
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
DETERMINATION OF WIRE SPECIFIC RESISTANCE
| The purpose of the work. To study the method of wire specific resistance determination | Devices and accessories Installation for wire specific resistance determination by ammeter-voltmeter method |
Task 1. Wire resistance determination
1.1. Set wire length l1 (set by a teacher) using moving contact.
1.2. Switch on installation. Button «Bridge» must be pushed. Switch button is pushed when scheme of figure 4.1. is used. And switch button is not pushed when scheme of figure 4.2. is used.
1.3. Write down ammeter and voltmeter readings. Enter the measured values of current and voltage into table 1.
Table 1
| Wire length, m | Exp. No | U, V | I, A | R³, Ω | R³ave, Ω | R³= R³ave – R0 | eR, % | ΔR, Ω |
| l1 = | ||||||||
| l2 = | ||||||||
| l3 = | ||||||||
| l0 = |
1.4. Change two times wire length and repeat measurements according to item 1.3.
1.5. Determine wire resistance R0 setting length l0 = 0 and repeat measurement according item 3. Enter the results into table 1.
1.6. Determine resistance Ri for each pair of measured U and I according to the formula:
R³ = 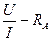 or R³ =
or R³ = 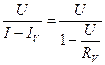 .
.
Calculate the mean value of resistance Ri ave for each wire length l.
1.7. Determine the fractional 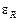 and absolute ΔR errors of resistance measurement. Enter the results into table 1.
and absolute ΔR errors of resistance measurement. Enter the results into table 1.
1.8. Determine wire resistance, taking into account wire resistance R0:
Ri = Ri ave – R0.
Enter the results into table 1.
Task 2. Wire specific resistance determination.
2.1. Measure wire diameter d by micrometer. Enter the results into table 2.
Table 2
| Exð. No | r³, Ω×m | rave, Ω×m | 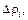 Ω×m Ω×m
| 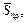 Ω×m Ω×m
| Δr, Ω×m | er, % | d, m |
2.2. Determine wire specific resistance at different values of li according to the formula:
ri = 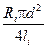 .
.
Enter the results into table 2.
2.3. Calculate arithmetic mean value ρave according to the formula:
where n = 3 is amount of calculations.
2.4. Calculate deviation from mean value 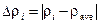 .
.
2.5. Calculate root-mean-square deviation 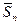 according to the formula:
according to the formula:

2.6. Determine the absolute error of wire specific resistance measurements according to the formula:
Dr = tSt · 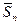 .
.
where the Student’s coefficient is tSt = 4,30 (n = 3 and a = 0,95)
2.7. Calculate fractional error according to the formula 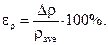
2.8. Write down the result in a form:
 = Ω×m.
= Ω×m.
Conclusions
The data of laboratory work fulfillment
Pass mark Signature
Mark of laboratory work defending Signature
questions to be admitted for doing laboratory work and its defending
1. What factors does specific wire resistance depend on?
2. What factors have no influence on specific resistance value?
3. How can wire specific resistance be obtained?
4. Write down formula for wire specific resistance determination.
5. What is measurement unit of wire specific resistance?
6. What does temperature resistance coefficient equal?
7. Write down formula for dependence of specific resistance on temperature.
8. What is specific conductivity?
9. Write down formula for dependence of specific conductivity on temperature.
10. What are reasons of systematic methodical error of wire resistance measurement? How is systematic methodical error avoided?
11. Deduce formula for determination of fractional error of specific resistance measurement.
12. How is wire resistance determined? How is branch wire resistance taken into account
LABORATORY WORK
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1538
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Table 2 | | | DETERMINATION OF HORIZONTAL COMPONENT OF THE EARTH MAGNETIC FIELD INDUCTION |