
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Afraid to do or afraid of doing?
A Afraid

|
David is afraid to climb the ladder. (= He doesn't want to climb the ladder because he is afraid.)
Here are some more examples.
I was afraid to say anything in front
of all those people. Claire was afraid to wander too far
from the hotel.
B Anxious, ashamed and interested
Compare these examples.
Zedco are anxious to increase their sales. (= They want to increase their sales.)
I'm ashamed to tell you what I scored in the test. (= I don't want to tell you because I'm ashamed.)
I'd be interested to meet Laura. (= I want to meet her.)
/ was interested to hear Mike's story. (= I found his story interesting.)
C Structures with sorry
To apologize for something we are doing, we use a to-infinitive.
I'm sorry to tell you this, but your test score is rather low.
I'm sorry to ring so late, but it's important. To express regret, we also use a to-infinitive.
/ was sorry to hear that Mike's uncle had died.
David is afraid of falling.
(= He is afraid because he might fall.
/ was afraid of sounding foolish, you see. She was afraid of getting lost.
Mark was anxious about presenting his report. (= He was worried because he had to present his report.)
I'm ashamed of getting such a low score.
{ I'm ashamed because I got such a low score.)
Laura is interested in painting.
(= It is an interest/a hobby of hers.)
To apologize for something we did, we can use about + ing-form.
I'm sorry about making all that noise last night.
(or I'm sorry I made all that noise last night.)
|
| 71 Exercises |
| 1 Afraid (A) Complete the sentences. Use these words and put the verb into the to-infinitive or ing-form: dive into the water, drop them, fall, move |
►He's afraid to dive into the water. 2 She's afraid ..
1 She's afraid . 3 He's afraid . .
2 Afraid (A)
Look at what people say and write a comment about each person. Rewrite the second sentence using afraid to or afraid of.
► Vicky: There's a large bull in the field. I don't want to open the gate.
Vicky is afraid to open the gate.
► Claire: I arrived at the airport in good time. 1 thought I might get stuck in traffic.
Claire was afraid of getting stuck in traffic.
1 Nick: I was going to do a bungee jump yesterday. But I couldn't jump.
2 Daniel: The policeman looked angry. I didn't want to argue with him.
3 Matthew: I'm keeping my shirt on. I might get sunburnt.
3 Afraid, anxious, ashamed and interested (A-B)
Complete the conversation. Put in a to-infinitive or a preposition + ing-form.
Laura: I'm ashamed ( ►) to admit (admit) it, but aeroplanes terrify me. I get really anxious
(►) about flying (fly). I'm afraid (1)......................... ... (buy) a plane ticket. I can't stand being
on a plane. I'm afraid (2)........................................ (get) killed. I feel ashamed
(3)
(be) so silly.
Sarah: Aren't there things you can do to overcome your fear?
Laura: Well, 1 was interested (4)............................
..(read) in the paper recently that you can go on a
course that helps you. I'm anxious (5) . (book) a place on it very soon.
4 Sorry (C)
Complete the conversation. Use a to-infinitive or about + ing-form. Look at the information in brackets. Alan: I'm sorry ( ►) to disturb you (I'm disturbing you), but could I just say something? I'm sorry
(1) (I was so rude) last night. I didn't mean what I said.
Mark: Oh, that's OK. I'm sorry (2) ..(I lost my temper).
Alan: Right. OK. And, as I said, sorry (3)....... .......................... (I'm interrupting you).
| 72 Used to do and be used to doing |

Used + to-infinitive means that something happened regularly or went on for a time in the past. I used to travel means that in the past I regularly travelled, but I no longer do so.
Here are some more examples.
We used to play that game when we were younger.
Nick used to smoke, but he gave it up. I used to like fish, but I never eat it now.
There used to be a dancehall here, but they knocked it down.
We cannot use this structure in the present tense. Claire travels a lot. not Claire uses- to~travel-a-lot.
We normally use didn't use to in negatives and did ... use to in questions. We didn't use to have computers, or We never used to have computers. Where did people use to buy their food before the supermarket was built? Did you use to live in London?

Be used to + ing-form means that something is familiar and is no longer strange. I'm used to travelling means that travelling is no longer strange or difficult because I have done it for so long.
Here are some more examples.
We're used to getting up early. We do it every day. not We're used to get up early.
Sarah is used to working late at the office. Most visitors to Britain aren't used to driving on the left.
I wasn't used to wearing glasses. It seemed very strange at first.
We can also say get used to to talk about things becoming more familiar. It was difficult at first, but Mike soon got used to working at night. After her husband died, the old woman had to get used to living on her own.
72 Exercises
Used to do (A)
1 Mrs Bell is a hundred years old. She's the oldest person in the village.
A radio reporter is interviewing her. Put in used to with the verb.
Mrs Bell: I've always lived in the village, but not always in this house.
Reporter: Where (►) did you use to live (you / live)?
Mrs Bell: When I was a girl, we lived at Apple Tree Farm.
(1) (we / like) it there.
Reporter: But life was hard, wasn't it?
Mrs Bell: Oh, yes. Things (2)
.(be) different from the way they are
now. In those days (3) .(we / not / have) electricity.
Reporter: And (4) (you / help) with the farm work?
Mrs Bell: Yes, (5) (I / look) after the hens.
2 Used to do and be used to doing (A-B)
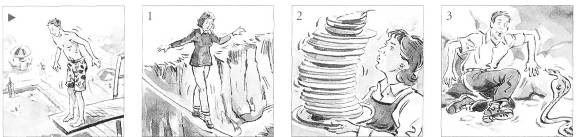
Look at the pictures and say what the people used to do or are used to doing.
Use these verbs: climb, fly, paint, play, sign
 Use these objects: autographs, badminton, mountains, pictures, planes
Use these objects: autographs, badminton, mountains, pictures, planes

? He used to paint pictures.
? She's used to signing autographs. 2 They.....................................
1 She .. 3 He
3 Used to do and be used to doing (A-B)
Put in a to-infinitive or to + ing-form. Use the verbs in brackets.
? When I was a child, I used to dream (dream) of being an astronaut.
? I'm terribly nervous. I'm not used to speaking (speak) to a large audience.
1 It took us ages to get used .................................... (live) in a block of flats.
2 Lots of trains used......................................... (stop) here, but not many do now.
3 Didn't Nick use........................................ (work) on a building site?
4 There didn't use........................................ (be) so many soap operas on television.
5 I'll have an orange juice, please. I'm not used . (drink) alcohol.
6 David doesn't seem to mind being in hospital. I suppose he's got used (be) there.
7 When Laura was at college, she used.............................. (have) a picture of Elvis Presley on her
bedroom wall.
73 Preposition or linking word + ing-form

|
A Introduction
Rachel: Shall we have some lunch?
Jessica: 1 usually go for a walk instead of eating. I'm on a diet.
Rachel: You're joking, aren't you? Since when?
Jessica: Since discovering I can't get into my old clothes.
Rachel: Well, just buy some new ones, then.
We can use an ing-form after some prepositions (e.g. instead of)
or linking words (e.g. since).
We cannot use an infinitive, not instead~of jto~eat.
B Preposition + ing-form
Here are some more examples.
As a result of losing my passport, I had to fill in a complicated form.
Vicky and Rachel might go to Canada as well as travelling around the US.
You can get skin cancer from being in the sun too long.
You aren't in favour of cutting down trees, are you?
Sarah went to work in spite of not feeling well.
We can't have a party without making a bit of noise.
We can use these prepositions before an ing-form: against, as a result of, as well as, besides, by, despite, for, from, how about, in favour of, in spite of, instead of, on, what about, without
We use what about/how about + ing-form to make a suggestion.
How about giving us some help? We use for + ing-form to say what we use something for.
This cloth is for cleaning the floor. We use by + ing-form to say how someone does something.
The thief got in by breaking a window. We use on + ing-form to mean 'as soon as'.
On hearing the news of David's accident, Melanie burst into tears.
(= As soon as she heard the news,...)
C Linking word + ing-form
Here are some examples.
I always have a shower after playing tennis.
Although hoping to get the job, Rachel wasn't really expecting to.
Sarah wanted to finish the report before going to bed.
The man has been unemployed since leaving prison.
You should always lock the door when leaving your room.
Mark was listening to the car radio while sitting in a traffic jam.
We can use these linking words before an ing-form: after, although, before, since, when, while
A linking word + ing-form can sometimes be a little formal. We can say the same thing like this. I always have a shower after I've played tennis. Although she was hoping to get the job, Rachel wasn't really expecting to.
70 Verb/Adjective + preposition + ing-form
73 Exercises
1 Preposition + ing-form (B)
Complete the sentences using the words in brackets.
► Rachel: Do you want to walk? Vicky: Yes, let's not get a bus. (instead of)
Vicky wants to walk instead of getting a bus.
1 Sarah: Did you get through the work? Mark: Yes, I stayed up all night, (by)
Mark got through the work ...................................................................................
2 Melanie: When do you take the pills? David: The minute I wake in the morning, (on)
David has to take the pills ..................................................................................................................................
3 Mike: So you got the answer? Harriet: Yes, and I didn't use a calculator, (without)
Harriet got the answer.............................................................................................................................................
4 Emma: Why the rucksack? Matthew: So I can carry the food, (for)
The rucksack is.......................................................................................................................................
5 Trevor: Sorry I forgot the sugar. Laura: Well, you had it on your list, (in spite of)
Trevor forgot the sugar ................................................................................................
6 Mark: Do you have to do the typing? Secretary: Yes, and book some flights, (as well as)
The secretary has to book some flights ......................................
2 Linking word + ing-form (C)
This structure is often used in instructions (sentences which tell people what to do). Put in before or after and the ing-form of the verb in brackets.
► Replace the top on the bottle after taking (take) the medicine.
1 Read the contract through carefully ............................................................ (sign) it.
2 You shouldn't have a bath straight ....................................................... (eat) a meal.
3 (leave) home ring the airport to check that your flight is on schedule.
4 Always put your skis away carefully .......................................................... (use) them.
5 Be sure to switch off the electricity ......................................................... (change) a fuse.
6 Make sure the safety chain is on............................................................. (open) the door.
3 Preposition or linking word + ing-form (B-C)
Ron Mason owns a supermarket business. Write the sentences for a magazine article about his life. Join two sentences into one using the words in brackets.
► He saw an empty shop. He was walking around town one day. (while)
He saw an empty shop while walking around town one day.
1 He thought carefully. He decided to buy it. (before)
2 He bought the shop. He had little money of his own. (despite)
3 He became successful. He gave the customers what they wanted, (by)
4 He put the profit back into the business. He didn't spend it on himself, (instead of)
5 He was happy. He was running his own business, (when)
6 He fell ill. He worked too hard, (as a result of)
1 He has made a lot of money. He bought his first shop ten years ago. (since)
| 74 See it happen or see it happening? |
| A Introduction |

David fell down the steps. David was walking with a stick.
Rachel saw him fall. Rachel saw him walking across the road.
B See it happen
After some verbs we can use an object + an infinitive without to.
VERB OBJECT INFINITIVE
Rachel saw David fall down the steps.
Vicky heard someone close the door.
Let's watch the parade go past.
We all felt the house shake.
We can use this structure with these verbs: feel, hear, listen to, notice, see, watch
C See it happening
We can also use an ing-form after the object.
| VERB | OBJECT | ING-FORM | ||
| Rachel | saw | David | walking | with a stick. |
| Can you | hear | someone | playing | the piano? |
| We | found | Matthew | exercising | in the gym. |
| I could | feel | an insect | crawling | up my leg. |
We can use this structure with these verbs: feel, find, hear, listen to, notice, see, smell, watch
D See it happen or see it happening?
SEE IT HAPPEN SEE IT HAPPENING
We saw Trevor plant the tree. We saw Trevor planting the tree.
(He planted the tree. We saw him do the (He was planting the tree. We saw him in the
whole job.) middle of the job.)
/ watched Nick light a cigarette. I watched Nick smoking a cigarette.
We noticed a young man sit down and order a We noticed a young man sitting at the table
meal. eating a meal.
When we talk about a short action, it often does not matter which structure we use. They heard a car turn/turning the corner. I didn't see anyone leave/leaving any litter.
74 Exercises
1 See it happen (B)
Henry is in court. He is answering questions about a Mr Lewis, who the police suspect of a number of crimes. Add a sentence using the verb in brackets. ► And you say a second man came into the restaurant? (see) Henry: That's right. / saw him come in.
1 Are you quite certain that Mr Lewis took the envelope? (see)
Henry: Yes, absolutely. .........................................................................................
2 Then Mr Lewis left the restaurant, did he? (watch)
Henry: He left soon afterwards..............................................
3 And he drove away, (hear)
Henry: Yes, he did........................................................
2 See it happening (C)
Look at the pictures and add a sentence with I can see/hear/smell... and the ing-form of these verbs: bark, burn, come, ring, wave
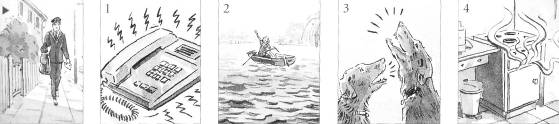
► The postman is on his way. I can see him coming.
1 There's a phone upstairs. ......................................................................................
2 There's a woman in the boat. ...............................................................................
3 There are some dogs outside........................................................................... ..
4 You've forgotten your lunch. ..............................................................................
3 See it happen or see it happening? (D)
There has been a bomb explosion in the city centre. TV reporter Kitty Beamish is asking people about it. What did people see or hear?
? Man: The bomb exploded. I heard it. It was a shock.
He heard the bomb explode.
? Woman: A man was lying in the road. I saw him. He was just lying there.
She saw a man lying in the road.
1 Woman: The building shook. I felt it. I couldn't believe it.
2 Man: People were shouting. I heard them. There was panic.
3 Girl: An alarm was ringing. I could hear it. It went on and on.
4 Boys: The police arrived. We saw them. They were over there.
5 Man: I saw a woman. She was crying. She was in a terrible state.
| 75 Some structures with the ing-form |
| A Two actions at the same time |

All afternoon Claire lay in a hammock reading a magazine.
When two things are happening at the same time, we can use a main verb (lay) and an ing-form (reading). Here are some more examples.
We had to stand in a queue waiting for the bank to open.
You can t sit watching television all day. All afternoon, Vicky lay on the sofa thinking about life.
We can also use this structure when one action comes in the middle of another. We use the ing-form for the longer action.
Matthew injured his knee doing gymnastics. (= He injured his knee while he was doing gymnastics.)
I went to sleep listening to the radio.
B One action after another
When there are two short actions, one straight after the other, we can use an ing-form for the first action. Opening the bottle, Mike poured the drinks. (= He opened the bottle and then poured the drinks.) Turning right into Madison Avenue, the car drove north for two blocks.
We can also use the perfect ing-form.
Having opened the bottle, Mike poured the drinks. (= After opening the bottle, Mike poured the drinks.)
If either of the actions is long, we must use the perfect.
Having photocopied all the papers, Sarah put them back in the file. Having repaired the car, Tom took it out for a road test. not Repairing the car, Tom took it-out for a road test.
These patterns are typical of written English. In spoken English, to talk about one action after another we use a sentence like this.
Tom repaired the car and then took it out for a road test.
C The ing-form saying why
We can use the ing-form to give a reason.
The fans queued for hours, hoping to get tickets. (= They queued for hours because they hoped to get tickets.) Being the youngest child, Natasha was her father's favourite. Not knowing the way, I had to ask for directions.
We can also use the perfect ing-form to give a reason.
Having spent all his money, Daniel couldn't afford a new jacket. We decided not to travel, having heard the terrible weather forecast.
| 75 Exercises |
| 1 One action in the middle of another (A) Say what accidents these people had. Use these phrases: lift weights, light a fire, open a tin, run, ski Put the verbs describing the longer action in the -ing form. |

► Harriet burnt her hand lighting a fire.
1 Matthew .. 3 Vicky .......... .
2 David .. 4 Trevor
2 One action after another (B)
Rewrite the sentences about a detective. Begin with an ing-form, e.g. doing or having done.
Mitchell picked up the phone and dialled a number. He let it ring for five long minutes and then slowly replaced the receiver. He took a gun out of the drawer and put it in his briefcase. He left the office and then had to wait a while for the lift. He reached the ground floor and hurried outside to a taxi. The taxi driver pulled out a gun and shot Mitchell.
? Picking up the phone, Mitchell dialled a number.
? Having let it ring for five long minutes, he slowly replaced the receiver.
2 ..
3 ..
4
3 The ing-form saying why (C)
Match the two parts and join them using an ing-form, e.g. doing or having done.
? Because she didn't want to be late, Harriet turned on the heating.
? As she had worked hard all day, Andrew took it back to the library.
1 Because he had studied the map, Daniel found it hard to communicate.
2 She felt cold, so Vicky ran to the bus stop.
3  Because he didn't know French, Trevor knew which way to go.
Because he didn't know French, Trevor knew which way to go.
4 He had finished the book, so Sarah was exhausted.
?  Not wanting to be late, Vicky ran to the bus stop.
Not wanting to be late, Vicky ran to the bus stop.
? Having worked hard all day, Sarah was exhausted.
1 ........................................................................................................................................................................
2 ....................................................................................................................................................................
3 .
4 .
TEST 13 The infinitive and the ing-form (Units 65-75)
Test 13A
Some of these sentences are correct, and some have a word which should not be there. If the sentence is correct, put a tick (/). If it is incorrect, cross out the unnecessary word and write it in the space.
? I'm used to driving in heavy traffic every day. /
? Although of- feeling tired, Polly didn't want to go to bed. of
1 It's important for to sign the form.
2 Peter broke his arm in playing rugby.
3 A woman accused Martin of stealing her money.
4 I wasn't sure whether to write a letter of thanks.
5 Do you remember a young man bumping into you?
6 The girl's parents wouldn't let her to stay out so late.
7 The book is too difficult enough for children to understand
8 Police found the woman for lying dead on the floor.
9 Cars are always expensive to repair them.
10 The man died as a result of falling asleep while driving.
Test 13B
This is an advertisement for the book 'Winning in Business'. Put in the correct form of each verb.
Are you fed up with (►) being (be) a failure in your job? Wouldn't you rather (►) succeed (succeed)?
Do you want (►) to earn (earn) more money? Are you anxious (1)
.. (get) ahead?
Do you believe in (2) (make) the most of your talents? Do you sometimes dream
about (3) .. (reach) the top? If the answer is yes, read on. Just imagine
yourself (4) (run) a big successful company. And now you can do something about it
instead of (5) . (dream). It'll happen if you want it (6) . ..(happen).
Make it a reality by (7) (order) your copy of the best-selling 'Winning in
Business'. It has a ten-point plan for you (8).............. ..(follow). Do it and you're
certain (9) (be) a success. You'll know what (10) . (do) in
business. You can make other people (11)........................................... (respect) you and persuade
them (12) . (do) what you want. Experts recommend (13) . (buy]
this marvellous book. You'd better (14) .(order) your copy today.
Test 13C
Combine each pair of sentences. Use a to-infinitive or an ing-form. Sometimes you also need a preposition,
? We've advised Nancy. She should get a lawyer.
We've advised Nancy to get a lawyer.
? I'm getting bored. I've been sitting on the beach.
I'm getting bored with sitting on the beach.
1 We saw Rupert. He was looking in a shop window.
2 I remember the clown. He fell over.
3 Tessa wasn't sure. Which way should she go?
4 The porter just stood there. He expected a tip.
5 How about it? Shall we go to the barbecue?
6 Susan is used to it. She's always lived in the country.
7 I'm afraid. I might hurt myself.
8 Christopher apologized. He'd forgotten to pay.
9 The food was too cold. Michelle couldn't eat it.
10 Polly was silly. She gave away the secret.
Test 13D
Read the story and write the missing words. Use one word only in each space.
Calvin Coolidge was elected US President in 1924. He didn't believe (►) in doing too much, and his slogan
was'Keep cool with Coolidge'. Soon (1)
.. moving into the White House, Coolidge invited some
old friends (2) .. have dinner with him there. They were all people he (3) to know in
the old days, and they were simple country people. They were interested (4). see inside the White
House, and they were looking forward to (5) .. dinner with the President. They thought it was nice
(6) him (7) . ... invite them. But there was one problem. They weren't used
(8) . attending formal dinners, and they were worried that they wouldn't know (9) . to
behave. They were afraid (10) looking foolish. So they decided it would be best
(11) .everyone to copy exactly what Coolidge did.
At last the day came. During the dinner, when Coolidge picked up his knife and fork, everyone did the same. When he drank, everyone drank, and so on. Finally Coolidge decided to amuse himself
(12)
playing a little trick on his visitors. He tipped some coffee into his saucer. Everyone did the
same. (13)
.done this, he added a little cream and sugar. Everyone did the same. Then, horrified,
they watched Coolidge bend down and (14)
. ... the saucer on the carpet for his cat.
Test 13E
Complete the conversations. Put in the correct form of each verb. ► A: I'm annoyed about being (be) late. B: Well, I told you to set (set) off in good time, didn't I?
1 A: Did you accuse Nigel of.............................................. (break) a plate?
B: Well, it was an accident, but he did break it. I saw him .. (knock) it off the table
with his elbow.
2 A: 1 came here .(see) Janet. She must have forgotten I was coming.
B: It seems rather careless of her............................................... (forget).
3 A: Are you going to have a rest now after
... (do) all the cleaning?
B: No, I've got some letters
..(write).
4 A: You say you need some advice?
B: Yes, I'm sorry (bother) you, but I don't know who ..... (ask).
5 A: Do you like Scrabble?
B: Well, I used (play) it quite a lot, but I got fed up with it. I'd
rather ............................ (watch) television, actually.
Date: 2014-12-22; view: 4421
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| The infinitive with and without to | | | Ship and water: countable and uncountable nouns |