
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
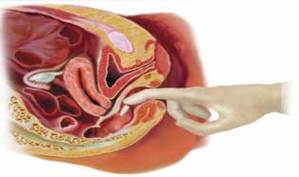
Rectal Suppository Administration
Medical Equipments:
Medication Administration Record (MAR)
Prescribed Rectal suppository
Water Soluble Lubricant (K-Y Jelly)
Non-sterile Gloves
Tissue
Bedpan (as optional)
Nursing Procedures:
Identify any allergies that patient has
Gather necessary equipments
Determine the written order on MAR
Wash your hands
Check the patientís identification
As patient if she or he wants to void
Explain the procedure to the patient briefly
Don non sterile gloves
Place patient in the Simís left lateral position with the upper leg flexed
Open the package of lubricant and remove the foil wrapper from the suppository
Apply a small amount of lubricant to the smooth rounded end of the suppository
Lubricate the gloved index finger
Ask the patient to breathe through the mouth
Insert the suppository into the rectal canal beyond the internal sphincter about 4 inches for an adult and 1 inch for a child
Avoid inserting the suppository into feces
Withdraw the finger and wipe the anal area with tissue
Ask patient to remain in bed for 15 minutes and to resist urge to defecate
Remove glove and wash hand
Record the name of the drug, dosage, route, and time of administration on MAR
Observe the effectiveness of medication
Oral Medications:
Pills
- Can be swallowed directly or sublingual (leave these under the tongue until dissolved)
- Open pack & drop into medicine cup
Granule/ Powders
- Pour into a cup up to correct dosage
Liquids
- Unit dose is a sealed container
- Water based liquid - read meniscus down
- Oil based liquid - read meniscus up
Parentral Meds:
Syringes
- Unit doses and self prepared
- The numbers represent:
1. Volume
2. Gauge of needle (diameter of inside of needle) the higher the number the smaller the needle hole
3. Length of needle
- Insulin syringes and needles
- Tuberculin syringes and needles
- The color of the packaging represents the gauge of the needle
- All needles are interchangeable except for the insulin syringe
- The tuberculin syringe is not lure-locked, needle pulls off- can measure in tenths and hundredths- pediatrics
- 2 types of insulin syringes -
a. 100 U = 1cc - each line = 2 Units
b. 50 U - each line = 1 Unit
- Unit dose syringe comes prefilled by the company - usually use entire contents - discard what
will not be used.
- Tubex syringe - cartridge with holder - prefilled - discard into sharps container.
Administering a Metered Dose Inhaler (self administration)

Equipments:
Medication Administration Record (MAR)
Inhaler
Non-sterile Gloves
Wash basin or sink to rinse mouth
Tissue (optional)
Nursing Actions:
Check any allergies that patient has or any medical condition that is contraindicated with the use of thd drug
Obtain all equipments
Check the written order on MAR
Wash hands
Follow the five right of medication administration
Check the patient identification
Allow the patient o hold and manipulate the canister and explain how the canister fits into the inhaler.
Have the patient demonstrate the insertion of the canister
Discuss the metered-dose concept and frequency of dose to the patient
Explain that the inhaler should be shaken before each use
Remove the mouthpiece and cap from the bottle and insert the stem into the small hole on the flattened portion of the mouthpiece. The patient should grasp the inhaler with thumb and first two fingers
Instruct the patient to exhale, place the mouthpiece into the mouth and tighten the lips (seal) around the mouthpieces
Ask the patient to firmly push the cylinder down against the mouthpiece only once, while slowly inhaling until the lungs feel full
Instruct the patient to remove the mouthpiece while holding the breath for about 10 seconds then exhale slowly through pursed lips
Repeat the doses as prescribed and waiting 1 minute between puffs
A mouthwash can be use by the patient to remove the taste of the medication
Demonstrate to the patient how to wash the mouthpiece under tepid running water to remove secretions
If two or more inhaler medication are prescribed, wait 5-10 minutes between inhalations or as specifically ordered by physician
Record all the drugís name, dose, date, and time for medication on MAR
Observe for effectiveness of medication and relief of the patientís symptoms
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 1514
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Administering Ear Medication | | | THE FUNCTIONS OF ARTICLES WITH COMMON NOUNS |