of the members who took part in the vote , it is published as an international standard .
In the ISO technical work involves over 40 000 experts from 35 countries.
Reviewed annually and received about 800 new international standards. By now adopted more than 14,000 ISO standards.
Control questions :
1 History and development prospects of international standardization.
2 Main goals and objectives of the ISO .
3 Number of standards produced by ISO and the main objects of standardization across industries and activities.
4 Organisation ISO - guiding and working bodies .
5 List of ISO committees . Tell them about the basic functions and activities .
Date: 2016-01-03; view: 1569
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Lecture 1 Purpose and objectives of the international standardization. Basic concepts. | | | Lecture 3 Prospects for the development of ISO |