
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Subtyping based on genetic linkage or association data
Several studies based on samples with well-characterized clinical phenotypes have examined associations between selected clinical features and previously established genetic linkage regions or putative candidate genes. Various approaches have been employed to interrogate genome-wide linkage or association data with a view to exploring pathways of disease expression. Thus, a potential 6p locus, associated with a quantitative trait assessing the severity of psychotic symptoms, was reported by Brzustowicz et al.175 Pulver et al.176 used diagnostic information to stratify 54 multiplex pedigrees by diagnostic phenotypes cosegregating in nonschizophrenic first-degree relatives of the probands and reported genome-wide significant linkage to 8p21 and suggestive linkage to 1p21 for schizophrenia spectrum personality disorders. Subsequent analyses of affected siblings from these families revealed that the linkage evidence for 8p21 was mainly contributed by a subgroup of 30 affected siblings sharing two alleles identity by descent in the 8p21 region and one allele at a locus on chromosome 14, suggesting an interaction effect. Phenotypically, this subgroup was characterized by a high prevalence of bizarre delusions, affective symptoms early in the course of illness, history of seizures, and attendance of special school.177
Using data from the Irish Study of High-Density Schizophrenia Families, Kendler et al.67 reported high levels of positive thought disorder, affective deterioration, and worse outcome in probands from families with evidence of linkage to 8p22–21, suggesting that a susceptibility gene in the region may be predisposing to a Kraepelinian, dementia praecox type of illness. Within the same cohort of families, family-based transmission disequilibrium tests produced suggestive evidence of association between affective symptoms and the His452Tyr polymorphism in the serotonin 2A receptor; between negative symptoms and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); and between negative symptoms and a high-risk haplotype in the dystrobrevin-binding protein 1 (dysbindin, DTNBP1) on 6p24–22.178, 179 Recently, an association between a six-locus haplotype in DTNBP1 and psychometrically assessed generalized cognitive deficit in schizophrenia patients was reported by Burdick et al.180
A special focus in the search for genetic subtypes of schizophrenia has been the 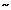 3 Mb region on chromosome 22q11, which contains at least three genes implicated in schizophrenia (COMT, PRODH2, and ZDHHC8) and is hemizygously deleted in the velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS, DiGeorge syndrome, or Shprintzen syndrome). The microdeletion has a population frequency of
3 Mb region on chromosome 22q11, which contains at least three genes implicated in schizophrenia (COMT, PRODH2, and ZDHHC8) and is hemizygously deleted in the velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS, DiGeorge syndrome, or Shprintzen syndrome). The microdeletion has a population frequency of 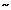 1 in 6000 births181 and is associated with increased risk for several neuropsychiatric syndromes, including schizophrenia,182 bipolar disorder, learning disability, and ADHD.183 Approximately, 1% of adult schizophrenia patients are carriers of the microdeletion184 but the frequency may be as high as 5% among individuals with childhood onset of schizophrenia.185 No evidence has been produced to date that such patients express a schizophrenia phenotype that is clinically distinguishable from schizophrenia in the absence of VCFS.186 However, schizophrenia patients with VCSF have more severe cognitive deficits of spatial working memory, visual recognition, and attention than VCFS individuals without schizophrenia.187 Compared to matched normal controls, schizophrenia patients with VCSF have smaller total grey matter volume, larger lateral ventricles,188 and decreased gyrification in the frontal and parietal lobes.189 Considering the potential to trace causal pathways linking specific gene effects with intermediate phenotypes and clinical disease expression, studies of rare genetic defects have a special place in schizophrenia research. The discovery of a translocation break point cosegregating with schizophrenia in a Scottish pedigree190 has facilitated the recent identification of Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) as a positional candidate gene with likely effects on brain development and neurocognition191, 192 in schizophrenia.
1 in 6000 births181 and is associated with increased risk for several neuropsychiatric syndromes, including schizophrenia,182 bipolar disorder, learning disability, and ADHD.183 Approximately, 1% of adult schizophrenia patients are carriers of the microdeletion184 but the frequency may be as high as 5% among individuals with childhood onset of schizophrenia.185 No evidence has been produced to date that such patients express a schizophrenia phenotype that is clinically distinguishable from schizophrenia in the absence of VCFS.186 However, schizophrenia patients with VCSF have more severe cognitive deficits of spatial working memory, visual recognition, and attention than VCFS individuals without schizophrenia.187 Compared to matched normal controls, schizophrenia patients with VCSF have smaller total grey matter volume, larger lateral ventricles,188 and decreased gyrification in the frontal and parietal lobes.189 Considering the potential to trace causal pathways linking specific gene effects with intermediate phenotypes and clinical disease expression, studies of rare genetic defects have a special place in schizophrenia research. The discovery of a translocation break point cosegregating with schizophrenia in a Scottish pedigree190 has facilitated the recent identification of Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) as a positional candidate gene with likely effects on brain development and neurocognition191, 192 in schizophrenia.
Top of page
Date: 2016-04-22; view: 863
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Familial–sporadic schizophrenia | | | Cognitive dysfunction as an endophenotype |