
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Table 2
| Temperature t, °C | Temperature Ò, Ê | 1/Ò, Ê–1 | Semiconductor resistance R, Ω | 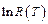
| Forbidden band width 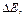 J J
|
3.3. Draw the graph semiconductor resistance logarithm against inverse temperature 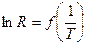 using data from table 2.
using data from table 2.

3.4. Determine  of graph inclination to the x-axis:
of graph inclination to the x-axis:
 = ___________.
= ___________.
Enter the results of  determination into table 2. Obtained value corresponds to the forbidden band width.
determination into table 2. Obtained value corresponds to the forbidden band width.
 |
Conclusions
The data of laboratory work fulfillment
Pass mark Signature
Mark of laboratory work defence Signature
 questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
and its defending
1. What is metal conductivity?
2. What does metal conductivity depend on?
3. Write down the law for temperature dependence of metal resistance.
4. Write down the law for temperature dependence of semiconductor resistance.
5. Give theoretical explanation for temperature dependence of metal resistance.
6. Give theoretical explanation for temperature dependence of semiconductor resistance.
7. Why does metal resistance grow while temperature increases?
8. Why does semiconductor resistance diminish while temperature increases?
9. How is temperature coefficient of metal resistance determined?
10. What substances are named semiconductors?
11. What substances are called intrinsic (pure) semiconductors?
12. What substances are called extrinsic (impurity) semiconductors?
13. How is forbidden bands width of a semiconductor determined?
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1200