
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Internal Combustion
The principle behind any reciprocating internal combustion engine: If you put a tiny amount of high-energy fuel (like gasoline) in a small, enclosed space and ignite it, an incredible amount of energy is released in the form of expanding gas. You can use that energy to propel a potato 500 feet. In this case, the energy is translated into potato motion. You can also use it for more interesting purposes. For example, if you can create a cycle that allows you to set off explosions like this hundreds of times per minute, and if you can harness that energy in a useful way, what you have is the core of a car engine!
Almost all cars currently use what is called a four-stroke combustion cycle to convert gasoline into motion. The four-stroke approach is also known as the Otto cycle, in honor of Nikolaus Otto, who invented it in 1867. The four strokes are illustrated in Figure 1.
- Intake stroke
- Compression stroke
- Combustion stroke
- Exhaust stroke
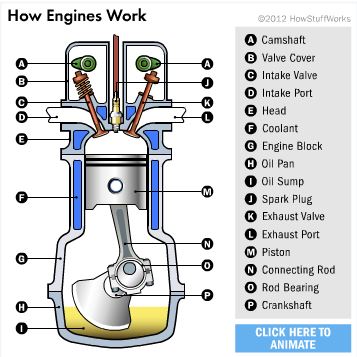
You can see in the figure that a device called a piston replaces the potato in the potato cannon. The piston is connected to the crankshaft by a connecting rod. As the crankshaft revolves, it has the effect of "resetting the cannon." Here's what happens as the engine goes through its cycle:
- The piston starts at the top, the intake valve opens, and the piston moves down to let the engine take in a cylinder-full of air and gasoline. This is the intake stroke. Only the tiniest drop of gasoline needs to be mixed into the air for this to work. (Part 1 of the figure).
- Then the piston moves back up to compress this fuel/air mixture. Compression makes the explosion more powerful. (Part 2 of the figure).
- When the piston reaches the top of its stroke, the spark plug emits a spark to ignite the gasoline. The gasoline charge in the cylinder explodes, driving the piston down. (Part 3 of the figure).
- Once the piston hits the bottom of its stroke, the exhaust valve opens and the exhaust leaves the cylinder to go out the tailpipe. (Part 4 of the figure).
Now the engine is ready for the next cycle, so it intakes another charge of air and gas.
Notice that the motion that comes out of an internal combustion engine is rotational, while the motion produced by a potato cannon is linear (straight line). In an engine the linear motion of the pistons is converted into rotational motion by the crankshaft. The rotational motion is nice because we plan to turn (rotate) the car's wheels with it anyway.
Now let's look at all the parts that work together to make this happen, starting with the cylinders.
Basic Engine Parts
The core of the engine is the cylinder, with the piston moving up and down inside the cylinder. The engine described above has one cylinder. That is typical of most lawn mowers, but most cars have more than one cylinder (four, six and eight cylinders are common). In a multi-cylinder engine, the cylinders usually are arranged in one of three ways: inline, V or flat (also known as horizontally opposed or boxer), as shown in the following figures.
Different configurations have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of smoothness, manufacturing cost and shape characteristics. These advantages and disadvantages make them more suitable for certain vehicles.
Let's look at some key engine parts in more detail.
Spark plug
The spark plug supplies the spark that ignites the air/fuel mixture so that combustion can occur. The spark must happen at just the right moment for things to work properly.
Valves
The intake and exhaust valves open at the proper time to let in air and fuel and to let out exhaust. Note that both valves are closed during compression and combustion so that the combustion chamber is sealed.
Piston
A piston is a cylindrical piece of metal that moves up and down inside the cylinder.
Piston rings
Piston rings provide a sliding seal between the outer edge of the piston and the inner edge of the cylinder. The rings serve two purposes:
- They prevent the fuel/air mixture and exhaust in the combustion chamber from leaking into the sump during compression and combustion.
- They keep oil in the sump from leaking into the combustion area, where it would be burned and lost.
Connecting rod
The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft. It can rotate at both ends so that its angle can change as the piston moves and the crankshaft rotates.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft turns the piston's up and down motion into circular motion just like a crank on a jack-in-the-box does.
Sump
The sump surrounds the crankshaft. It contains some amount of oil, which collects in the bottom of the sump (the oil pan).
Date: 2015-01-29; view: 1891
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| How Car Engines Work | | | Engine Problems |