
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT INVESTIGATION of PROPERTIES OF PLANE POLARIZED LIGHT
| The purpose of the work: - to study the method of plane polarized light observation with the help of polaroids; - to test Malus law, observation of double refraction and interference of polarized rays | Devices and accessories: 1. optic bench; 2. two polaroids; 3. laser; 4. photosensitive device; 5. lens; 6. iceland spar crystal |
Task 1. Polarized light testing
1.1. Rotating the analyzer from 0 to 3600 with the step of 100. Write down the readings of device
Ù-4316 into table 1.
Table 1
| Analyzer rotation angle, j, grad. | Device reading | cos j | cos2 j | Analyzer rotation angle, j, grad. | Device reading | ||
| amount of points | mA | amount of points | mA | ||||
1.3. Plot the graph of the function 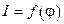 in polar coordinate.
in polar coordinate.
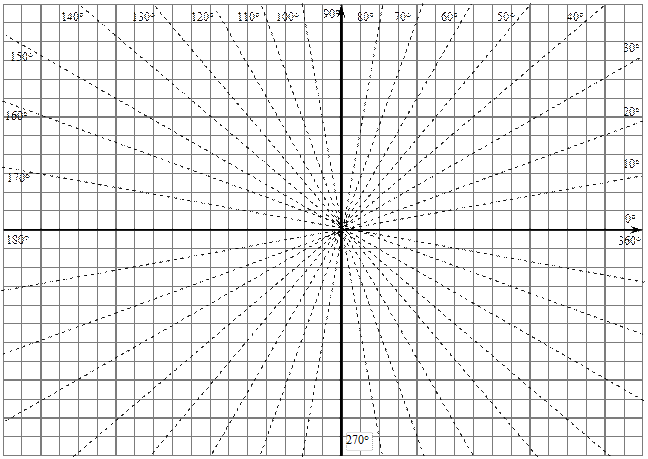
Task 2. Malus’s law testing
2.1. Determine the value of trigonometric function 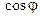 and
and 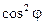 using calculator from 0° to 90°.
using calculator from 0° to 90°.
 2.2. Plot the graph of function I = f (cos2 j) for angles within intervals from 0 to 90°.
2.2. Plot the graph of function I = f (cos2 j) for angles within intervals from 0 to 90°.
Task 3. Double refraction observation
3.1. Obtain the first bright spot on the screen turning analyzer. Write down the angle according to the analyzer scale:
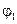 = __________.
= __________.
3.2. Obtain the second bright spot on the screen turning analyzer. Write down the angle according to the analyzer scale:
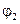 = __________.
= __________.
3.3. Determine angles difference:

 = __________.
= __________.
Conclusions
The data of laboratory work fulfilment
Pass mark Signature
Mark of laboratory work defence Signature
 questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work
and its defending
1. What is the difference between natural and polarized light?
2. What types of polarized light do you know?
3. What are polarization plane and oscillation plane?
4. What methods of polarized light obtaining do you know?
5. What are polarizer and analyzer?
6. What is the principal plane of crystal?
7. What is the difference between the ordinary and extraordinary rays?
8. What is the Nicol prism?
9. Give definition of Malus low.
10. What is the essence of double refraction?
11. What is the essence of Kerr effect?
12. What is the essence of the polarization plane rotation?
13. What are the conditions for interference of polarized rays observation?
14. What are the min and max conditions of polarized rays interference?
 QUESTIONS FOR CURRENT TEST PAPERS AND MODULE CONTROL
QUESTIONS FOR CURRENT TEST PAPERS AND MODULE CONTROL
(theoretical information)
1. Free harmonic oscillations. Differential equation of free harmonic oscillations.
2. Equation and characteristics of free harmonic oscillations.
3. Addition of two oscillations of same frequency in a straight line. Vector diagram method.
4. Addition of two oscillations with nearly equal methods. Beats.
5. Addition of two oscillations acting at right angles. Lissajous figures
6. Damped oscillations. Differential equation of the free damped oscillations and its solution.
7. Damped oscillations characteristics: Damping factor, damping decrement, logarithmic damping decrement quality factor.
8. Forced oscillations at periodic force action. Amplitude and phase of forced oscillations. Resonance.
9. Free electromagnetic oscillations.
10. Damped electromagnetic oscillations.
11. Forced electromagnetic oscillations
12. Waves. Transverse and longitudinal waves. Wave equation.
13. Phase and group wave velocities.
14. Elastic wave energy.
15. Stationary waves.
16. Doppler’s effect for sound and electromagnetic waves.
17. Electromagnetic wave. Wave equation and equation of wave. Wave characteristics.
18. Electromagnetic wave energy.
19. Electromagnetic wave radiation.
20. Light waves properties.
21. Interference of light. Light waves coherence.
22. Phases difference. Optical path difference. Relationship between them.
23. Methods of coherent waves getting: Young’s splits, Fresnel’s bemirror, Fresnel’s biprism.
24. Interference in thin films.
25. Newton’s rings.
26. Practical application of light interference.
27. Diffraction of light. Observation conditions.
28. Hugence principle. Hugence-Fresnel principle.
29. Fresnel’s zone.
30. Fresnel’s Diffraction at circular aperture.
31. Fresnel’s Diffraction at dense disk.
32. Diffraction of plane light waves at single slit.
33. Diffraction of plane light waves at diffraction grating.
34. Practical application of light diffraction.
35. Polarization of light. Types of light polarization.
36. Polarized light getting. Brewster’s law.
37. Polarized light getting using anisotropic crystals.
38. Polarized light properties: Malus’ law, polarized light interference.
39. Artificial optical anisotropy. Kerr’s effect.
40. Dispersion of light. Types of dispersion.
41. Dispersion of light. Rayleigh’s Law.
42. Absorption of light. Burger—Lambert—Berr Law.
Module IV. quantum and ATOMIC PHYSICS
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1419
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| DIFFRACTION OF LIGHT. DETERMINATION of WAVELENGTH OF MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT USING DIFFRACTION GRATING | | | STUDY OF THERMAL RADIATION LAWS DETERMINATION OF STEFAN CONSTANT |