
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Content of the report
Laboratory work Ή 4-6
I. Homework
(answer the control questions from p.28).
II. Laboratory work Ή 4-6 implementation protocol.
1) Topic:
EXPLORING of FORCED OSCILLATIONS in SERIES RLC-CIRCUIT.
2) Goal: 1. Studying of effective value of voltage on capacitor and effective value of current dependencies in the series RLC-circuit versus ratio of driven frequency to the circuits eigenfrequency.
2. Studying resonance phenomena in AC RLC-circuit.
3) Scheme of laboratory research facility:
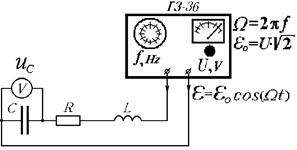
| V voltmeter; C capacitor; R resistor; L inductor (coil); ΓΗ-36 AC generator; |
4) Table of measuring instruments:
| Ή | Name | Type | Serial Ή | Grid limit | Grid unit | Accuracy class |
| 1. | Voltmeter | M996 | 25 V | 0.5 V | 1.5% | |
| 2. | Sound generator | ΓΗ-36 | 20 - 20000 Hz | 100 Hz |
5) Equations for calculation:
1. Generator cyclic frequency:
ΩGEN = 2πνGEN,
where νGEN generator linear frequency in Hz.
2. Amplitude of current in the circuit:
Im = 2π·νGEN·C·UC Ö2,
where C capacity of a circuit (one of the set), UC effective voltage on capacitor.
3. Quality factor of the circuit:
 ,
,
where UCRES effective voltage on capacitor at resonance; UGEN effective driving EMF (ΓΗ-36 output voltage, determined by Γ3-36 voltmeter scale).
4. Inductance of the circuit:
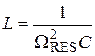 ,
,
where ΩRES resonance frequency.
5. Resistance of the circuit:
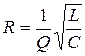 .
.
6) Table of measurements
C= F; UGEN = V.
| Ή | νGEN, kHz | ΩGEN, kHz | UC,,V | Im, mA |
7) Quantities calculation:
Q = ;
L = mHn;
R = Ohm.
8) Graphs of UC(Ω) and I(Ω) dependencies:
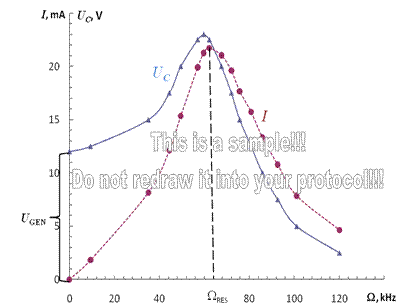 |
9) Final results :
1. Q = ;
2. L = mHn;
3. ΩRES = kHz;
4. R = Ohm.
10) Conclusion:
Work done by: Work checked by:
WORK 5-1
EXPLORING OF STANDING WAVES VIA MELDE METHOD
Goal of the work
1. Studying parametric resonance phenomena.
2. Studying conditions of standing waves generation.
3. Determination of vibrator oscillations frequency.
Main concepts
Waves.
A wave is a propagation of oscillations in space. Oscillations of elastic medium cause elastic waves, oscillations of electric and magnetic fields electromagnetic waves. An oscillating mechanism that is a source of waves is called vibrator.
Elastic waveis the mechanical disturbance (deformation) of a medium propagates through that medium. Propagation of elastic waves is in excitation of oscillations of more and more remote points of a medium. Set of oscillating points of given medium is called thewave field.Oscillation of each point is forced by vibrator (or another points). A locus of points having the same phase is called thewave surface. The wave front is a wave surface whith maximal distance from source at present moment. With respect to the shape of wave front there are traveling waves, plane waves, spherical waves.
In longitudinal waves the points of medium oscillate at parallel to the direction of propagation. This type of waves related with compressive deformation of medium and able to propagate in solids, liquids, and gaseous mediums. In transverse waves the points of medium oscillate at perpendicular to the direction of propagation. These waves can only occur in media that oppose to shear deformation. Only solids have such property. That is why transverse waves propagate only in solids.
The phase velocityof a wave 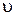 is physical quantity which numerically equal to distance at which any point of wave surface travels by unit of time. Vector of phase velocity
is physical quantity which numerically equal to distance at which any point of wave surface travels by unit of time. Vector of phase velocity 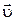 points in the direction of wave propagation, perpendicularly to wave surface. The wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is a distance between any two next points with the same phase. From another standpoint, wavelengthis a distance which any phase of wave transits for a period.
points in the direction of wave propagation, perpendicularly to wave surface. The wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is a distance between any two next points with the same phase. From another standpoint, wavelengthis a distance which any phase of wave transits for a period.
 , ,
| (65) |
where 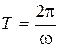 period of a wave (smallest time interval after which the value of oscillating quantity is being repeated), f frequency of a wave (number of oscillations per unit time), k
period of a wave (smallest time interval after which the value of oscillating quantity is being repeated), f frequency of a wave (number of oscillations per unit time), k 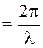 the wavenumber (number of wavelengths per 2π distance).
the wavenumber (number of wavelengths per 2π distance).
Each point of one-dimensional traveling wave oscillates according the waveequation (equation of traveling wave in differential view)
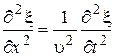 , ,
| (66) |
General solution for this differential equation (66) will be equation of traveling wave
| x (t,x)= A cos(ωt kx+j0) | (67) |
Phase of the wave (ωt kx+j0) is function of position x and time t. For fixed x the displacement ξ(t,x) is harmonic function of time, and for fixed t - a cosinusoid.
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 877
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Description of laboratory research facility and methodology of measurements | | | Parametric resonance. Standing waves. |