
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Types of White Blood Cells
Neutrophil: A type of white blood cell, a granulocyte that is filled with microscopic granules, little sacs containing enzymes that digest microorganisms. Also known as polymorphonuclear leukocyte or poly.Neutrophils are the largest group of white blood cells, making up 45 to 75 percent of the white blood count. Neutrophils are phagocytes, major players in fighting off bacterial infections and viruses. A drop in neutrophils below 1,000 cells per microliter increases the risk of developing infections. Neutrophils are the "first responders" in inflammation: the first on the scene to destroy bacteria and viruses. Neutrophils have a short life span, only about 10 hours. Immature neutrophils, called bands, are numerous in an active infection. A decrease in neutrophils is known as neutropenia; causes of neutropenia include chemotherapy treatment, bacterial and viral infections, and allergic reactions.
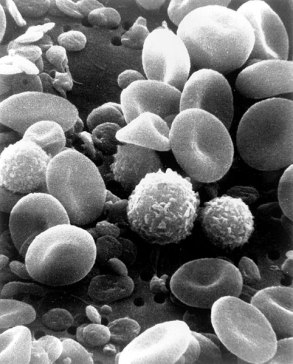
Eosinophil: A normal type of white blood cell that has coarse granules within its cytoplasm. Eosinophils are produced in the bone marrow and migrate to tissues throughout the body. When a foreign substance enters the body, other types of white blood cells (lymphcytes and neutrophils) release substances to attract eosinophils and then release toxic substances to kill the invader. The numbers of eosinophils in blood often rise when an allergic reaction occurs. Elevated eosinophil counts are also common in some diseases, such as parasite diseases and asthma.
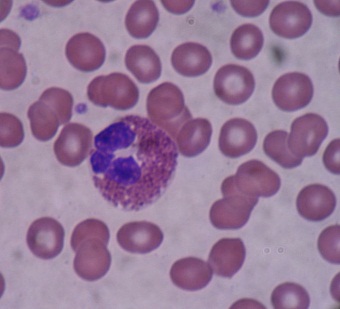
Basophil: A type of white blood cell (leukocyte) with coarse, bluish-black granules of uniform size within the cytoplasm. Basophils are so named because their cytoplasmic granules stain with basic dyes. Basophils normally constitute 0.5 to 3 percent of the peripheral blood leukocytes, and contain histamine and serotonin. Also known as a basophilic leukocyte.
Lymphocytes: A small white blood cell (leukocyte) that plays a large role in defending the body against disease.
Lymphocytes are responsible for immune responses. There are two main types of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. The B cells make antibodies that attack bacteria and toxins while the T cells attack body cells themselves when they have been taken over by viruses or have become cancerous. Lymphocytes secrete products (lymphokines) that modulate the functional activities of many other types of cells and are often present at sites of chronic inflammation.
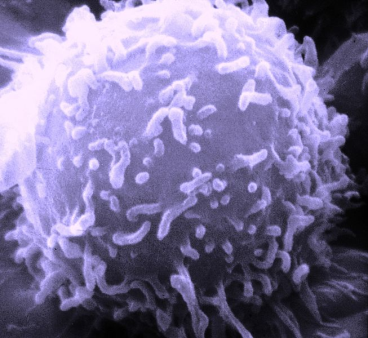
Monocyte: A white blood cell that has a single nucleus and can take in (ingest) foreign material.Monocytes make up 1 to 10 percent of white blood cells. Monocytes move out of the bloodstream and into tissue, where they turn into macrophages, large scavenger cells that destroy foreign cells, remove dead tissue and kill cancer cells. Monocytes are elevated in chronic infections and autoimmune disease; chemotherapy may cause decreased levels.
Macrophage: A type of white blood cell that ingests foreign material. Macrophages are key players in the immune response to foreign invaders of the body, such as infectious microorganisms. They are normally found in the liver, spleen, and connective tissues of the body.
Dendritic cell: A special type of cell that is a key regulator of the immune system, acting as a professional antigen-presenting cell (APC) capable of activating nave T cells and stimulating the growth and differentiation of B cells.
Dendritic cells are found, for example, in the lymph nodes and spleen. As an APC, a dendritic cell can retain antigen for long periods on its surface, present the antigen to a T or B cell and so influence their behavior.
The word "dendritic" means "branched like a tree." It comes from the Greek "dendron" (tree).
Date: 2015-01-29; view: 1982
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Lecture five: Origins of the Cold War, 1945-48 | | | Government employee: Job description and activities |