
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
PSC 26 - Nuclear Physics 2
NUCLEAR PHYSICS – 2
| Mass of neutron is 1.008665 u; Mass of proton is 1.00728 u; Mass of deuterium is 2.0140 u; Mass of alpha particle is 4.0026 u; Mass of | 1 u = 1.66056 × 10-27 kg qe = 1.60 × 10-19 C Avogadro`s number NA=6.02 × 1023 mol-1 e0 = 8.85 × 10-12 F m-1 |
1. The atomic mass unit (amu or u) is defined such that the mass of a neutral carbon-12 atom (mass of its nucleus and electrons) is exactly 12 u. Calculate the binding energy of 12C.
2. In nature, the element potassium contains two isotopes. One isotope constitutes 93.4% of the whole and has an atomic mass of 38.975 u; the other 6.6% has a mass of 40.974 u. Calculate the atomic mass of naturally occurring potassium.
3. When a helium nucleus is formed from two deuterium nuclei an energy of 23.8 MeV is released. In the fission of 235U an energy of approximately 200 MeV is released. Compare the total amount of energy released in the fusion of 1g of deuterium with that released in the fission of 1 g of 235U.
- A 5.6-MeV alpha particle is shot directly at a uranium atom (Z = 92). About how close will it get to the centre of the uranium nucleus?
Note: the electric potential energy of two-charge system is given by the equation 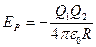
- When an atom of 235U undergoes fission in a reactor, about 200 MeV of energy is liberated. Suppose that a reactor using uranium-235 has an output of 700 MW and is 20% efficient. (a) How many uranium atoms does it consume in one day? (b) What mass of uranium does it consume each day?
- a) Fission of an uranium nucleus can be induced according to the following equation:
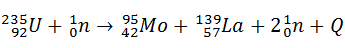
The atomic masses of the nuclei concerned are: U-235 235.04277 u ; Mo-95 94.90553 u ;
La-139 138.90534 u
Calculate the energy released in this reaction in joules and in MeV.
b) Another possible reaction of induced fission is:
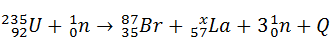
What number is represented by x?
*7. The following deuterium reactions and corresponding reaction energies Q are found to occur:
|
 14N(d,p)15N, Q1 =8.53 MeV
14N(d,p)15N, Q1 =8.53 MeV
15N(d,α)13C, Q2 =7.58 MeV
13C(d,α)11B, Q3 =5.16 MeV What is the Q value, in MeV, of the reaction 11B(α,n)14N?
Date: 2015-02-16; view: 1323
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| RUSSIAN UNIVERSITY GROUP | | | MANAGEMENT |