
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Pastoral-based Industries consist of
A) Shoes
B) Paper
C) Cotton textile
D) cane
E) Iron and steel industry
10. What region presented ferrous metallurgy of Kazakhstan
A) East Kazakhstan
B) North Kazakhstan
C) Central
D) West Kazakhstan
E) Southern Kazakhstan
11. Normalized current assets don't treat:
A) work in progress
B) stocks of raw materials and materials
C) finished goods in a warehouse
D) production stocks
E) cars and equipment
12. Define an indicator of extensive loading of the equipment, if actually fulfilled time - 4000 hours, losses of working hours on planned repair of the equipment of 10 percent from regime fund of time, an operating mode - the 3rd replaceable for 6 hours in each change, quantity of the working days in a year - 300.
A) 1,2
B) 1,5
C) 0,6
D) 0,82
E) 1,7
13. Current assets are:
A) subjects and instruments of labor
B) finished goods
C) production stocks
D) set of the money advanced for creation and use of current funds and funds of the address for ensuring of process of production and realization of production
E) the current business assets serving the sphere of production which completely transfer the cost on cost of finished goods
14. The part of the population, which has the necessary physical development, knowledge and experience to work in the economy is:
A) labour market
B) labour
C) manpower
D) economic activity
E) unemployment
15. Labor market is
A) total supply of personnel available or engaged for a specific job or task
B) part of the population, which has the necessary physical development, knowledge and experience to work in the economy
C) different from the commodity market because a labor force is a specific commodity
D) Total labour force of a nation, including both men and women
E) the form of relative overpopulation
16. Types of unemployment, this is occurs when real wages for a job are set above the market-clearing level, causing the number of job-seekers to exceed the number of vacancies
A) cyclical
B) involuntary
C) classical
D) full
E) structural
17. Call the type or model of unemployment on this picture:
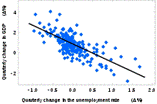
A) cyclical
B) involuntary
C) classical
D) full
E) structural
18. Distributive function of wages
A) forms and systems of the wage should stimulate the high-performance work
B) supplying with extended production of the qualitative labor force of the work-hand and members of his family
C) stimulating of the labor influx to a certain branches and its outfall from others
D) pecuniary expression of the labor force commodity value or its price
E) A form of remuneration paid periodically by an employer to an employee, the amount and frequency of which may be specified in an employment contract
19. Call competitive advantages of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
A) strong motivation and high intensity of RK;
B) enormous mineral raw material resources;
C) a numerous manpower with high educational level;
D) answers of B and C are true
E) A and B answers are true
20. How many percent of volume of foreign trade give industrially developed countries?
A) 47.8 %;
B) 28 %;
C) 67.8 %;
D) 30.5 %
E) 54.3 %
Keys
| Answer number | Right answer | Answer number | Right answer | |
| D | E | |||
| E | D | |||
| A | D | |||
| B | C | |||
| B | C | |||
| D | C | |||
| C | E | |||
| C | C | |||
| A | D | |||
| C | C |
Criteria for studentsí knowledge assessment
| Number of right answers | Grade |
| 19-20 | Excellent |
| 16-18 | Good |
| 10-15 | Satisfactory |
| lower than 10 points | Unsatisfactory |
16. EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
1. Need of intervention of the state in economy.
2. State as consumer, producer and regulator.
3. Economic functions of state.
4. Methods and instruments of state regulation.
5. Economic and political components of state.
6. Normative and positive analyze of economy.
7. Interrelation of economy and policy.
8. Essence of economic policy.
9. Objects of economic policy.
10. Historical and social-economic conditions, depending choice of economic system and economic procedure.
11. Production mechanism and its functions.
12. Subjects of economic policy.
13. Economic interests of subjects.
14. Principles of economic policy.
15. Carriers of economic interests.
16. Spokesman of economic interests.
17. Elements of economic policy.
18. Types of economic policy.
19. The main purposes of economic policy.
20. The target function of economic policy.
21. Factor of time, time lags in perception of a governmental activity.
22. The main forms of economic policy.
23. Productivity of economic policy.
24. The general purpose and tree of purposes of economic policy.
25. Classification of purposes of economic policy.
26. Collateral consequences of economic policy.
27. Principles of organization of purposes of economic policy.
28. Polygons of purposes of economic policy.
29. Models of economic policy.
30. The market system.
31. Macro-approach in the economy analysis.
32. Essence of macroeconomic policy.
33. Macroeconomic balance and its models.
34. Instruments of macroeconomic policy.
35. The main directions of macroeconomic policy.
36. The main indicators of macroeconomics.
37. Models of state regulation of economy.
38. Requirements imposed to instruments of economic policy.
39. The purposes of fiscal policy.
40. Instruments of fiscal policy.
41. Essence and functions of taxes.
42. Classification of taxes.
43. Elements, systems of taxation.
44. Principles of tax system.
45. Tax policy of Republic of Kazakhstan.
46. Essence and functions of public expenditures.
47. Classification of public expenditures.
48. Condition of state budget.
49. Types of fiscal policy.
50. Discretionary fiscal policy.
51. Non-discretionary fiscal policy.
52. Budget-tax policy of Republic of Kazakhstan.
53. Essence and functions of monetary policy.
54. Functions of National Bank on development and realization of monetary policy.
55. The main instruments of monetary policy.
56. Additional instruments of monetary policy.
57. Essence and instruments of securities market.
58. State regulation of securities market.
59. Choice of direction of monetary policy.
60. Policy of cheap and expensive money.
61. Monetary policy of Republic of Kazakhstan.
62. Competitiveness and monopoly.
63. State and economic procedure.
64. Antimonopoly legislation.
65. Policy of limited monopolism.
66. Mechanism of regulation of monopoly activity.
67. Policy of stimulation of competitive procedure.
68. The main methods of monopolization and counteraction to it.
69. Economic management of production activity of natural monopoly.
70. Anti-monopoly activity on the world market.
71. Economic inequality in the market system.
72. Essence and purposes of social policy.
73. State regulation of salary (wage).
74. Social protection.
75. Strategy of social policy.
76. Priorities of social policy.
77. Degradation of the nature and economic environment.
78. Natural resources and problems of their use without prejudice to environment.
79. Purposes of ecological policy.
80. Instruments of regulation of the relations of environmental management.
81. Ecological safety as global problem.
82. State policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the solution of environmental problems.
83. Character of the international economic relations.
84. Economic integration.
85. Place and role of national economy in world economic space.
86. Main directions of foreign economic activity.
87. Instruments of regulation of foreign economic activity.
88. Kazakhstan in the world market.
89. Consumer basket, subsistence minimum and poverty.
90. Norms of competitive behavior.
17. PROGRAM AND MULTIMEDIA MAINTENANCE OF STUDIES
| Theme | Type of lesson | Type of software support | Place of access to software and multimedia support | Specialized rooms |
| The essence, objects and subjects of economic policy | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| The role of the state in the market economy | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Formation of economic policy | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Macroeconomic policy: the essence and instruments | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Fiscal policy | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Monetary policy | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Antimonopoly activity of the state | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Social policy. Social protection | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| State policy in the ecology sphere | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
| Regulation of foreign economic activity | Lecture, practical classes | Presentation | Hall of multimedia resources | Computer classes, specialized classrooms ##405, 450 |
Date: 2015-02-28; view: 1137
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| THE SCRIPT OF THEMES OF WRITTEN WORKS | | | ANIMALS IN TRANSLATION |