
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Halogenated polymers
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) became well known in the 1960's. It was then first used as a material for plastic raincoats and simulated leather goods. It is manufactured in a similar way to polystyrene. To make it soft enough for clothing and simulated leather, it has to be mixed with a plasticizer or softener. In its harder form, it is used in pipes, panels, and other molded parts. Its use has declined slightly since the monomer, chloroethene (vinyl chloride), was shown to cause a rare form of liver cancer if inhaled. A well-known fluorine-containing polymer is Teflon (polytetrafluoroethy-lene or PTFE). It is a very low friction, slippery material. This makes it ideal for coating cooking pans to keep food from sticking to the surfaces.
Natural and synthetic rubbers
Rubbers are special polymers with elastic properties. This means that they return to their original shape after being deformed or stretched. Natural rubber is obtained from Hevea trees. It is used in cements, adhesives, tape for insulating electrical equipment, and for cable wrapping. It becomes more useful when vulcanized. Vulcanization is a process in which sulfur reacts with the carbon-carbon double bonds to form "bridges" of sulfur atoms that cross-link the molecules. Vulcanized rubber is principally made into tires. It is also used in hoses, footwear, and a variety of other items. There are also a wide variety of
Monomer
CH2= CH
H
Ethene
CH2= CH
CI
Chloroethene
CH2= CH
CN
Propenonitrile

Phenylethene CH2= CH
OCOCH.
Ethenyl ethanoate
CH2=CH
CH,
Propene
CH,
CH
CH = CH,
Butadiene
Polymer
+-CH2— CH-
H
Polyethylene
f-CH2 — CH-
Cl
Polyvinyl chloride
| CH- |
| CH, |
\
CN
Acrylic polymer
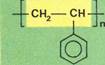
Polystyrene
■CH,
CH----
Quot;
0COCH3
Polyvinyl acetate
---- CH2—CH-j-
CH,
Polypropylene
CH2—CH
CH—CH2-
Synthetic rubber -1"
Polyethyleneis made by polymerizing ethene or ethylene. It was one of the first polymers to be synthesized. Many others can be best understood by considering their monomers as derivatives of ethene. In this diagram, the chemical formulae of the monomers (left-hand column! have been presented so as to emphasize this common factor. The double-bonded "ethene" parts of the molecules are on pink panels. After polymerization, this element of the molecule (but now only singly bonded) forms the long repeating backbone or chain of the polymer. These single-bonded "ethene" parts are shown on yellow panels in the right-hand column.
Rubberis valued for its resilience and elasticity, two essential properties for the inflatable children's "castle." Once only a natural product, most types of rubber are now synthetic polymers.
 102 Organic chemistry: Polymers
102 Organic chemistry: Polymers
 |

|
Date: 2015-12-11; view: 1398
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Synthetic procedures | | | Thousands of logs are |