
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
The Gauss-Jordan Method
Consider the Gauss method in the case where the number of equations coincides with that of unknowns:
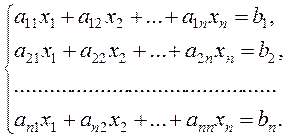 (6)
(6)
Suppose that à11 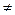 0; let us divide the first equation by this coefficient:
0; let us divide the first equation by this coefficient:
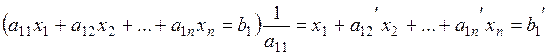 . (*)
. (*)
Multiplying the resulting equation by –à21 and adding it to the second equation of system (6), we obtain
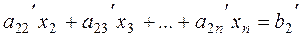 .
.
Similarly, multiplying equation (*) by –àn1 and adding it to the last equation of system (6), we obtain
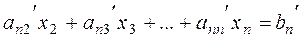 .
.
At the end, we obtain the new system of equations with n–1 unknowns:
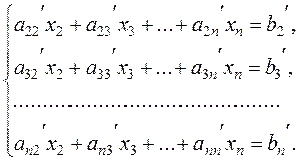 (7)
(7)
System (7) is obtained from system (6) by applying linear transformations of equations; hence this system is equivalent to (6), i.e., any solution of system (7) is a solution of the initial system of equations.
To get rid of õ2 in the third, the forth, …, nth-equation, we multiply the second equation of system (7) by 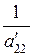 and, multiplying this equation by the negative coefficients of õ2 and summing them, obtain
and, multiplying this equation by the negative coefficients of õ2 and summing them, obtain
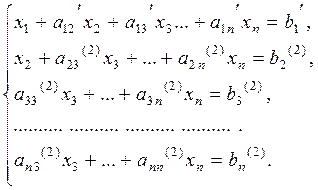
Performing this procedure n times, we reduce the system of equations to the diagonal form
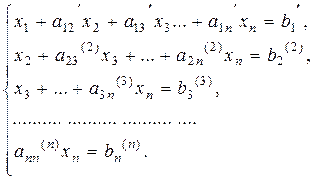
We determine õn from the last equation, substitute it in the preceding equation and obtain xn-1, and so on; going up, we determine õ1 from the first equation. This is the classical Gauss method.
Consider the system of m equations with n unknowns
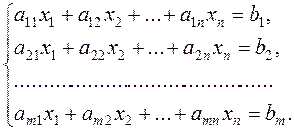 (8)
(8)
Definition. The matrix composed of the coefficients of system (8) is called the principal matrix of this system:
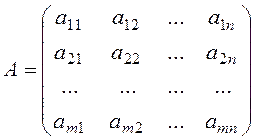 .
.
Adding the column of free terms of system (8) to this matrix, we obtain the augmented matrix
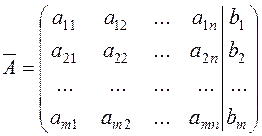 .
.
The following linear operations on the rows of such a matrix are allowed:
- permutation of rows;
- multiplication of a row by some number and adding it to another row;
- permutation of columns (but we must remember to which unknowns they correspond);
- no operations on columns are allowed (columns cannot be multiplied by numbers, summed, etc).
The Gauss-Jordan method consists in reducing (by linear operation on rows) the principal matrix to the identity matrix, i.e., to the form
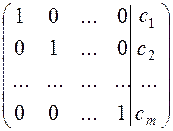 .
.
If the columns were not interchanged, the solution of the system of linear equations is
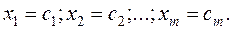
Examples. Solve the following system of equations by the Gauss-Jordan method:
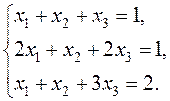
We compose the augmented matrix of the system and, applying linear combinations of rows, reduce the principal matrix to the identity:
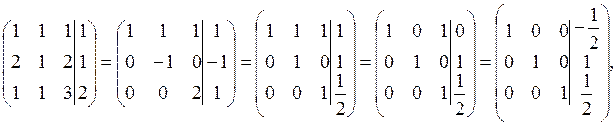
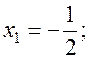
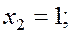
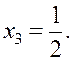
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 3516
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Matrices and Operations on Them | | | Rank of a Matrix |