
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Furnaces
Coal is the product of vegetable matter that has beenvformed by
the action of decay, weathering, the effects of pressure, temperature and time millions of years ago.
Although coal is not a true mineral, its formation processes are
similar to those of sedimentary rocks.
According to the amount of carbon coals are classified into;
brown coals, bituminous coals and anthracite. Brown coals are in
their turn subdivided into lignite and common brown coal.
Although carbon is the most important element in coal, as
many as 72 elements have been found in some coal deposits, including
lithium, chromium, cobalt, copper, nickel, tungsten and others.
Lignite is intermediate in properties between peat and bitumi-
nous coal, containing when dry about 60 to 75 per cent of carbon
and a variable proportion of ash. Lignite is a low-rank brown-to-black
coal containing 30 to 40 per cent of moisture. Developing heat it
gives from 2,500 to 4,500 calories. It is easily inflammable but burns
with a smoky flame. Lignite is liable to spontaneous combustion. It
has been estimated that about 50 per cent of the world's total coal
reserves are lignitic.
Brown coal is harder than lignite, containing from 60 to 65 per
cent of carbon and developing greater heat than lignite (4,000-7,000
calories). It is very combustible and gives a brown powder. Bituminous
coal is the most abundant variety, varying from medium to high
rank. It is a soft, black, usually- banded coal. It gives a black powder
and contains 75 to 90 per cent of carbon. It weathers only slightly
and may be kept in open piles with little danger of spontaneous
combustion if properly stored. Medium-to-low volatile bituminous
coals may be of coking quality. Coal is used intensively in blast
furnaces for smelting iron ore. There are noncoking varieties of
coal.
As for the thickness, the beds of this kind of coal are not very
thick (1-1.5 metres). The great quantities of bituminous coal are
found in the Russian Federation.
Anthracite or "hard" coal has a brilliant lustre containing more
than 90 per cent of carbon and low percentage of volatile matter. It
is used primarily as a domestic fuel, although it can sometimes be
blended with bituminous grades of coal to produce a mixture with
improved coking qualities. The largest beds of anthracite are found
in Russia, the USA and Great Britain.
WRITING
Task 16
Write an abstract of the text “ Coal and Its Classification” according to the plan:
1. The classification of coal.
2. The characteristic of lignite, brown coal, anthracite
3. The largest deposits of coals in the world
WORDLIST
| available | доступный |
| to concentrate | сосредоточиваться |
| decay | распад |
| to refer to | объяснять, ссылаться, относиться |
| to give off | выделять, испускать |
| to divide | делить |
| manufactured | промышленного производства, искусственный |
| peat | торф |
| plant | растение |
| to include | включать в себя |
| coke | кокс |
| charcoal | древесный уголь |
| commercial | промышленный, коммерческий |
| steel industry | сталелитейное производство |
| tendency | тенденция, стремление |
| to increase | возрастать, увеличиваться, усиливаться |
| raw material | сырье |
| petrochemical | нефтехимический |
| to design | разрабатывать, конструировать, проектировать |
| coal conversion | переработка угля |
| strip mining | открытая разработка |
| to haul | перевозить, транспортировать |
| to drive from | происходить |
| crude oil | сырая нефть |
| to furnish | поставлять, снабжать |
| to refine | очищать |
| pollutant | загрязняющее вещество, примесь |
| distribution | распределение, размещение |
| to promise | обещать |
| extensive | обширный, пространный |
| storage | хранение, накопление |
| compartment | отделение, камера |
| to pipe | пускать по трубам |
| trial | испытание, опыт |
| exhaust | выхлопная труба, выхлоп |
| consequence | последовательность |
| to spill (spilled, spilt) | проливаться, разливаться |
| instantaneously | мгновенно |
| dissipate | рассеиваться |
| emergency | авария |
| to be aware | знать, сознавать |
| damage | повреждать |
| liable | подверженный, склонный |
| reduction | восстановление |
| harmful | вредный |
| eject | выбрасывать, выпускать |
| coal deposit | угольное месторождение |
| peat | торф |
| bituminous | битумный |
| low-rank | низкосортный |
| inflammable | легко воспломеняющийся |
| liable | подверженный |
| lignite | лигнит, бурый уголь |
| lignitic | гумат(для обработки буровых скважин) |
| to weather | подвергаться (атмосферным воздействиям) |
| pile | отвал, отвал грунта |
| blast furnace | доменная печь |
| coking | коксование |
| lustre | блеск |
| blended | смешанный |
| grade | сорт |
Furnaces
TUNING – IN
Task 1
Name the principal function of the furnace
Task 2
Study the diagram below of a condensing furnace. Answer these questions using the diagram and your own knowledge of engineering.
1. What are the main parts of a condensing furnace?
2. What is the role of condensate drain hose?
3. What is the difference between condensing furnace and non-condensing one?
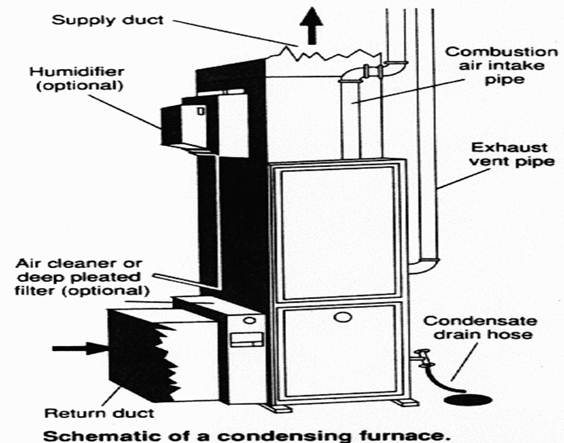
duct – канал, трубопровод
humidifier – увлажнитель
pleated filter - гофрированный (бумажный) фильтр
intake pipe – впускная (подводящая) труба
exhaust vent pipe – выпускная вентиляционная труба, труба для отбора пара
hose – гибкая труба, шланг
WORDLIST
| 1. to release | освобождать |
| 2. to ensure | обеспечивать, гарантировать |
| 3. gas-tight | газонепроницаемый |
| 4. to pulverize | распылять, размельчать |
| 5. ignition | воспламенение |
| 6. combustion | горение |
| 7. correct | соответствующий, правильный |
| 8. regardless of | несмотря на |
| 9. to maintain | поддерживать, сохранять |
| 10. due to | благодаря |
| 11.to reduce | уменьшать, сокращать |
| 12.to escape | давать утечку, улетучиваться |
| 13.instantaneous | мгновенный, немедленный |
| 14. flame | пламя |
| 15.cyclone furnace | термическая печь с принудительной циркуляцией газа |
| 16.pulverized coal furnace | пылеугольная топка |
| 17.spreader stoker | топка с разравнивающей решёткой |
| 18.chain grade stoker | механическая топка с цепной решёткой |
PRONUNCIATION
Task 3
Remember the pronunciation of the following words
| pulverized | ignition |
| excess | chimney-gas |
| turbulence | effectiveness |
| combustion | absorb |
| instantaneous | cyclone |
| thoroughly | stoker |
WORD-BUILDING
Task 4
Fill in the table
| Noun | Adjective |
| satisfaction | - |
| gas | - |
| combustion | - |
| - | particular |
| - | correct |
| importance | - |
| effect | - |
| - | molecular |
| dependence | - |
READING
Task 5
Read the text and look for answers to these questions:
1. What is a furnace? 2. What does the design of the furnace depend upon? 3. What is the design of a satisfactory furnace based upon?
4. What is the ignition temperature?
5. What is turbulence?
6. What conditions is the required furnace volume dependent upon?
7. What kinds of furnaces do you know?
The design of the furnace depends considerably upon the fuel to be burned. On the other hand, it also depends upon the supplement equipment so that satisfactory ignition and heat release may be ensured.
A furnace is a gas-tight and well-insulated space, in which gas, oil or pulverized coal may be burned. If combustion is to be complete, the combustible gases must be brought into close contact with oxygen. Also, the oxygen must be kept to a minimum and the excess air from room temperature to chimney-gas temperature also is to be low. The design of a satisfactory furnace is based upon the "three T's of combustion": temperature, turbulence, and time.
For each particular fossil fuel, there is a minimum temperature, known as the ignition temperature, below which the combustion of that fuel in the correct amount of air will not take place. If the combustible gases are cooled below the ignition temperature, they will not burn, regardless of the amount of oxygen present. A furnace must therefore be large enough and be maintained at a high enough temperature to permit the combustible gases to burn before they are cooled below the ignition temperature. Thus, the principle function of the furnace is to provide space in which the fuel may be burnt with a minimum amount of excess air and with a minimum loss due to the escape of unburned fuel.
Turbulence plays an important role in combustion. It is the turbulence that gives an effective combustion. Violent mixing of oxygen with the combustible gases in a furnace increases the rate of combustion, shortens the flame, reduces the required furnace volume, and decreases the chance that combustible gases will escape from the furnace without coming into contact with the oxygen necessary for their combustion.
Since combustion is not instantaneous, time must be provided for the oxygen to find and react with the combustible gases in the furnace.
In burning fuels such as gas, oil, or pulverized coal, the incoming fuel-air mixture must be heated above the ignition temperature by radiation from the flame or hot walls of the furnace. Since gaseous fuels are composed of molecules, they burn very rapidly when thoroughly mixed with oxygen at a temperature above the ignition temperature.
The required furnace volume is dependent upon the kind of fuel burnt, the method of burning the fuel, the quantity of excess air in the furnace, and the effectiveness of furnace turbulence. The shape of the furnace depends upon the kind of fuel burnt, the supplement equipment, and the type of boiler used to absorb the energy if the fuel is burnt for steam generation. There are different kinds of furnaces, namely, cyclone furnaces (crushed coal), pulverized coal furnaces, spreader stokers and chain-and traveling - grade stokers.
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 2284
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Coal and Its Classification | | | VOCABULARY |