
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
The derivative of the function. Geometric and mechanical meaning. Table of derivatives. The differential of a function
LECTURE PLAN:
1. The derivative of a function
2. Differential of a function
Derivative of Functions
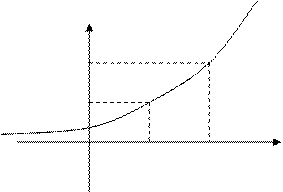
Suppose that there is y=f(x) on the interval [a;b]. We increment Dõ to the argument õ; then the function obtains the following increment
ó®ó+Dó, ó+Dó=f(õ+Dõ), Dó=f(õ+Dõ)–ó.
 ó
ó
f(x+Dx)
f(x)
0 x x+Dx õ
Definition. The ratio limit of a function increment to an argument increment, where the latter tends to zero, is called a derivative of function.
Notation:
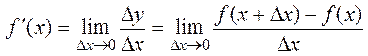 . (1)
. (1)
The notations in the form of f¢(x), ó¢ or ó¢õ are the Lagrange notations, and the notations of the form  or
or 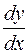 are the Leibniz notations.
are the Leibniz notations.
The geometric and mechanical interpretation of a derivative
The mechanistic interpretation of a derivative, i.e., the derivative of distance with respect to time, is the velocity at a moment t.
The geometric sense of a derivative is that the derivative at the point Ì0 equals a slope of a tangent at this point to ÎÕ -axis.
The function differentiability
Definition 1. Obtaining an assigned function is said to be a function differentiation.
Suppose that there is ó=f(x) given on [a;b].
Definition 2. Suppose that there is the derivative at the point õ=õ0:
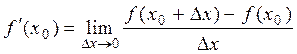 ,
,
then f(x) is said to be differentiable at the point õ0.
If f(x) is differentiable at any point of [a;b], the function is said to be differentiable on the interval.
The derivative of constant, sum, difference,
product and fraction of functions.
1. The derivative of a constant is
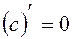 .
.

1.The derivative of sum (difference) of two functions equals the sum (difference) of the derivatives of functions:
(u±v)¢= u¢±v¢.
3.The constant factor can be factored outside the sign of the derivative
(k·u)¢= k(u)¢.
4.The derivative of the product of two functions equals the derivative of the first function, multiplied by the second, plus the derivative of the second, multiplied by the first, i.e.,
(u· v)¢= u¢v+uv¢. (2)
Example. Find the derivative:
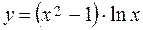 .
.
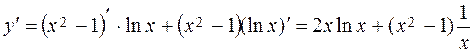 .
. 
5.The derivative of fraction is defined by the following formula
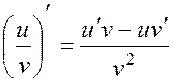 . (3)
. (3)
Example. 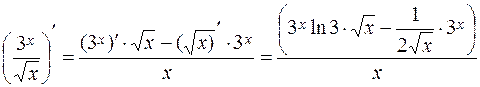 .
.
Differentiation of Composite Function
Suppose that there is a composite function denoted by the two-component chain y=F(u); u=j(x), each of these functions is differentiable F¢(u), j¢(x). Find the derivative of the composite function F[j (x)].
Theorem. If functions F(u)and j(x) are differentiable with respect to their variables, then there is a derivative of composite function. It is defined as follows:
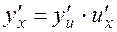 . (4)
. (4)
Examples.1. Find the derivative y=cos5x.
Expand the composite function into the chain of the elementary
y=u5; u=cos x.
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 3720
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Fundamental Theorems on Limits | | | Using formula (4), we obtain |