
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S EYE
Introduction
Background Information:
This experiment was conducted with the following members:
1. Anastasia Karpenko
2. Cassandra Mezalon
3. Leah Jonson
4. Alicia Dtayes
Additional Information:
The experiment was performed inside the lab classroom with a regular temperature a natural light.
Hypothesis:
Our team assumed that the sheep eye is almost looks like a human eye. Also, the main purpose of this dissection is to learn the structure of the eye.
Materials and Methods
Materials that we used were:
· dissection pan
· sheep’s eye
· dissection kit:
-scalpel
-probe
-scissors
Step-by-step directions for conducting the experiment:
1. Observing External Structures
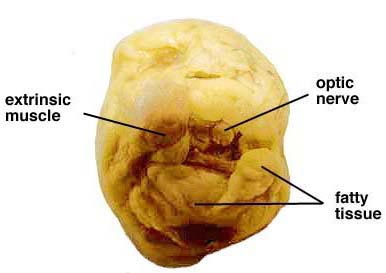
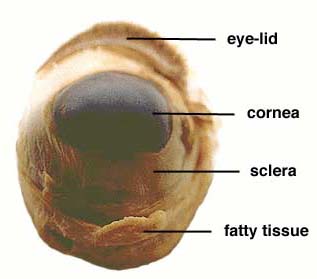
We put on the gloves and begun the observation of the sheep eye. It had a smell of some chemicals. Weexamined the front of the eye and found the eye-lid, cornea, sclera and fatty tissue. Examined the back of the eye and found extrinsic muscle bundles, fatty tissue and the optic nerve.
2. Dissection
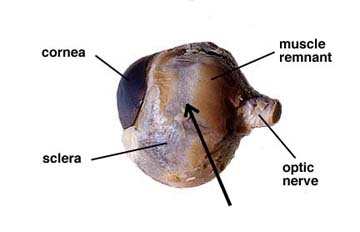
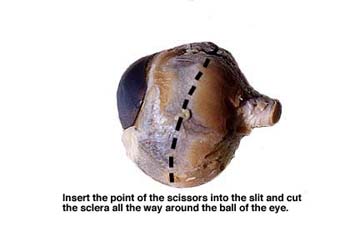
Upon the dissection of the sheep eye the adipose (fatty) cushion was removed and exposed the cornea the sclera the extrinsic muscle attachments and the optic nerve.
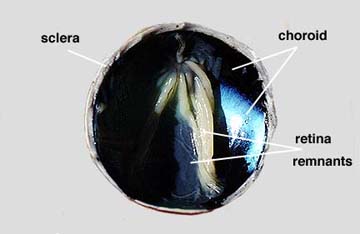
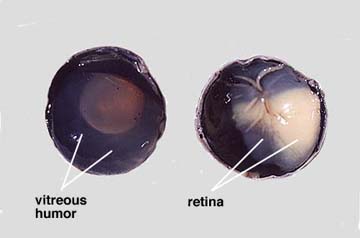
Further dissecting of a sagittal cut of the eye reveal the vitreous body humor which is the transparent jelly that fills a large space called the vitreous chamber.
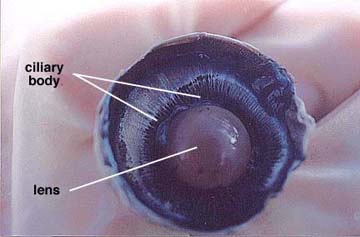
The fluid that pour out of the chamber is called the aqueous humor which was secreted by the colony body.Removal of the vitreous humor revealed the lens, ciliary body and suspensory ligaments
Discussion and Conclusion.
Our team was able to conclude, that majority of the sheep’s eye parts are similar to the one in human eye. This fact supports our original hypothesis, however one of the differences to mention is that the eye of the sheep is smaller when compared to the human eye.
Date: 2015-04-20; view: 5570
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Chapter Sixteen | | | The problems of taking drugs, smoking and drinking |