
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Morphological characteristics
The Adjective and the Adverb
According to their morphological composition adjectives can be subdivided into simple, derived and compound.
In the case of simple adjectives such as kind, new, fresh, we cannot always tell whether a word is an adjective by looking at it in isolation, as the form does not always indicate its status.
Derived adjectives are recognizable morphologically. They consist of one root morpheme and one or more derivational morphemes - suffixes or prefixes. There are the following adjective-forming suffixes:
| -able -al -ary -ed -en -que -fold -ful -ic -id -ish -ive -less -like -ly -most -ory -ous -some -y | understandable musical, governmental documentary beaded, barbed wooden, silken, shrunken picturesque twofold, manifold careful, sinful pessimistic, atomic torpid, morbid feverish, bluish effective, distinctive careless, spotless manlike, warlike kindly, weekly, homely uttermost observatory glorious lonesome, troublesome handy, messy |
Some adjectives are former participles and therefore retain participial suffixes: charming, interesting, cunning, daring.
The suffixes -ly, -ed, -ful, -ary, -al, -y are not confined to adjectives only. Thus, many adverbs are derived from adjectives hy means of the suffix -ly (strongly, bitterly, quickly). Most of the verbs form their past tense and participle II with -ed. There are many nouns with the suffixes -al (festival, scandal, criminal), -ary (boundary, missionary), -ful (mouthful, handful), -y (sonny, doggy), etc.
Morphological characteristics
Adjectives in English do not take any endings to express agreement with the head-word.
The only pattern of morphological change is that of degrees of comparison, which is possible only for descriptive qualitative adjectives the meaning of which is compatible with the idea of gradation of quality.
There are three grades of comparison: positive, comparative, and superlative. The superlative is generally used with the definite article. Ways of formation may be synthetic, analytic, and suppletive (irregular). The synthetic way is by adding the inflection -er, -est, as fine -finer - finest. This means is found with monosyllabic and some disyllabic adjectives in which the stress falls on the last syllable:
1) full - fuller - fullest
| polite profound complete | - politer - profounder - completer | - politest - profoundest - completest |
2) in which the second syllable is the syllabic [1]:
| able noble | - abler - nobler | - ablest - noblest |
3) with adjectives in -er, -y, -some, -ow:,
| tender happy handsome narrow | - tenderer - happier - handsomer - narrower | - tenderest - happiest - handsomest - narrowest |
Synthetic inflection, however, is often found in other disyllabic adjectives:
You are the horridest man I have ever seen.
Polysyllabic adjectives form their degrees of comparison analytically, by means of more and most:
difficult - more difficult - most difficult
curious - more curious - most curious
Several adjectives form their degrees of comparison by means of (suppletive forms) irregularly:
| good/well bad little many | - better - worse - less - more | - best - worst - least - most |
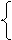
| far | farther - farthest (with reference to distance) further - furthest (with reference to distance, abstract notions and in figurative use) |
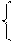
| old | older - oldest (with reference to age) elder - eldest (with reference to the sequence of brothers and sisters) |
Adjectival compounds can be inflected in two ways, either the first element is inflected (if it is an adjective or adverb), or comparison is with more and most, for example:
| well-known dull-witted kind-hearted | - better-known - more dull-witted - more kind-hearted | - best-known - most dull-witted - most kind-hearted |
The following adjectives generally do not form degrees of comparison:
1. Limiting qualitative adjectives which single out or determine the type of things or persons, such as:
previous, middle, left, childless, medical, dead, etc.
2. Relative adjectives (which are also limiting in their meaning) such as:
woollen, wooden, flaxen, earthen, ashen.
3. Adjectives with comparative and superlative meaning (the so-called gradables) which are of Latin origin:
former, inner, upper, junior, senior, prior, superior, etc. (originally with comparative meaning), and
minimal, optimal, proximal, etc. (originally with superlative meaning).
With most of them the comparative meaning has been lost and they are used as positive forms (the inner wall, the upper lip, superior quality, minimal losses).
However, some comparatives borrowed from Latin (major, minor, exterior, interior, junior, senior) may form their own comparatives with a change of meaning.
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 2972
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| TASK 24. Use the best suitable word in each gap. | | | Substantivized adjectives |