
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Methods of separation
are important in noninstru-mental chemical analysis. Solvent extraction methods are often used in organic analysis. Components in a mixture of substances are dissolved out of solution. This is done selectively in turn by different solvents. Liquids of different boiling points can be separated by distillation. The mixture is first heated. The component liquids are then distilled off one at a time near their boiling points.
|
cent years—the ability to measure very small amounts of different substances has outstripped the ability to understand their significance. Thus, it is now possible to measure the presence of almost unbelievably small concentrations of certain impurities in food. What is not understood, in many cases, is whether or not there is a threshold level. Below such a level, an impurity would exert no harmful effect. Its presence would therefore be of no significance. This, however, is not really a problem for the analytical chemist, whose basic task is to find ways of obtaining the information.
Three types of analysis
An analytical chemist can perform one of three types of analysis on a given substance. Qualitative analysis identifies the various types of elements and compounds that are in a substance. Quantitative analysis measures the amounts of the different chemicals in the substance being analyzed. Radiochemistry involves the identification and production of radioactive elements and their use in the study of chemical processes.
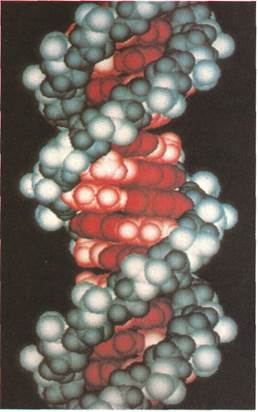
The modelof the double helix structure of a molecule of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) was "drawn" by a computer. Laboratory computers have become an essential part of modern instrumental analysis. They can store and compare data or present results as printouts, displays on a screen, or colored computer graphics.


|
Routine testingfor quality control, particularly in the petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries, often employs the methods of classical analysis. The testing involves modern apparatus and laboratory facilities such as this enclosed cabinet, which can be used for hazardous materials.
Classical analysis
There have been considerable advances in recent years in instrumental methods of chemical analysis. However, many analyses are still carried out by what are termed "classical methods." These employ techniques and procedures that have proved to be reliable and reproducible over many years. Such methods are of particular value for use in laboratories that lack the more advanced instruments. Classical methods fall into two main groups: qualitative analysis is used to find out what is present in a given substance; quantitative analysis deals with the procedures for determining how much of a substance is present in that substance.
Date: 2015-12-11; view: 3477
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Analytical chemistry | | | Qualitative organic analysis |