
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
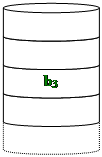
Redundancy Through Hamming Code
à Disks are synchronized
à Very small stripes
à Error correction calculated across corresponding bits on disks
à Multiple parity disks store Hamming code error correction in corresponding positions.
à Lots of redundancy
à Expensive
? Not used
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
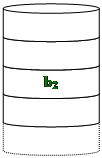
RAID 3
Bit-Interleaved Parity
à Similar to RAID 2
à Only one redundant disk, no matter how large the array
à Simple parity bit for each set of corresponding bits
à Data on failed drive can be reconstructed from surviving data and parity info
à Very high transfer rates
 |  |  |  |  |
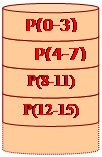
RAID 4
Block-Level Parity
z Each disk operates independently
z Good for high I/O request rate
z Large stripes
z Bit by bit parity calculated across stripes on each disk
z Parity stored on each disk
 |  |  |  |  |
RAID 5
Block-Level Distributed Parity
z Like RAID 4
z Parity striped across all disks
z Round robin allocation for parity stripe
z Avoid RAID 4 botl-neck at parity disk
z Commonly used in network servers
 |  |  |  |  |
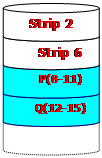
RAID 6
Redundancy Through 2 Different Codes
z The scheme of functioning suggests calculation of 2 control codes stored in different blocks distributed through all disks.
z Control codes P and Q are calculated by different algorithms, it allows to restore lost data when even two disks have been failed.
z The hardware is more complicated.
 |  |  |  |  |  |
Optical Memory
Optical Disk Products:
z CD
A nonerasable disk that stores digitized audio information. The standard system uses 12-cm disks and can record more than 60 minutes of uninterrupted playing time.
CD-ROM
A nonerasable disk used for storing computer data. The standard system uses 12-cm disks and can hold more than 550 Mbytes.
DVD
Digital video disk. The technology of video-signals recording and other data of a large volume is used and it?s based on methods of information (data) compression.
WORM
Write-Once Read Many is more easily written than CD-ROM, making single-copy disks commercially feasible; holds from 200 to 800 Mbytes of data.
Date: 2016-06-13; view: 135
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Data Organization and Formatting. | | | Erasable Optical Disk |