
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Table 1 - The evaluation of dangerous and hazardous factors for human life
| ¹ | Factors | Individual rating
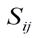
| 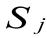 The average rating The average rating
| The relative share
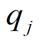
|
| Airlift | ||||
| Road transport | ||||
| Nuclear Power | ||||
| Alcohol | ||||
| Occupational accidents | ||||
| Murder | ||||
| Ponds (swimming, recreation) | ||||
| Diagnostic radiation | ||||
| Electric current | ||||
| Rail transport | ||||
| Infectious diseases | ||||
| Other factors | ||||
| Smoking | ||||
| Medicines | ||||
| Drugs | ||||
| Personal injury | ||||
| Work with human rights movement | ||||
| Fires | ||||
| Self-murder | ||||
| AIDS | ||||
| Sports and events | ||||
| Natural disasters | ||||
| Terrorism | ||||
| Food poisoning | ||||
| Surgery |
It is important to note that awareness of the existence of hazardous and harmful factors for human life is only the first step to safe life. It is necessary to establish conditions under which these factors lead to undesirable consequences, and to divert the possibility of such conditions.

1. Problem of human activity and society safety in the contemporary conditions.
2. Objects, methods and functions of the principles of personal and social safety.
3. The content and the tasks of the discipline.
4. The key concepts of the discipline: a human, a life, activity, safety, danger, system, ecosystem, system analysis.
5. Jeopardy as a quantitative characteristic of dander level estimation.
6. The assessment of risk and the control over it.
7. System analysis in principles of personal and social safety.
8. The classification of dangers by sources of their origins and general features.
9. The classification of jeopardies by the character and natural action.
10. Nomenclature, identification and the taxonomy of the hazards.
11. The sources of social and political perils.
12. The general definition of human activity environment and its classification.
 13. The characteristic of the natural environment, its parameters and significance for the security of human activity.
13. The characteristic of the natural environment, its parameters and significance for the security of human activity.
14.Natural dangers.
15. Technological perils.
16. Social and political jeopardies.
17. Physical factors of danger.
18. Chemical factors of peril.
19. Biological factors of jeopardy.
20. Psycho-physiological factors of danger.
21. Main environmental problems of today.
22. Identification and dose of ionizing radiation.
23. Radiation safety.
24. Effects of electric current on human body.
25. Sources of electromagnetic radiation.
25. The impact of electric current on a person
26. The sources of electromagnetic radiation
28. Person’s psychological peculiarities and their importance in SHL
29. The importance of neural system
30. Health, its biological, social and psychological aspect
31. Organism’s adaptation to the exterior factors of environment
32. Homeostasis, its importance for safe activity
33. Extraordinary situations and how to prevent them
34. Liquidation of extraordinary situations’ results
35. The impact of noise on a person
36. Radiation of optical range, their impact on a person
37. Toxic effect of harmful chemical substances on a person
38. Poisonous plants
39. Poisonous animals
40. Pathogenic organisms, diseases they cause and protection from them
41. SHL (safety of human life) management
42. Basic legislative and regulative acts on biological security and SHL
43. The authorities of a governance and control over the compliance of requirements of SHL
44. General governance’s principles of SHL in Ukraine
45. Global governance of SHL
46. Fundamentals of SHL’s governance
47. Global experience of SHL’s governance
48. Dangers in urbanized environment
49. Ecological safety
50. Dangers connected with professional activity
Educational publication
| |||
|
Date: 2015-01-29; view: 3439
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Table 1 – The organism consumption of energy during various kinds of activities. | | | Causes of language changes |