
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Political System of the USA
A) General Information
| Official name: | the United States of America |
| Capital: | Washington D.C. (District of Columbia) |
| Number of states | 50 states |
| Form of Government | Federation |
| Political System | Federal State |
| Government | Federal Government |
| Leader of the Country | the President |
| Current President | Barak Hussein Obama (2009-present) the 44th President |
NB! A “Federal State” means that the states are joined as equals under the common government (Federal Government), granting some of their powers to the common government, but retaining some to themselves.
The distribution of powers between the Federal Government and the Governments of the states
| the Federal Government | the Governments of the states |
| ¨ to represent the country on the international arena; ¨ to defend the whole nation; ¨ to deal with the foreign policy; ¨ to deal with the international trade; etc. | ¨ to deal with education; ¨ to deal with taxes and finance; ¨ to deal with the internal communication; etc. |
B) The Constitution
| Leading Document of the Country | The US Constitution |
| Adopted | 1787 |
| Came into Force | March 4, 1789 |
| Authors | The Founding Fathers |
| Structure | The Preamble + 7 Articles + 27 Amendments |
| Changes | No, only 27 Amendments |
| Making Changes | Article 5 (should have 2/3 of votes from the US Congress + ratification by the state legislature) |
| 1st Amendments | The Bill of Rights |
| Local Constitutions | Each state has got one, that doesn’t contradict the Federal one. Each constitution is structured the same as the main one. |
 NB! The Founding Fathers of the American Constitution are the outstanding leaders of the new nation. They were part of the Constitutional Convention, which was formed on May 25, 1787 in order to work out and adopt a new constitution. Among the 55 delegates there were 6, the most prominent ones. They were:
NB! The Founding Fathers of the American Constitution are the outstanding leaders of the new nation. They were part of the Constitutional Convention, which was formed on May 25, 1787 in order to work out and adopt a new constitution. Among the 55 delegates there were 6, the most prominent ones. They were:
 Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton
James Madison played the leading roles
George Washington
William Johnson
Governor Morris
Rufus King

The significance of the US Constitution:
1) It established the existing federal system, in which the power is shared between a central authority and the states that retain some powers for themselves.
2) It also provided the division of powers into three branches: legislative (the Congress), executive (the President) and judicial (the Supreme Court).
3) It established the system of checks and balances which ensured that none of the branches would abuse its power. Thus the system gives each branch a mechanism to restrain the other two.
E.g. the President has the right to veto a bill passed by the Congress, but the Congress may override it by 2/3of majority. But the Supreme Court has the power to declare a bill illegal if it doesn’t agree with the Constitution.
4) It also ensured that the changes (amendments) can be introduced to the Constitution. Article 5 states that the changes can be made only if they are passed by the Congress (only 2/3 of the votes are needed).
NB! When the Constitution was written there existed only13 states, but the Founding Fathers foresaw that with time some changes could be needed. As a result a method of adding amendments was introduced in the main text of the Constitution (article 5).
Throughout the whole history of the US Constitution (that is more than 200 years) only 27 Amendments have been made. The most notable are:
¨ The 1st 10 Amendments (known as “the Bill of Rights”) deals with the civil rights.
NB! The Bill of Rights is a collective name for the first 10 Amendments to the American Constitution, adopted on December 15, 1791. The first 4 of them deal with the individual rights of a citizen, the next 4 – the system of justice, and the last 2 contain very broad statements of the constitutional authority.
E.g. the 2nd Amendment guarantees the right to bear arms. The 7th Amendment assures trial by jury in civil cases involving anything valued at more than $20.
¨ The 13th Amendment abolished slavery, introduced in 1865.
¨ The 14th Amendment established a clear and simple definition of citizenship, including the civil rights of the former slaves (adopted in 1868).
¨ The 19th Amendment deals with the universal suffrage, thus giving the US women the right to vote (ratified in 1920).
¨ The 27th Amendment states that elections to the Congress should be before the pay rise (proposed in 1789, but ratified in 1992).
5) It served as the basis for the states’ constitutions. So as they would not contradict with the main one. But it should be mentioned that some of them has changed with time and turned from small and short in size into very detailed documents of several volumes.
E.g. Louisiana has rewritten its constitution 11 times and the most recent version is of 1974.
C) The Executive Branch – the Congress
| Residence | Capitol (Hill), Washington D.C. |
The Congress is the strongest branch and plays very important part in the representative government. It consists of two Houses:
| the Senate | the House of Representatives | |
| General information | @ the smallest house; @ it used to be elected by state legislatures, but since 1913 there’s a direct election. | @ membership is based on population |
| Members | Senators | Members of the House of Representatives (Congressmen) |
| Represent | home state (for each senator) | district in a home state (the average size of a district is 530,000) |
| Number of members | 100 (2 representatives from each state) | 435 (ensured that each state has got at least 1 member, but in reality the number varies from state to state; e.g. California = 53 representatives; Delaware = 1 representative;) |
| How to become a member? | One must be: @ at least 30 years old @ a citizen of the US for 9 years @ a resident of the state, elected from | One must be: @ at least 25 years old @ a citizen of the US for 7 years @ a resident of the represented state |
| Elections | every 2 years (1/3 of the senators is being changed, while 2/3 remain so as to have some with the experience in legislature) | every 2 years (some members are reelected several times to have a group of experienced legislators) |
| Term | for 6 years | for 2 years |
| The Presiding officer (always member of the majority party) | the Vice-President the President pro tempore (elected for the time when the VP isn’t present in the House) | the Speaker (elected at the start of each Congress) |
| Sessions | The Congress meets in regular sessions starting from January 3 and continuing all the year round. But the President has the right to call a special session if necessary. |
NB! “The Big Four” is a small body made up by the Speaker, the Vice-President and majority party leaders (Democratic and Republican). Its main functions are: a) to maintain close contacts with the President; b) to influence making laws; c) to consider home and foreign policy.
The Committees
The work of the Congress is maintained by numerous committees. Today there are 22 standing (permanent) committees in the HofR and 16 in the Senate, plus 4 joint permanent committees from both Houses. All these have about 300 subcommittees that deal with specific problems. Furthermore, standing committees may specialize in a certain sphere of lawmaking (foreign policy, defense, agriculture, etc.). The majority party in each house controls the work of each committee, and the minority party is represented in them according to their numbers in each House.
Powers of the Congress
@ to declare war against foreign nation
@ to remove federal officials for crimes
@ to approve/ reject the candidates for the Supreme Court, federal judges, Secretaries (Cabinet Ministers), ambassadors, suggested by the President.
Passing a Bill (stages)
1) Introduction of a bill
NB! Each of the houses in the Congress has the right to introduce any bill on any subject. Important bills can be suggested by the President himself or by other executive officials.
2) The committee stage
NB! After the introduction the bill is sent to a special committee for discussion and making some changes if needed. If approved the bill is passed into the house.
3) Debates & Voting
NB! When the bill is back to the house where it has been introduced, it is being debated and afterwards voted to approve or defeat it. If approved it is sent to the next stage.
4) The Second House (HofR or the Senate)
NB! The bill goes through the same proceedings as the ones mentioned above.
5) The President’s Approval
NB! The bill gets to this stage only after having been passed by both houses. When signed by the President it becomes a Law. However, the President may veto a bill, but it can be reproved by the 2/3 votes in both houses. After this the bill becomes a law known as an Act of Congress.
NB! The bills introduced by the White House or the Cabinet usually go through all the stages without any difficulty.
D) Executive Branch – the President, the Federal Government, State and Local Governments
| The President | |
| General information | Head of the executive branch |
| Official Residence | The White House, Washington D.C. |
| How to become the President of the US? | One must be: @ at least 35 years old @ a resident of the US for 14 years @ a national born citizen |
| Elections * | every 4 years (the 1st Tuesday after the first Monday in November) |
| Term | 4 years (the 22nd Amendment (1951) ensured that the President can serve only 2 terms) |
| Succession to the Presidency |        the President the Vice-President the Speaker of the HofR the President pro tempore the Secretary of State the Secretary of Treasury the Secretary of Defence other Cabinet Ministers the President the Vice-President the Speaker of the HofR the President pro tempore the Secretary of State the Secretary of Treasury the Secretary of Defence other Cabinet Ministers
|
| Functions of the President | @ head of the Federal Government (legislative role) ü recommends laws ü approves/ vetoes a bill ü requests money for the FG operations @ head of the political party @ chief executive officer ü issues executive orders (have the force of a law) ü influence public opinion @ the commander-in-chief of the armed forces @ appoints heads of the executive departments & agencies @ appoints high-ranking officials (ministers, judges of any level) @ chooses the heads of the executive committees @ represents the States on the international arena @ grants full/conditional pardon to anyone accused of breaking the federal law |
* NB! Presidential Elections
The elections of a president in the USA is a peculiar thing because people do not choose (vote) for the candidate for the presidency directly. Instead the states elect “the presidential electors”, the number of which corresponds to the number of the Senators and Representatives from the corresponding state. These electors are selected by the special party machines. The candidate with the highest number of votes in each state wins all the electoral votes of the state. The candidates usually form the Electoral College, which is usually made up from the electors of all 50 states + 3 electors from the District of Columbia (total number is 538), but the College never meets as a body. After the election the electors gather in the state capitals and cast their votes for the candidate with the largest number votes in their respective states. To become the President candidate for the presidency must get 270 votes. In case none of the candidate wins the majority, the members of the HofR vote for the candidates and each state and District of Colombia is given only one vote. The presidential term starts with the special ceremony on the steps of the Capitol, when (s)he publicly takes an oath of the office. It usually happens on January 20 the next year after the elections.
Executive Departments (ministries)
Today there are 15 departments which deal with national and international affairs. The heads (ministers) of these departments, chosen by the President and approved by the Senate, form the Cabinet. Besides, there are over 50 agencies, which have certain responsibilities and duties. They are directly accountable to the President.
State and Local Governments
Each state has got a local state constitution, that doesn’t contradict the Federal one. Each constitution is structured the same as the main one. The central part in it is occupied by the questions of the division of powers and forming the spheres of activities. Thus the legislative branch is represented by the state “Congress” usually consisting of 2 Houses (the Senate & the House of Representatives/ the House of Delegates/ the General Assembly). The members of the Houses may serve from 2 (HofR) to 4 (Senate) years. The executive branch is the Governor, who usually serves 4 years and is elected by a popular vote. The judicial power is headed by the State Supreme Court.
NB! The local “congresses” may not pass laws that would contradict the Constitution. According to the doctrine of “national supremacy”, in case of any conflict between federal and state authorities, the federal should always have the upper hand.
As the US is a highly urbanized country with lots of cities, there is an issue of running them. In many aspects the cities function independently of the states. But still most big cities function in cooperation with both state and federal organizations. There are 3 distinct types of city government:
a) the mayor-council
b) the commission
c) the city manager
(for more details see Hello, America! Unit 25, p.149)
Political Parties
The importance of political parties:
a) They are the basis of the American political system;
b) They are important institutions in the American democratic life;
At the national level, the US has a 2 party system, which remained practically unchanged throughout the history. The major parties are:
 The Democratic Party The Democratic Party
| The Republican Party | |
| When it was formed? | 1792 (historical) 1828 (modern) | 1854 |
| Who formed it? | Andrew Jackson | the people of the northern and western states |
| Symbol | the donkey | the elephant |
| Nicknames | - | the Grand Old Party (GOP) |
| Who is the current leader? | Debbie Wasserman Schultz (chairman) Barak Obama (the President of the US) Joe Biden (the Vice-President of the US) | Reince Priebus (chairman) John Boehner (the Speaker) |
| Views | ¶ more liberal views ¶ they think that the federal government should provide social economic programmes for the needed ¶ they established Social Security Programme | ¶ more conservative views ¶ they think that social programmes are rather costly and may hurt the economy ¶ they rely more on private enterprises |
| Party Membership | It is rarely formal. Any person may become a member during the electoral campaign by a) a simple declaration; b) associating oneself with the party. They do not have to join a party to vote or become a candidate for public office. The voting is by a secret ballot so none knows how the voices are distributed. |
Other Parties
The main competition during the elections is between the 2 major parties. Though there are some smaller parties, they haven’t got enough popular support to win the elections. However, some of them are quite influential in some states or cities.
| Party (Official 2012 Nominee) | Year Founded# | Registered Members | Party Logo | Party Policy (major issues) |
| 1. Constitution Party (Virgil Goode) | 366,937 | 
| e Non-intervention foreign policy e Imposing immigration restrictions e Stand for the capital punishment e Imposing abortion restrictions | |
| 3. Green Party (Cynthia McKinney (in 2008)) | 289,177 | 
| e Non-intervention foreign policy e Stand for limiting private financing campaigns e Imposing progressive taxation e Stand for the universal healthcare e Stand for drug liberalization e Stand for the legalization of the same-sex marriages | |
| 4. Libertarian Party (Gary Johnson) | 235,500 | 
| e Non-intervention foreign policy e Stand for drug liberalization e Stand for the legalization of the same-sex marriages |
The distribution of seats in the Congress in terms of political parties
| Political Party | The Senate | The House of Representatives |
| Democratic Party | 53 | 199 |
| Republican Party | 45 | 233 |
| Independents* | 2 | 0 |
| Vacant | 3 | 0 |
NB! * Independents
Some political candidates, and many voters, choose not to identify with a particular political party. In some states, independents are not allowed to vote in primary elections, but in others, they can vote in any primary election of their choice. Independents can be of any political persuasion, but the term most commonly refers to politicians or voters who hold centrist views that incorporate facets of both Democratic and Republican ideology.
E) Judicial Branch – the Supreme Court and the system of courts
The US has the most complex judicial system in the world. It consists of a system of courts spread throughout the country and is headed by the Supreme Court.
Structure:
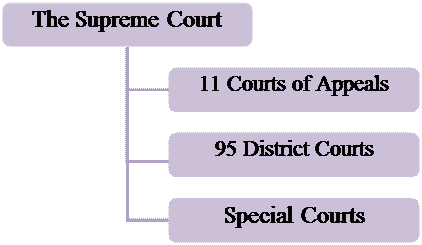 Important issues of the American judicial system:
Important issues of the American judicial system:
¨ The US has 2 distinct system of courts – federal and state;
¨ Alongside with the federal system each state has its own judicial system headed by the State Supreme Court;
¨ All in all there 51 sets of courts (50 states + 1 District of Columbia);
¨ All the courts are independent;
¨ The Congress has the power to create and abolish federal courts;
¨ The Congress has the power to determine the number of federal judges;
¨ The Congress cannot abolish the Federal Supreme Court;
¨ The federal judges are appointed by the President for life (until they die or retire);
¨ The federal judges can only be removed for misconduct after a trial in the Congress;
¨ Federal Courts deal with the cases of arising out of the Constitution, laws and treaties, foreign citizens’ cases, etc.
| The Supreme Court | |
| Residence | the Supreme Court Building, Washington D.C. |
| Members | @ The Chief Justice @ 8 Associate Justicies |
| Meetings | on the 1st Monday of October till June |
| Duty | @ to decide whether the laws of the Congress are constitutional @ to decide on the appeals from the lower courts (most cases) |
| The number of cases per session | 150 cases |
| Courts of Appeals | |
| Created | 1891 |
| Total number | 11 |
| Districts | The country is divided into 11 separate regions |
| Members | 3-15 members |
| Duty | @ to hear the appeals from the district courts |
| District Courts | |
| Total number | 50 states = at least 1 court of appeal, but some states have got 2-4 |
| Districts | The US is divided into 89 districts + 1 District of Columbia + 1 Puerto Rico |
| Size of a district | It is determined by: ü population ü size (territory) ü volume of work |
| Members | 1-27 judges 1 judge may deal with cases of more than 2 districts |
| Duty | @ to hear all criminal and civil cases of the district |
| Special Courts | |
| Purpose | the Congress may set up the court for special purposes |
| Members | appointed for life the President |
| Examples: | The Court of Claims |
| Created | 1855 |
| Members | @ chief justice @ 4 associate justices |
| Duty | To deal with monetary claims against the Federal Government |
| The Customs Court | |
| Members | 9 judges |
| Duty | @ to deal with the cases on taxes on the imported goods |
Date: 2015-01-11; view: 3386
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| | | A/ READING |