
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Geography of the United States
Canada
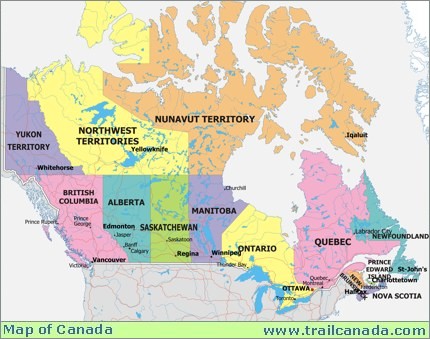 Canada has a very large and diverse range of geographic features. Canada is divided into 10 provinces and 2 territories. Canada stretches from the Pacific Ocean on the west, to the Atlantic Ocean on the east. Northern Canada reaches into the Arctic Circle, while southern Canada stretches below the northern points of the United States. Canada has a very small population, 28 million people, for its geographic size. Much of Canada is still wilderness, cover by forests. The Rocky Mountains cover a major part of western Canada -- British Columbia, the Yukon Territory, and the western part of Alberta. West-central Canada is mostly prairie, consisting of large grain farms. The east-central part of Canada are the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. These are major population and industrial areas. The Maritime provinces on the east coast rely very heavily on the Atlantic Ocean for their way of life.
Canada has a very large and diverse range of geographic features. Canada is divided into 10 provinces and 2 territories. Canada stretches from the Pacific Ocean on the west, to the Atlantic Ocean on the east. Northern Canada reaches into the Arctic Circle, while southern Canada stretches below the northern points of the United States. Canada has a very small population, 28 million people, for its geographic size. Much of Canada is still wilderness, cover by forests. The Rocky Mountains cover a major part of western Canada -- British Columbia, the Yukon Territory, and the western part of Alberta. West-central Canada is mostly prairie, consisting of large grain farms. The east-central part of Canada are the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. These are major population and industrial areas. The Maritime provinces on the east coast rely very heavily on the Atlantic Ocean for their way of life.
The majority of Canada is still wilderness. This makes Canada a popular spot for hunting and fishing. Niagara Falls is one of Canada's best known tourist attractions. It is the largest falls in the world, measured in volume of water. Most of Canada's northern islands are located inside the Arctic Circle.
 The industry varies as you look across Canada. British Columbia, on the west coast, has historically relied on natural resources such as mining and timber. Manufacturing is now becoming much more important to the economy. Alberta has benefited from considerable natural resources including oil and natural gas. It is also rich in minerals such as zinc, silver, nickel and uranium. The prairie provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan and parts of Alberta produce more than 20% of the world's wheat. Other forms of farming and cattle also contribute to the economy. Ontario and Quebec are the industrial center of Canada. They have a wide variety of manufactured goods. The lower part of Ontario also has very rich farm land, with many orchards. This Niagara area is also known for its wine production. The maritime provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland rely heavily on fishing and natural resources such as timber. Prince Edward Island is also well now for its potatoes.
The industry varies as you look across Canada. British Columbia, on the west coast, has historically relied on natural resources such as mining and timber. Manufacturing is now becoming much more important to the economy. Alberta has benefited from considerable natural resources including oil and natural gas. It is also rich in minerals such as zinc, silver, nickel and uranium. The prairie provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan and parts of Alberta produce more than 20% of the world's wheat. Other forms of farming and cattle also contribute to the economy. Ontario and Quebec are the industrial center of Canada. They have a wide variety of manufactured goods. The lower part of Ontario also has very rich farm land, with many orchards. This Niagara area is also known for its wine production. The maritime provinces of New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland rely heavily on fishing and natural resources such as timber. Prince Edward Island is also well now for its potatoes.
Australia
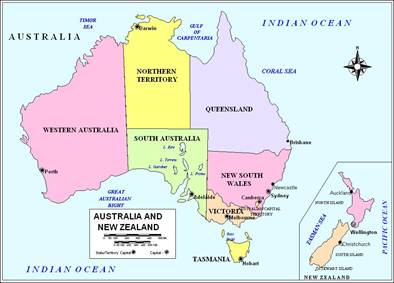
Australia has a very dramatic landscape. Australia is famous for its "outback," the remote lands of the interior. The desert outback covers most of the interior. It is too hot, dry and barren to support many people. Eastern Australia has large areas of grasslands, used primarily for sheep and cattle ranches. Australia also has some mountainous areas and plateaus scattered throughout the country. The Blue Mountains, on the south-eastern end of Australia, get their name from the blue haze caused by oil droplets given off from the eucalyptus trees. As an island, Australia also has many beautiful coastal beaches. Sydney, Australia Over 70% of Australians now live in cities or towns. Most of this population lives in the eastern and southern coasts, and around Perth in the west.
Kangaroo Australia is home to many animals not found anywhere else in the world. Shark Off the northeast coast of Australia is the Great Barrier Reef. The Great Barrier Reef is over 1,200 miles of coral. It has developed over the last million years, and is now the largest living structure in the world.
Australia's major industries are mining and farming. Mining includes bauxite, coal, copper, gold and iron ore. Most of the land is too dry for planting crops, although some areas do grow sugarcane, grapes and wheat. The grape vineyards help to support a growing wine industry. Australia is probably best known for its sheep farming. Large numbers of sheep are raised for their wool and meat. There is also some cattle ranching to provide meat.In addition, Australia's climate and dramatic scenery have made tourism a major industry.
New Zealand
New Zealand consists of a number of different islands with varying climates. Most of the country has mild temperatures with high rainfall. The mountains however, can be extremely cold.The main portions of the country are the North and South islands that are separated by the Cook Strait. The North Island is consists of low, volcanic mountains. Because of its volcanic past, the North Island features hot springs and geysers. The South Island contains the Southern Alps-a northeast-southwest oriented mountain range covered in glaciers. Its highest peak is Mount Cook, also known as Aoraki in the Maori language, at 12,349 ft (3,764 m). To the east of these mountains, the island is dry and made up of the treeless Canterbury Plains. On the southwest, the island's coast is heavily forested and jagged with fjords. This area also features New Zealand's largest national park, Fiordland.
One of the largest industries in New Zealand is that of grazing and agriculture. From 1850 to 1950, much of the North Island was cleared for these purposes and since then, the rich pastures present in the area have allowed for successful sheep grazing. Today, New Zealand is one of the world's main exporters of wool, cheese, butter and meat. Additionally, New Zealand is large producer of several types of fruit, including kiwi, apples and grapes. In addition, industry has also grown in New Zealand and the top industries are food processing, wood and paper products, textiles, transportation equipment, banking and insurance, mining and tourism.
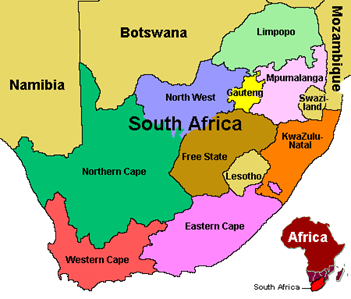 South Africa
South Africa
South Africa is divided into three major geographic regions. The first is the African Plateau in the country's interior. It forms a portion of the Kalahari Basin and is semiarid and sparsely populated. It slopes gradually in the north and west but rises to 6,500 feet (2,000 m) in the east. The second region is the Great Escarpment. Its terrain varies but its highest peaks are in the Drakensberg Mountains along the border with Lesotho. The third region are the narrow, fertile valleys along the coastal plains. The climate of South Africa is mostly semiarid; but, its eastern coast regions are subtropical with mainly sunny days and cool nights. South Africa's west coast is arid because the cold ocean current Benguela, removes moisture from the region which has formed the Namib Desert that extends into Namibia. In addition to its varied topography, South Africa is famous for its biodiversity. South Africa currently has eight wildlife reserves, the most famous of which is Kruger National Park along the border with Mozambique. This park is home to lions, leopards, giraffes, elephants and hippopotamus. The Cape Floristic Region along South Africa's west coast is also important as it is considered a world biodiversity hotspot which is home to endemic plants, mammals and amphibians.
South Africa has a growing market economy with a plethora of natural resources. Gold, platinum and precious stones such as diamonds account for nearly half of South Africa's exports. Auto assembly, textiles, iron, steel, chemicals and commercial ship repair also play a role in the country's economy. In addition agriculture and agricultural exports are significant to South Africa.
Geography of the United States
The United States is a country in the Western Hemisphere. It consists of forty-eight contiguous states on the North American continent; Alaska, an enormous peninsula which forms the northwestern most part of North America, and Hawaii, an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean. It also holds several United States territories in the Pacific and Caribbean. The term "United States", when used in the geographical sense, means the continental United States, Alaska, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Virgin Islands of the United States. The country shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and water borders with Russia, the United Kingdom, and The Bahamas.
Area
By total area including water, the United States is either slightly larger or smaller than the People's Republic of China, making it the world's third largest country. Total U.S. area is 3,718,711 square miles (9,631,418 km²), of which land is 3,537,438 square miles (9,161,923 km²) and water is 181,273 square miles (469,495 km²).
General characteristics
The United States shares land borders with Canada (to the north) and Mexico (to the south), and a territorial water border with Russia in the northwest. The contiguous forty-eight states are otherwise bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean on the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Alaska borders the Pacific Ocean to the south, the Bering Strait to the west, and the Arctic Ocean to the north, while Hawaii lies far to the southwest of the mainland in the Pacific Ocean.
Forty-eight of the States are in the single region between Canada and Mexico; this group is referred to, with varying precision and formality, as the continental or contiguous United States, and as the Lower 48. Alaska, which is not included in the term contiguous United States, is at the northwestern end of North America, separated from the Lower 48 by Canada. The State of Hawaii is an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean. The capital city, Washington, District of Columbia, is a federal district located on land donated by the state of Maryland. (Virginia had also donated land, but it was returned in 1847.) The United States also has overseas territories with varying levels of independence and organization.
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 4670
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Geography of English speaking countries | | | Physiographic divisions |