
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Section 1. Ship’s statics
Words and Terms to be Remembered
| sailing area roader motor ship (vessel) turbine nuclear reactor light alloy fishing ship ferry cruise ship fishery research ship special ship icebreaker | tug (towboat) salvage (rescue) ship strand fire (-lighting) boat research ship maintenance port industry dredger floating workshop cable-layer drilling rig supply vessel |
Read the text and find the answers to the following questions.
1. What are the main indications of ships' classification?
2. Into what groups can all sea-going ships be divided according to their duties?
3. What types of ships are included into the fishery group?
4. What types of ships are referred to special ones?
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION OF SHIPS
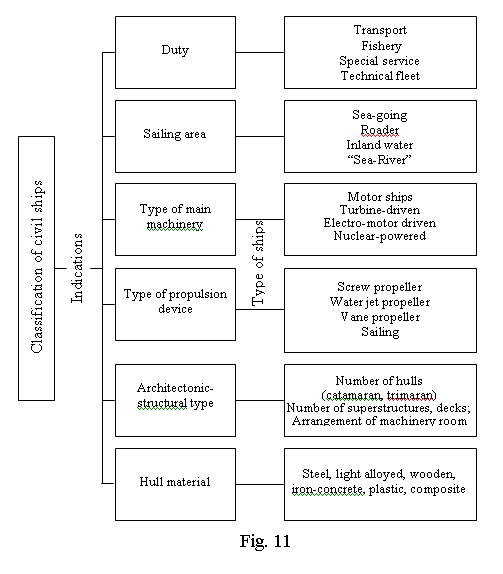
All civil ships can be classified according to the following principles:
1) Sailing area - sea going ships (deep-sea unlimited and coastal navigation), roaders, inland water ships and "sea-river" ships.
2) Kind of main machinery - motor ships (diesel engine), turbine driven ships (steam or gas turbine), electro-driven ships (electro-motor), nuclear powered ships (nuclear reactor).
3) Type of propulsion device - ships with screw propeller, water jet and vane propeller devices, paddle, sails.
4) Architectonic-structural type - number of hulls (catamaran, trimaran), number and position of superstructures, decks; position of the engine room.
5) Kind of material employed in hull structure - steel, light-alloyed, plastic, wooden, iron-cement, composite ships.
6) Duty of a ship, that is the service they are designed for.
According to the last principle all civil ships can be divided into transport, fishing ships, special service and technical fleet ships. Transport ships can carry passengers and cargo. In international law any ship with space for more than 12 passengers is a passenger ship. These ships range from ferries with passenger accommodation to luxurious cruise ships which carry more than 2000 passengers around the world. Passenger liners are employed on regular routes according to a fixed schedule. Nowadays the number of passenger vessels has been greatly reduced because of competition from air transport.
The group of fishery ships includes fishing (fish-catching) ships - trawlers, seiners, etc., - floating fishery mother ships or factories for processing the catch and for supplying service to the crews of fishing ships. There are fish searching and fishery research ships as well.
The group of special ships consists of auxiliary or service ships. Among them are ice-breakers, used for keeping open a navigable passage through ice; tugs used for towing or assisting vessels at sea; fire-fighting ships fitted with fire-fighting equipment for assisting vessels against damage by fire; rescue (salvage) ships fitted with special equipment for salving stranded vessels and for towing.
Referred to special service ships are research ships, medical and training ones. Technical fleet includes the facilities which allow to perform technical maintenance of various ships, port industry and waterways. Among them are dredgers used for deepening channels and harbors, floating cranes, floating workshops, cable-layers, floating docks. Technical facilities for developing the continental shelf and World Ocean include drilling rigs, drilling ships, pipe-layers.
 Exercises and assignments
Exercises and assignments
Ex. 1. Study the diagram of ship classification. Consult the text and vocabulary items.
Ex. 2. Match the words on the left with their synonyms on the right. Find in the text all the sentences in which they are used and translate them into Russian:
| area reactor alloy ferry research tow salvage stranded maintenance dredge supply duty facilities | provision saving purpose aground aids shuttle clean plant range service mixture (metal) pull (by rope) investigation |
Ex. 3. Find in the text the sentences with the words of the same roots and translate them into Russian:
classify, sail, navigate, machine, propel, architect, accommodate, compete, fish, process, supply, salving, facilitate, maintain.
Ex. 4. Fill in the blanks. Make use of the appropriate words from the text.
1. Transport ships can carry _________ and _________.
2. Passenger liners are employed on _________ routes according to a _________.
3. The number of passenger vessels has been reduced because of _________ from air transport.
4. The fishery ships include fishery floating mother ships for _________ the catch.
5. Icebreakers keep open a _________ through ice.
6. Technical fleet includes _________ to perform technical _________ of various ships.
7. Architectonic-structural type indicates the number of _________, _________ and _________.
8. Screw propeller, water jet and vane propellers are _________.
Ex. 5. Match the listed types of ships with the definitions of their duties.
| I | II |
| 1. Cable layer | a) to catch bottom feeding fish |
| 2. Fishery mother ship | b) to carry out scientific investigations |
| 3. Ferry | c) to save personnel and equipment in case of sea disasters |
| 4. Rescue ship | d) to shuttle people and vehicles between relatively nearby points on land |
| 5. Research ship | e) to process fish caught by other fishing ships |
| 6. Trawler | f) to lay and repair underwater cables |
Ex. 6. Choose the terms under the line below for the following definitions:
1) a ship intended for or carrying more than 12 passengers;
2) a vessel used directly for catching fish or for catching and processing the catch;
3) a ship specially intended for the towage and pushing of other ships and floating facilities;
4) a ship provided with a main propulsion plant using nuclear energy;
5) a luxurious motor-ship designed for pleasure voyages;
6) a vessel designed for the carriage of supplies and cargoes to the mobile and fixed units;
7) ships employed for laying down, maintenance and repairs of cables and pipes.
pipe-layer, cable layer, nuclear ship, supply vessel, tug, passenger ship, cruise ship, fishing ship.
Section 1. Ship’s statics
Words and Terms to be Remembered
| seakeeping conform buoyancy immerse displacement submerge counteract exert light displacement load displacement | deadweight cargo carrying capacity ship's poise trim heel (list) draft mark stability capsize flood unsinkability |
Read the text and find the answers to the following questions.
1. What two principle forces act on a freely floating ship?
2. What kinds of displacement are distinguished?
3. What does "stability" imply?
4. How can unsinkability be provided?
 Exercises and assignments
Exercises and assignments
Ex. 1. Match the words on the left with their synonyms on the right:
| buoyancy weight immerse quantity seakeeping act counteract exertion external equilibrium quality capacity force sufficient attach upright devise unsinkability | power possibility seaworthiness floodability property outside invent balance fasten effort oppose floatability gravity submerge vertical affect amount enough |
Ex. 2. Complete this table with all missing derivatives. Consult the text.
| Verb | Noun | Adjective | Adverb |
| conform | |||
| stability | |||
| floatable | |||
| forcefully | |||
| displacement | |||
| refer | |||
| submerged | |||
| exertion | |||
| incline | |||
| distribution | |||
| slowly | |||
| floodable | |||
| sufficiently |
Find in the text the sentences in which these words are used and translate them into Russian.
Ex. 3. Read the text and find the vocabulary items which mean:
a) floating ability;
b) force of gravity
c) upward force of liquid upon a floating body;
d) to put under the surface of water;
e) vessel's lifting capacity;
f) transverse inclination of a vessel;
g) longitudinal deviation of a vessel from the designed waterline;
h) sufficiency of a vessel in construction for service;
i) tendency of a ship to return to its initial position;
j) ship's fore and aft inclinations;
k) ship's transverse inclinations;
l) ship's ability to stay afloat with some flooded compartments.
Ex. 4. Fill in the blanks. Make use of the active vocabulary items and structures.
1. The force of buoyancy acts _________ and forces of gravity _________.
2. Gravity and buoyancy set up forces tending to _________ the ship until equilibrium is attained.
3. The quality of any ship to return to her original position is called _________.
4. This _________ inclination is termed the trim of a vessel, which the _________ inclinations are known as the _________.
5. The principle factor in deciding any ship's stability is the manner of _________ in the vertical direction.
6. _________ displacement is the weight of a vessel when unloaded and _________ displacement when the ship has its weights on board.
7. Unsinkability can be provided by _________ dividing the ship into isolated compartments.
8. _________ is floating ability of a ship.
9. The loss of stability is more dangerous than the loss of _________.
10. Two principle forces acting on a floating ship are _________.
Ex. 5. Find in the text the following word combinations and translate the sentences in which they are used. Consult a maritime dictionary:
immersed section, stable equilibrium, unstable equilibrium, neutral equilibrium, angle's value, initial stability, stability at large angles of inclination, sudden loads, definite freeboard height, reserve of buoyancy, damage stability, loss of buoyancy draft mark, ship's poise, trimming angle, unit of volume, intact displacement, useful deadweight, cargo carrying capacity.
Ex. 6. Give the opposite meaning to the following words:
upward, sail, light displacement, sufficient statics, abovewater, external, dependent, lift, slowly, stable, loading, preserve, decrease, definite, damaged, longitudinal.
Date: 2014-12-28; view: 1851
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Section 1. General classification of civil ships | | | Section 2. Types of cargo ships |