
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Table 4
| Ring number, k | Mean value of lens curvature radius Rave, m | Air clearance thickness 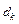 , m , m
| Half-wavelength amount, 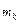
|

Conclusions

The data of laboratory work fulfilment
Pass mark Signature
 Mark of laboratory work defence Signature
Mark of laboratory work defence Signature
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work and its defending
1. What is phenomenon of light interference? What is the condition for observing light interference?
2. Wright down max and min conditions of light interference.
3. What are optical path difference and phase difference? What is connection between them?
4. What waves are called coherent?
5. What ways of coherent waves obtaining do you know?
6. How are coherent waves received in this laboratory work?
7. Why is the interference pattern observed as rings in this laboratory work?
8. Deduce formulae to determine R and λ.
9. How does the radius depend on wavelength and curvature of lens?
10. Why are the radii diffused?
11. Why is the dark spot in the centre of the pattern observed?
12. What do we observe when the optical system lights by daylight?
13. What rays are interfered for Newton’s rings formation in transmitted and reflected light? Draw the ray path.
14. What are “fringes of equal thickness” (isopachic fringes) and “fringes of equal inclination” (isoclinic fringes)?
15. In what case can we observe a bright (white) spot in the centre of the interference pattern?
16. Where are interference rings arranged more compact: in the centre or in the periphery and why?
17. Why does the interference pattern disappear with increasing the distance between the plate and lens?
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1182
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Module ˛˛˛. Physics of oscillations and waves. optics | | | DIFFRACTION OF LIGHT. DETERMINATION of WAVELENGTH OF MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT USING DIFFRACTION GRATING |