
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Relation between main classes of inorganic substances
Scheme of genetical relationships of classes
  Chemical element Chemical element
 + +
|  Oxygen O2 Oxygen O2
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||

| |||||||||||||||||||||
|  OXIDES OXIDES
| 
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Salifiables | Non-Salifiables | ||||||||||||||||||||
 Basic Basic
| Amphoteric | Acidic | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| HYDROXIDES | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Typical bases | Amphoteric | ACIDS | |||||||||||||||||||
| 
| 
| |||||||||||||||||||
| SALTS | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | Neutral | Acidic | Double | Mixed | Complex | ||||||||||||||||
Oxides
Oxides - complex substances, consisting of two elements, one of them is Oxygen. Practically all elements (excepting three noble gases - He, Ar and Ne) may form oxides.
Classification of oxides:
| Non-Salifiables | - non-salts forming (CO, N2O, NO) |
| Salifiables | - salts forming, subdivided into: |
| Basic - it is a metal oxides in which metals display low oxidation number +1, +2 (Na2O, MgO, CuO); | |
| Amphoteric (for some metals with oxidation number +3, +4, sometimes +2) - ZnO, Al2O3, Cr2O3, SnO, PbO, MnO2; | |
| Acidic - it is oxides of non-metals and some metals with oxidation number from +5 to +7 (SO2, SO3, P2O5, Mn2O7, CrO3). |
Preparation
1. Interaction of simple and complex substances with Oxygen:
2Mg + O2 = 2MgO;
4Al + 3O2 = 2Al2O3;
S + O2 = SO2;
2H2S + 3O2 = 2SO2 + 2H2O;
2C2H2 + 5O2 = 4CO2 + 2H2O;
4FeS + 7O2 = 2Fe2O3 + 4SO2.
2. Decomposition of some substances containing Oxygen (oxides, bases, acids, salts) on heating:
4CrO3 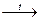 2Cr2O3 + 3O2;
2Cr2O3 + 3O2;
Cu(OH)2 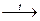 CuO + H2O;
CuO + H2O;
2Fe(OH)3 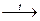 Fe2O3 + 3H2O;
Fe2O3 + 3H2O;
H2CO3 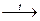 CO2 + H2O;
CO2 + H2O;
H2SiO3 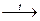 SiO2 + H2O;
SiO2 + H2O;
CaCO3 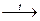 CaO + CO2;
CaO + CO2;
2AgNO3 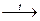 2Ag + 2NO2 + O2.
2Ag + 2NO2 + O2.
Date: 2015-01-12; view: 1654
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Rules for work carrying out and results design | | | Chemical properties |