
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
STUDY OF HYDROGEN ATOM SPECTRUM RYDBERG’S CONSTANT DETERMINATION
| The purpose of the work: - to determine wavelengths of hydrogen atom visible spectrum; - to calculate Rydberg’s constant; - to determine energy and mechanical characteristics of hydrogen atom | Devices and accessories: 1. spectroscope; 2. discharge tube; 3. current source |
Task 1. Monochromator calibration graph drawing
1.1. Obtain readings of monochromator drum for all wavelength of krypton atom. Enter the results into table 1.
Table 1
| Spectrum line color | Theoretical values of wavelengths | Drum reading | |
 λ, Å λ, Å
|  λ, m λ, m
| ||
| Bright red | |||
| Orange | |||
| Yellow-orange | |||
| Yellow | |||
| Green | |||
| Blue | |||
| Blue | |||
| Violet | |||
| Violet | |||
| Violet |
Draw calibration graph using plotting paper.
Task 2. Determination of wavelengths of hydrogen atom visible spectrum lines
2.1. Determine positions of red, blue, dark blue and violet lines of hydrogen atom using drum scale.
2.2. Determine wavelengths of hydrogen atom visible spectrum lines Íα, Íβ, Íγ, Íδ using monochromator calibration graph. Enter the results into table 2
Table 2
| Color of Spectrum line | Line symbol | Drum reading | Spectrum line wavelength determined by graphical method, λ, m | Rydberg’s constant, R¥, m–1 | Average value of Rydberg’s constant, R¥ave, m–1 | Absolute error, DR¥ ,m–1 | Fractional error, e, % |
| Red | Ha | ||||||
| Blue | Hb | ||||||
| Dark blue | Hg | ||||||
| Violet | Hd |

Task 3. Rydberg’s constant determination
3.1. Calculate Rydberg’s constant according to the formula:
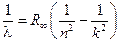 ,
,
where n = 2; k = 3, 4, 5, 6.
3.2. Rydberg’s constant measurement error calculation.
— Determine average value:
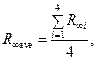
— Calculate deviation of each value from average one:

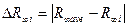
— Calculate root-mean-square deviation from average value:
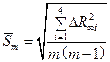
where ò = 4.
— Calculate the absolute error of Rydberg’s constant measurement:
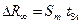
where 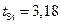 (ò = 4 and
(ò = 4 and 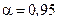 ).
).
— Calculate the fractional error of Rydberg’s constant measurement according to the formula:
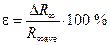 .
.
— Write down the result in the following form:
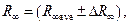 m–1,
m–1,
Enter the results into table 2.
Task 4. Determination of energy and mechanical characteristics of hydrogen atom. Enter the results into table 3.
Table 3
| Prinsipal quantum number, n | Total energy Åï, J | Radius of electron orbit rï, m | Photon energy of Balmer’s series, e, J | Ionization energy Eion, åV | |||
| k = 3 | k = 4 | k = 5 | k = 6 | ||||
| n = 1 | |||||||
| n = 2 | |||||||
| n = 3 | |||||||
| n = 4 |

Conclusions
The data of laboratory work fulfilment
Pass mark Signature
Mark of laboratory work defence Signature
 questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
and its defending
1. What is linear spectrum?
2. Formulate Bohr’s postulates.
3. Name spectral series in hydrogen atom radiation spectrum.
4. Deduce formula for electron orbits radius determination in hydrogen atom.
5. Deduce formula for determination of electron total energy in hydrogen atom.
6. Deduce Balmer’s serial formula using Bohr’s theory.
7. Draw energy levels scheme of hydrogen atom. Explain it.
8. Write down Schrodinger’s equation. Explain the essence of ψ-function.
9. What quantum numbers do you know? What is their physical essence?
10. What is electron state? How is electron state denoted?
11. Formulate the selection rule for orbital quantum number.
12. Draw the quantum scheme formation of hydrogen atom radiation series.
13. What is spectroscope calibration graph? How is spectroscope calibration graph drawn? How is it used?

 LABORATORY WORK
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1932